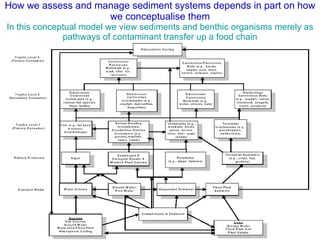
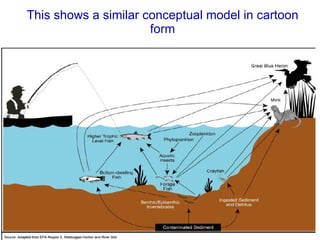
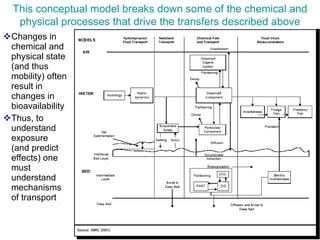
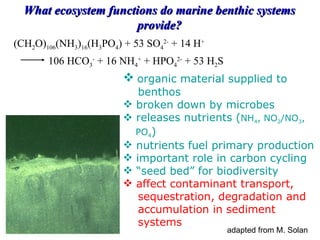
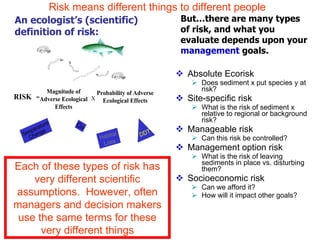
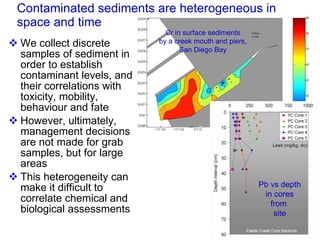
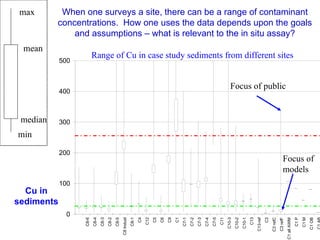
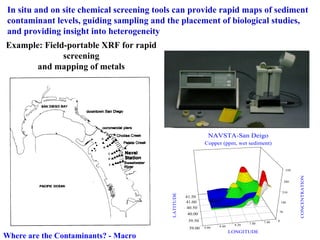
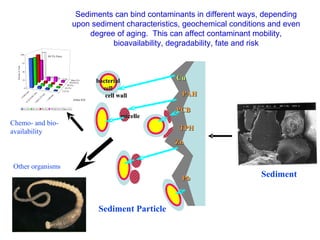
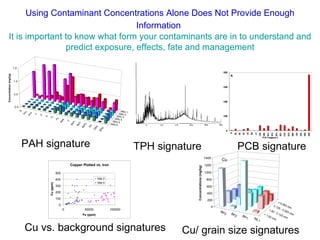
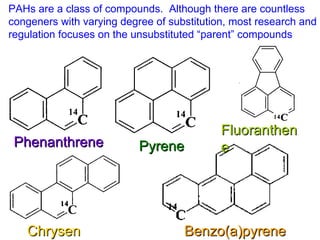
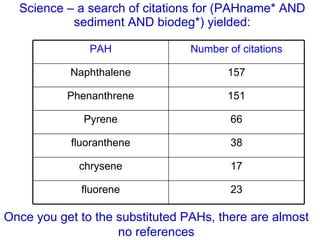
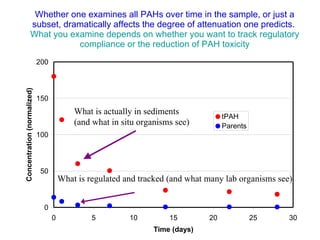
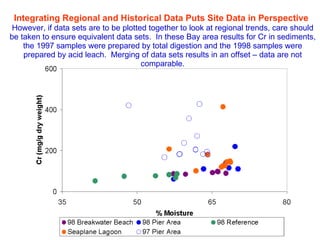
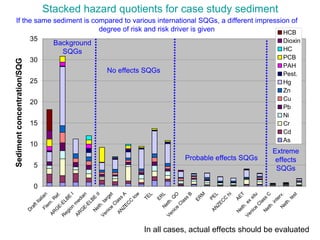
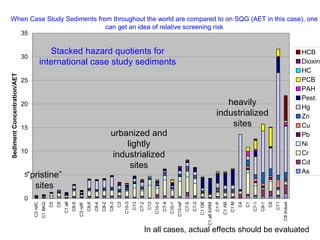
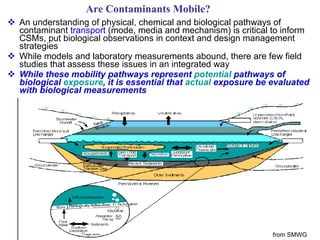
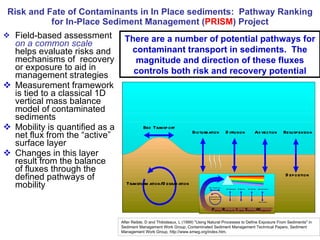
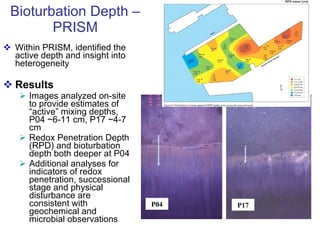
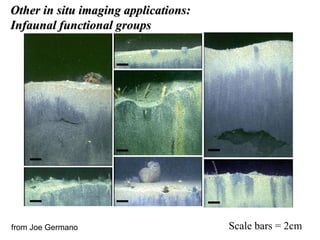
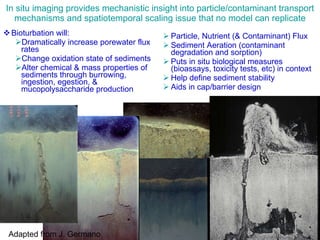
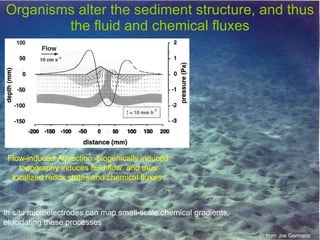
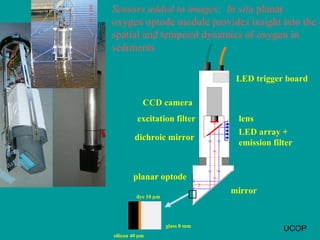
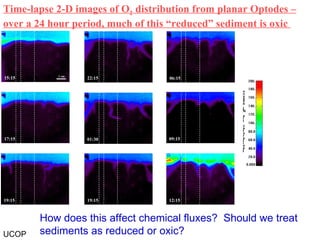
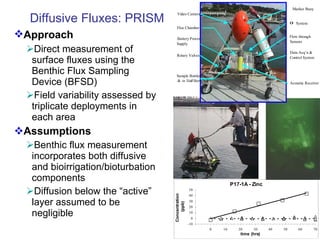
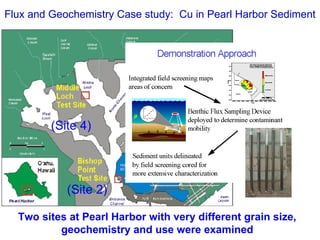
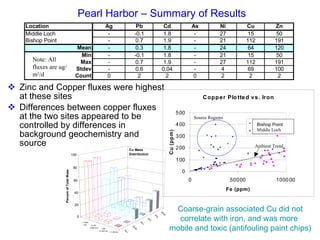
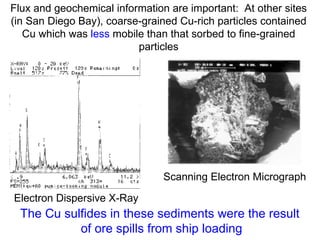
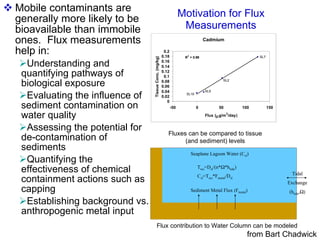
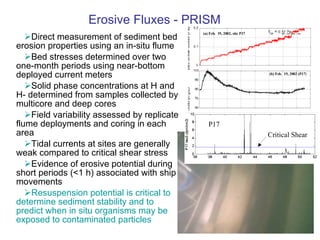
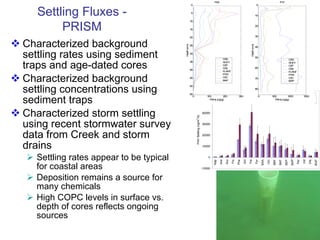
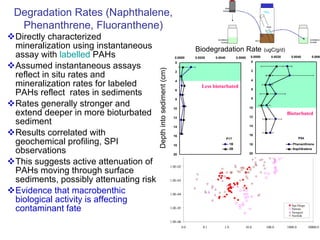
The document discusses in situ benthic observation tools for characterizing sediments and assessing risk. It describes how such tools provide insights into contaminant transport pathways, sediment-organism interactions, and chemical fluxes that influence exposure and effects. Integrating these observations with modeling helps evaluate risks of management strategies for contaminated sediments.
![In Situ Benthic Observation Tools in Sediment Risk Assessments - and- The Need for Biogeochemistry in Characterizing In-situ Exposure and Effects Sabine E. Apitz, Ph.D. SEA Environmental Decisions, Ltd 1 South Cottages, The Ford Little Hadham, Hertfordshire SG11 2AT, UK 01279 771890 [email_address] … Linking science and applications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insitushorcoursesetacseav4-13154834516479-phpapp02-110908071319-phpapp02/75/In-situ-lecture-1-2048.jpg)