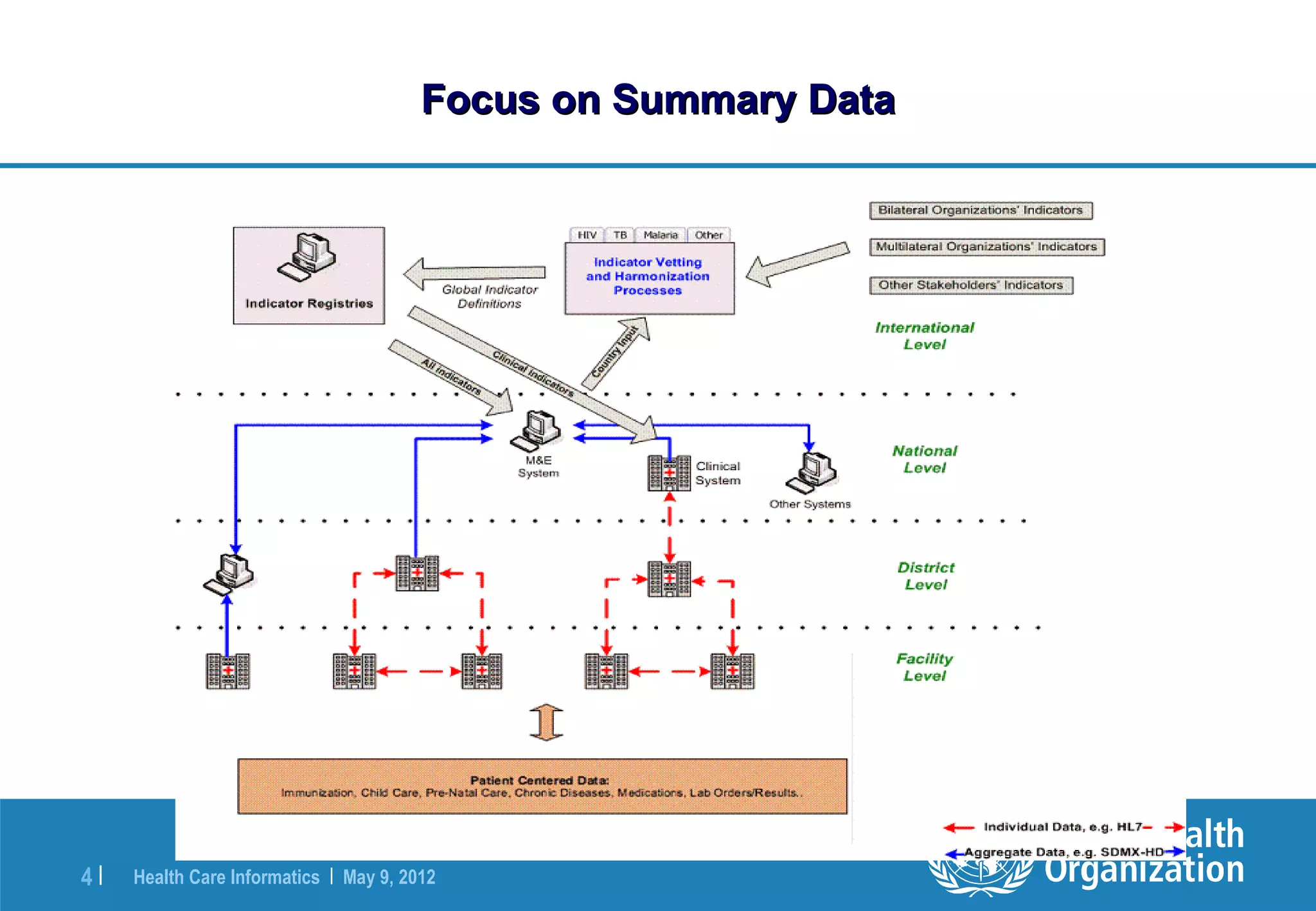
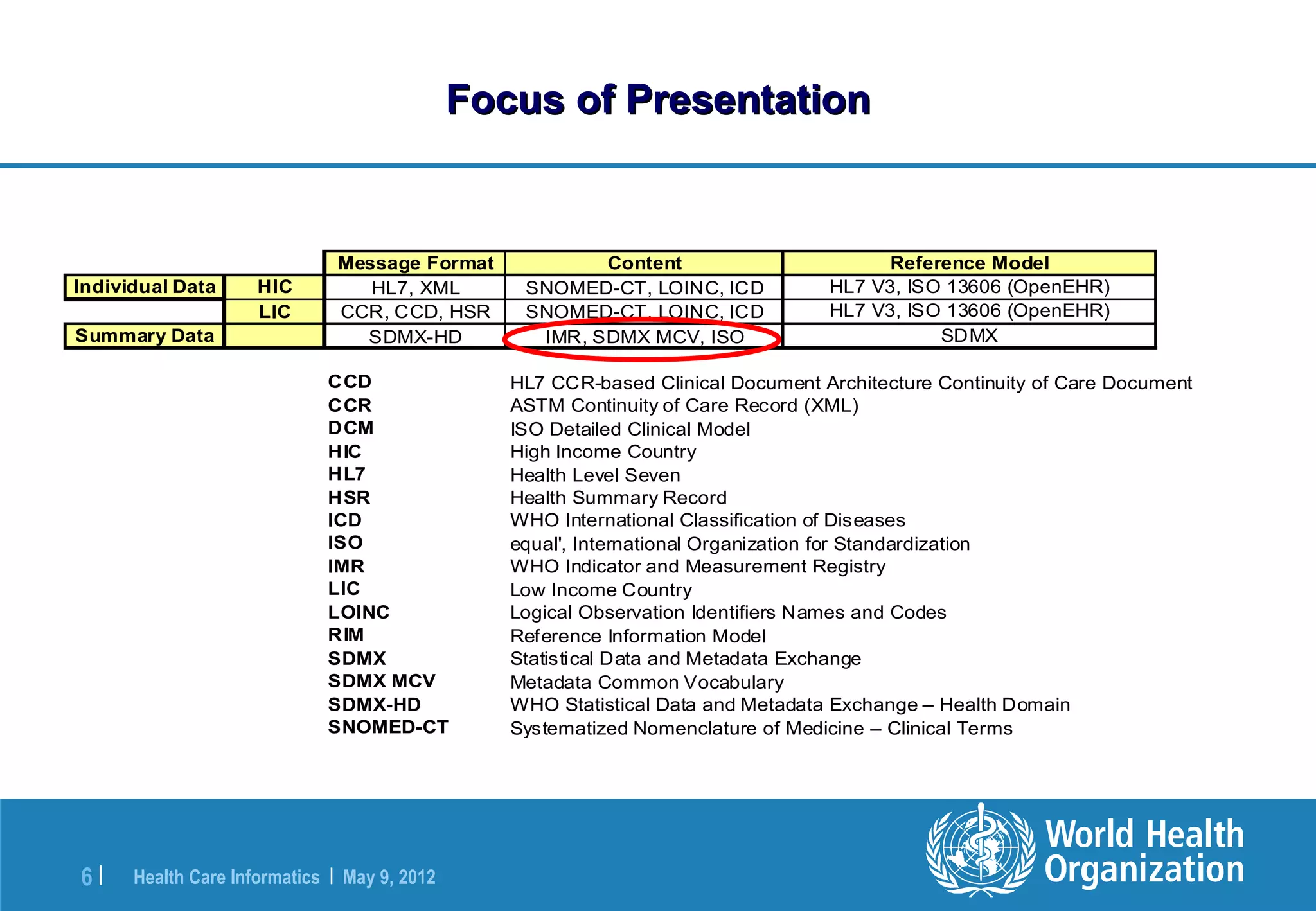
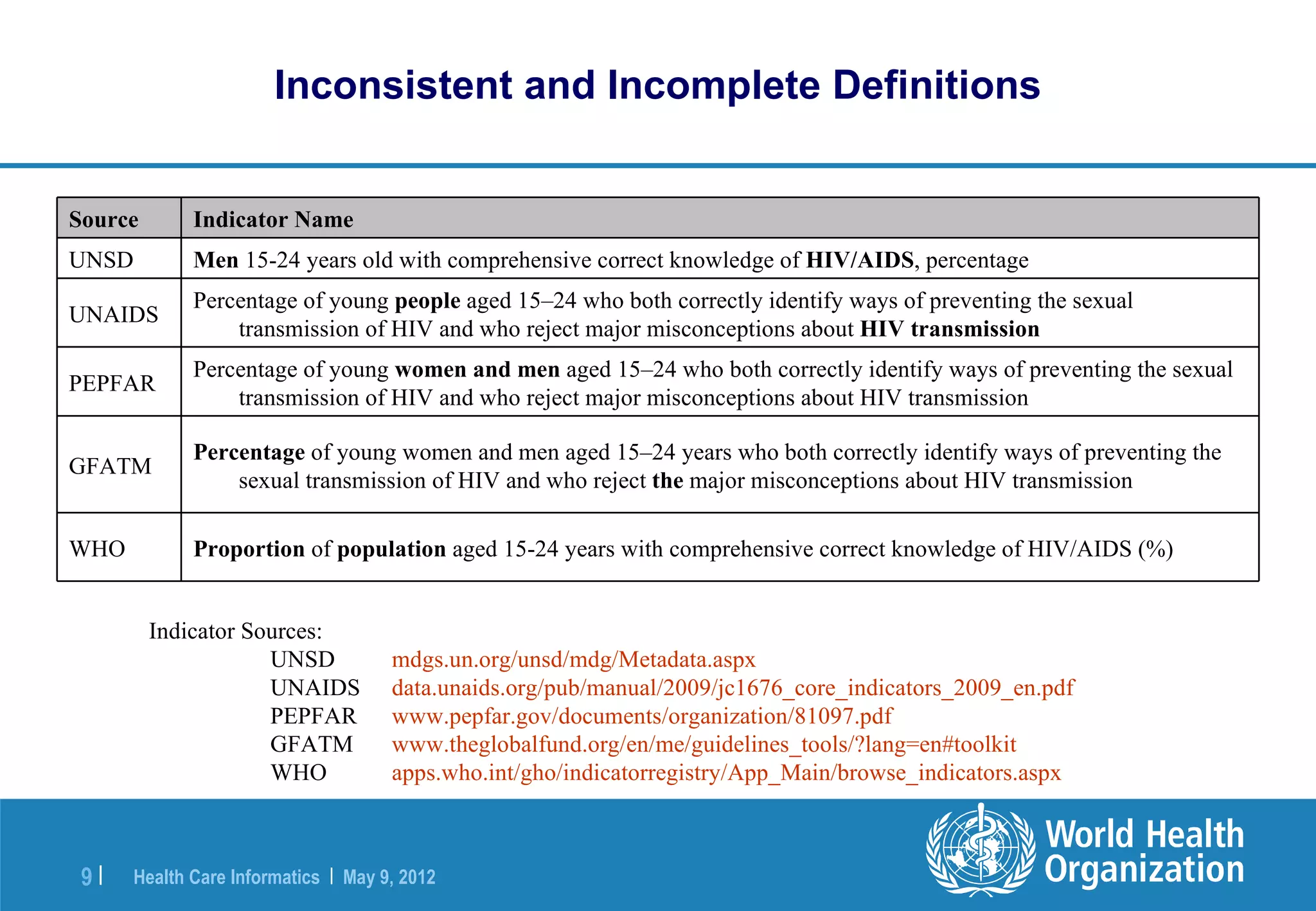
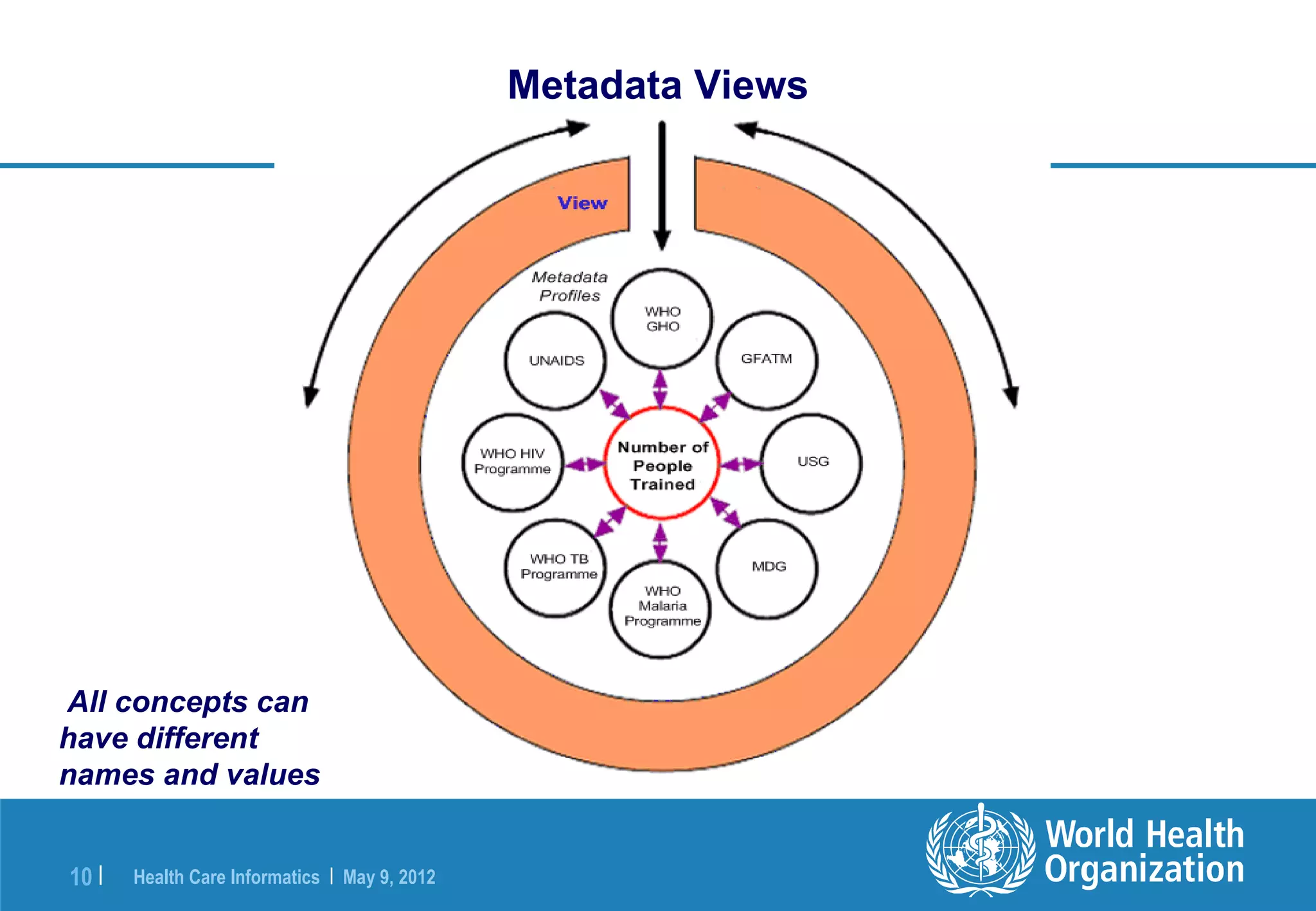
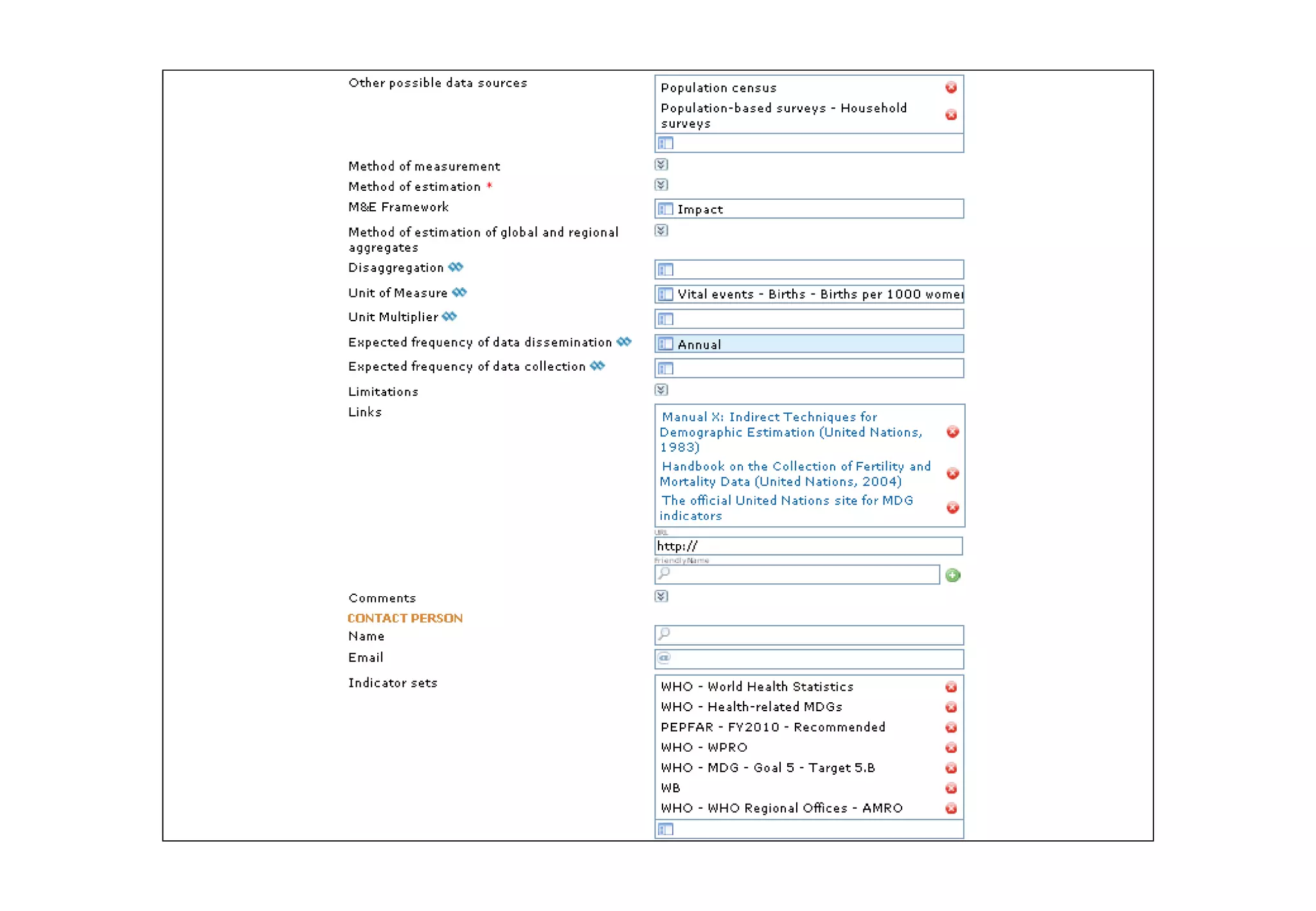
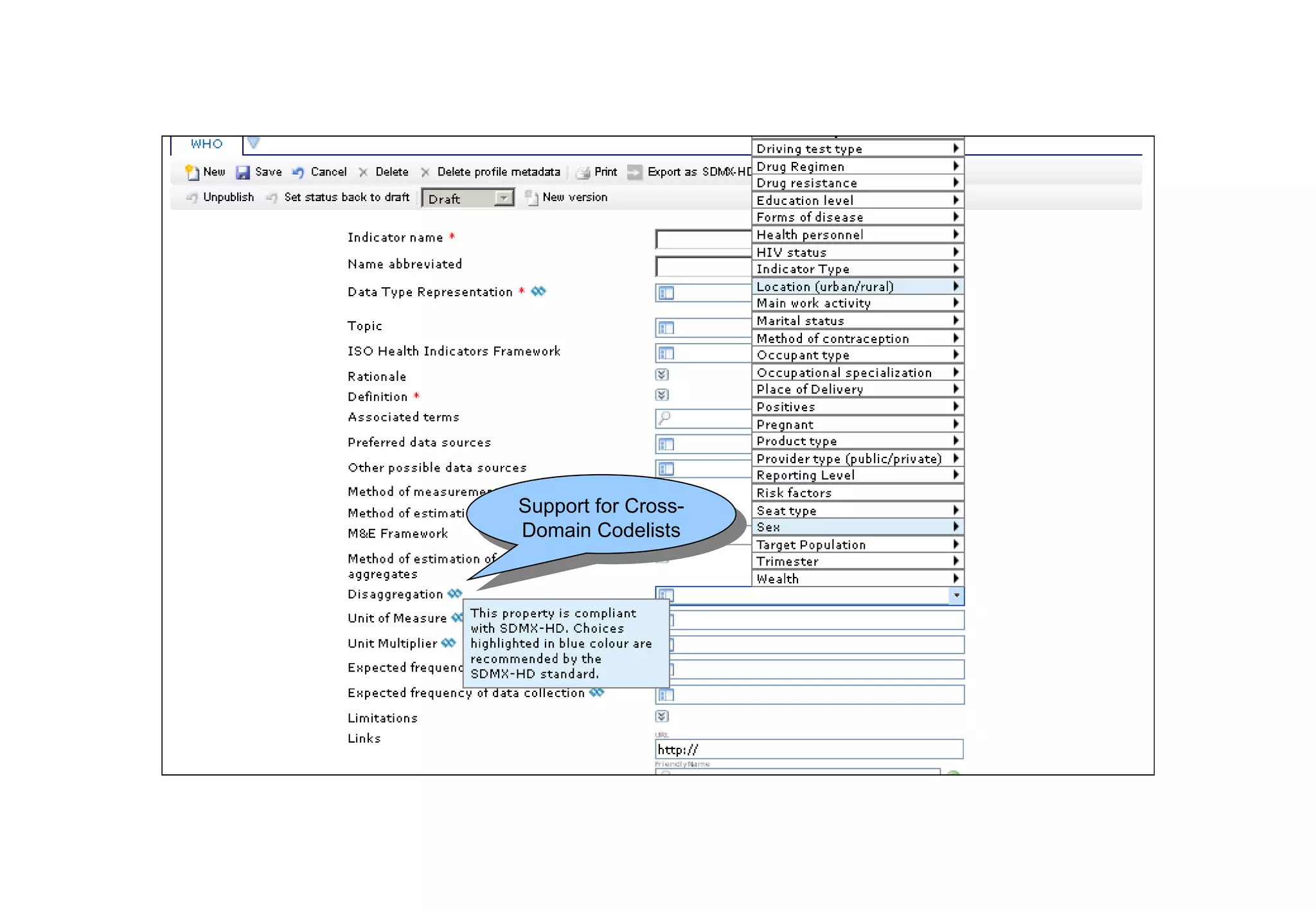
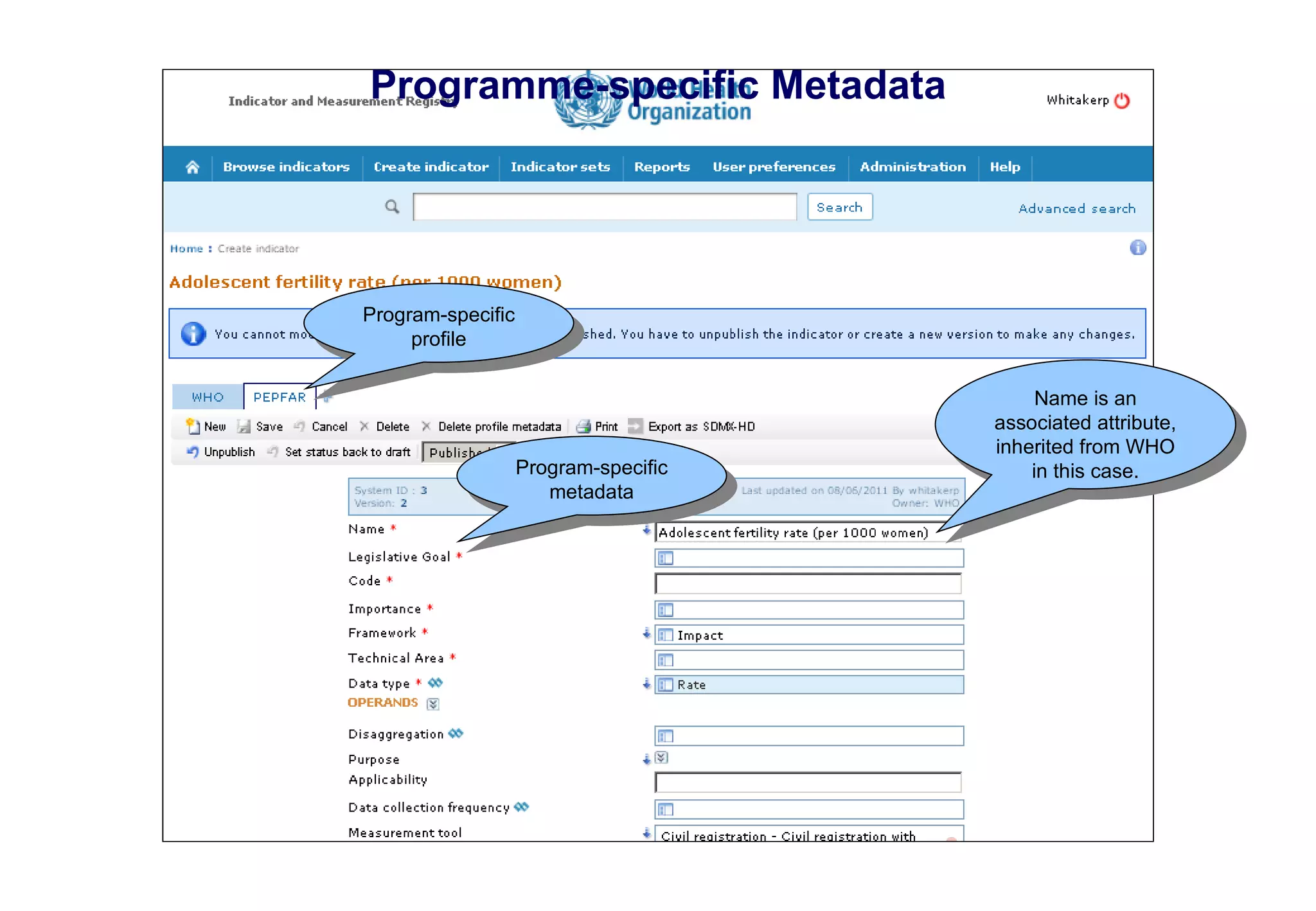
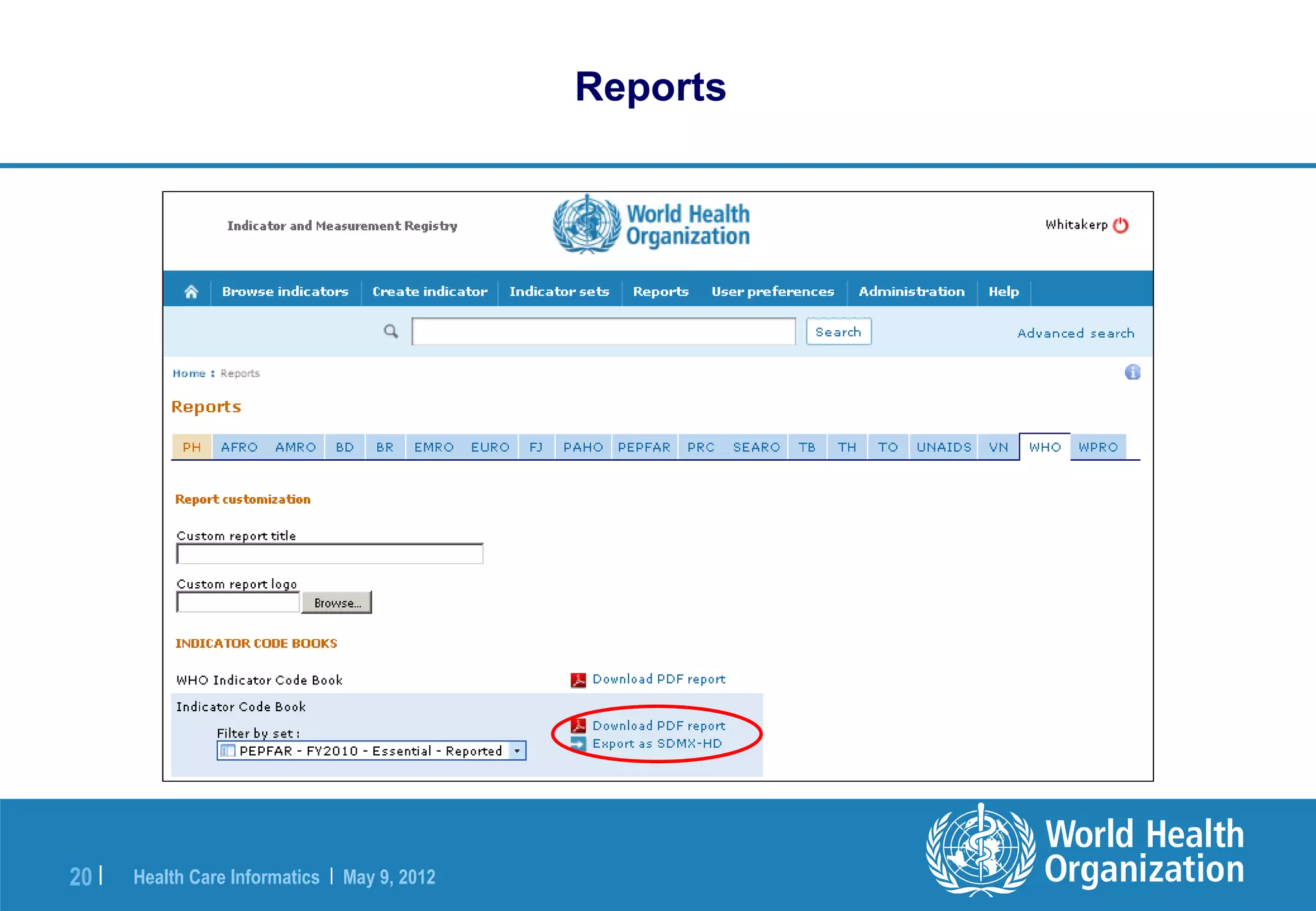
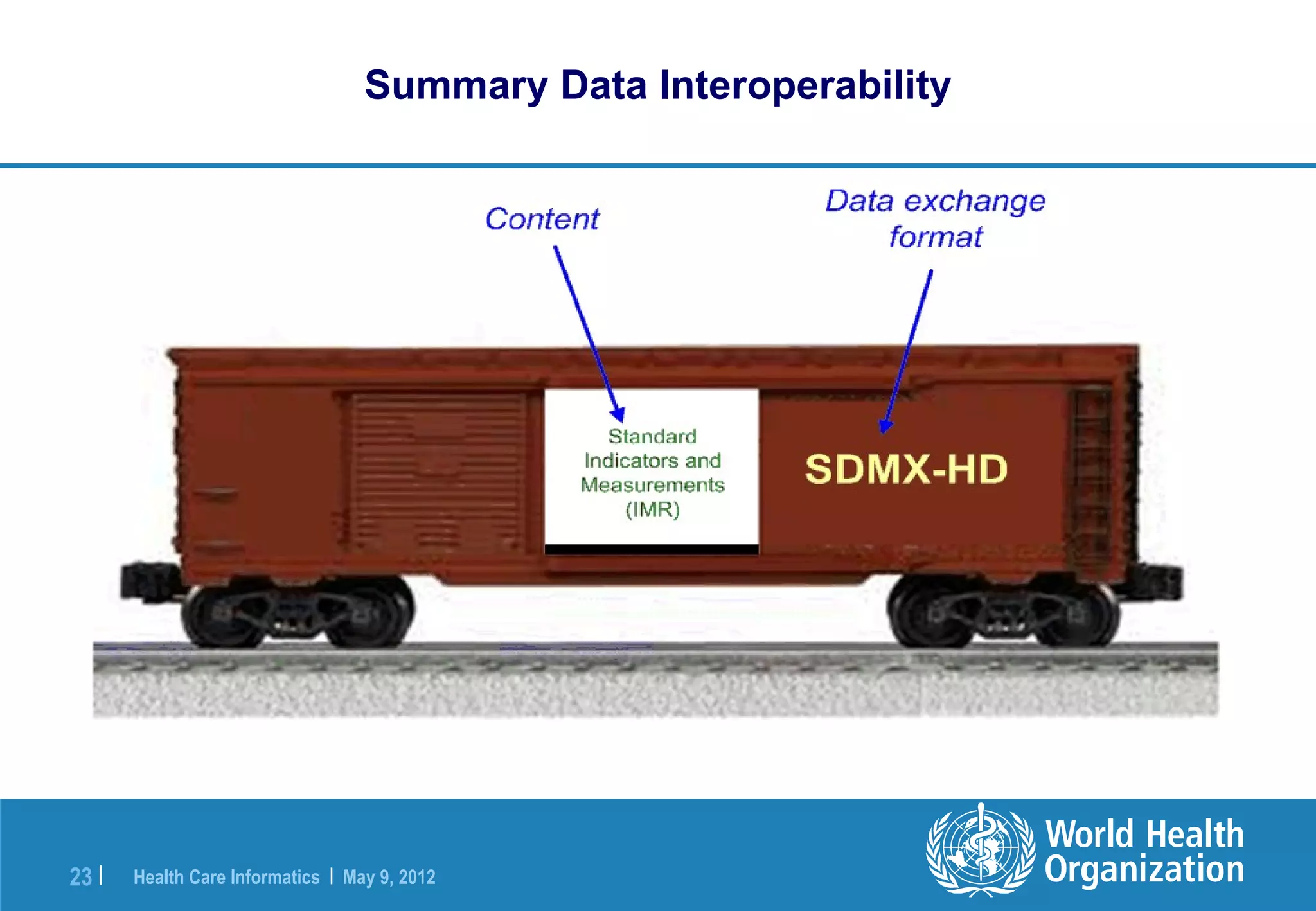
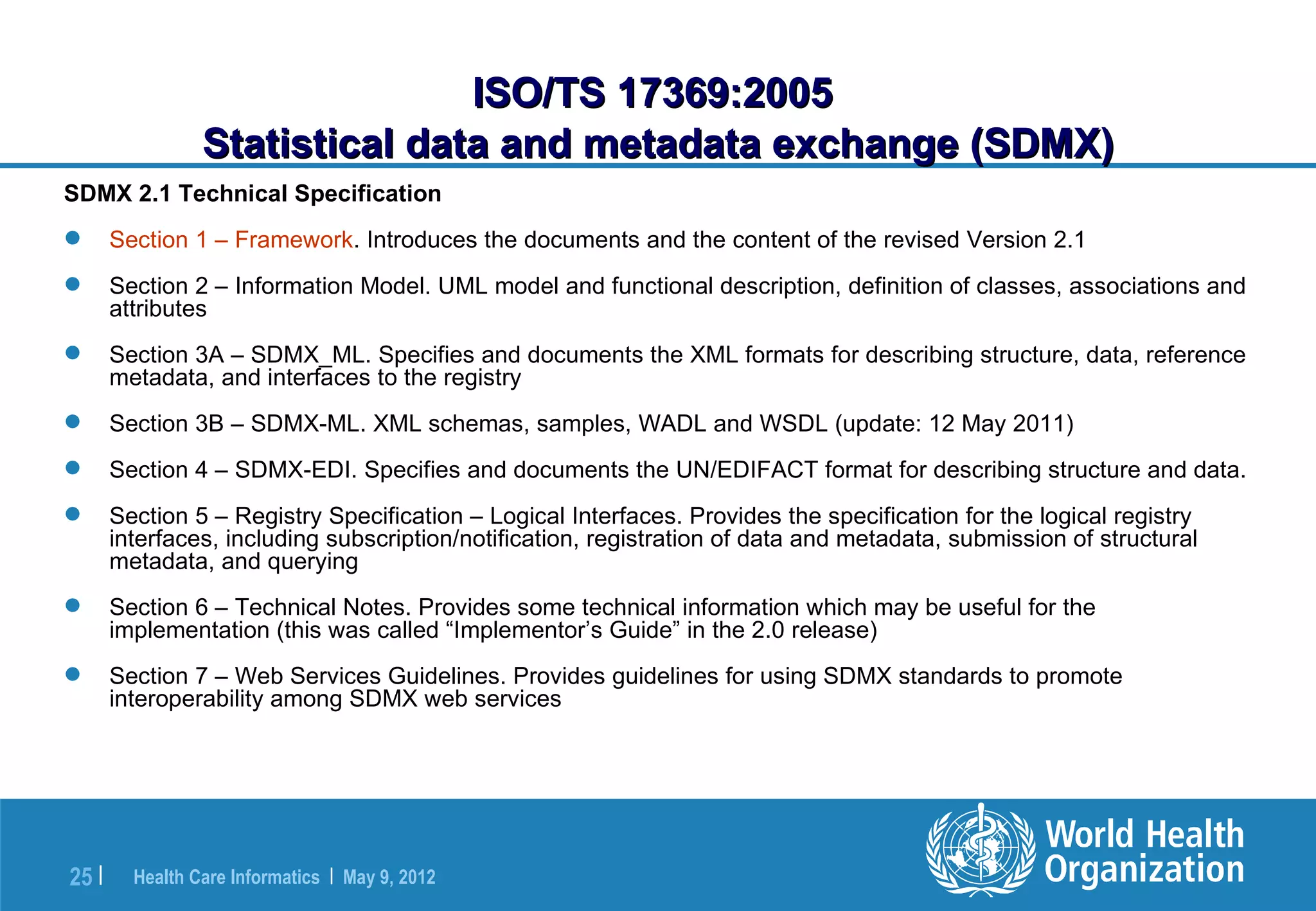
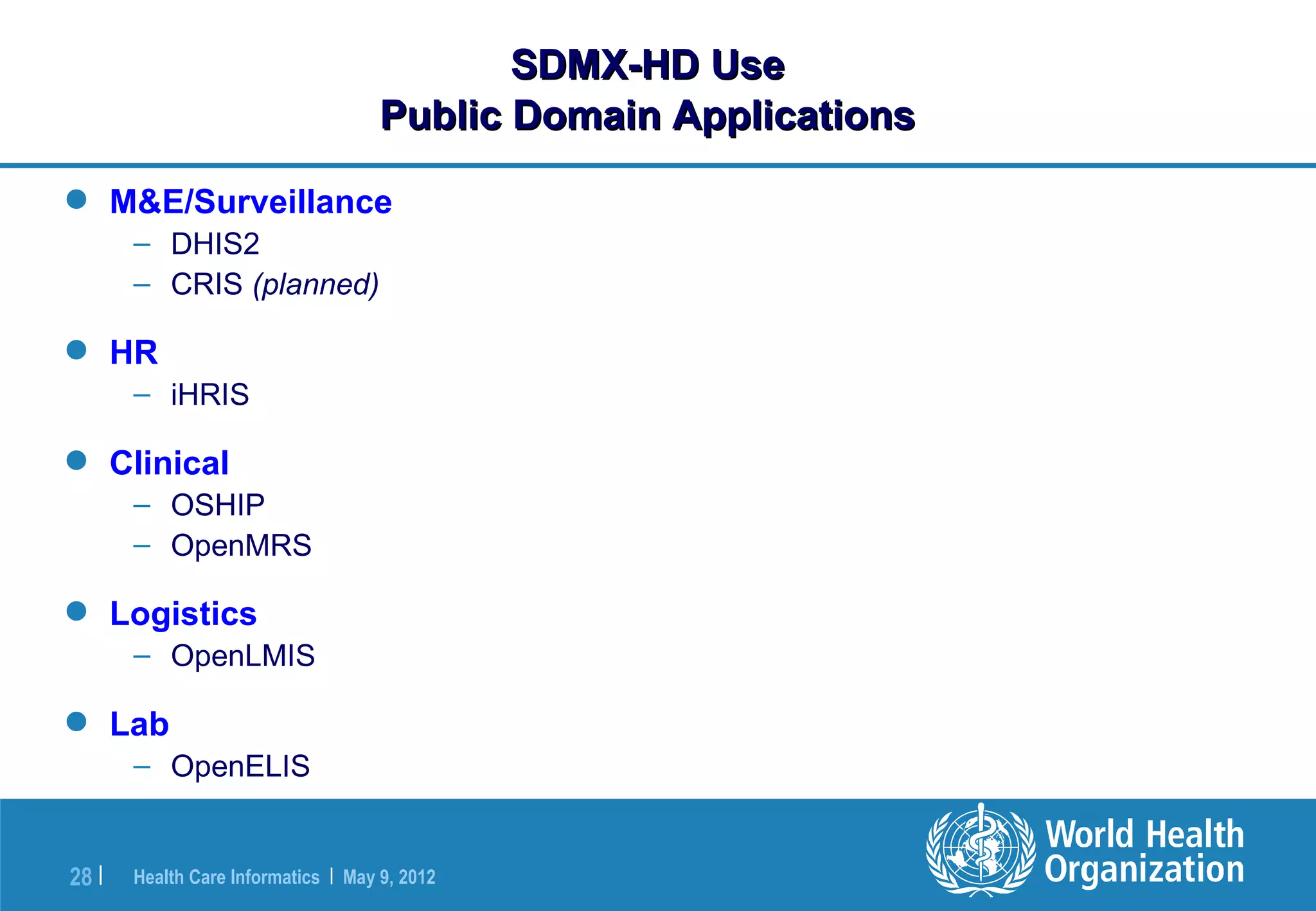
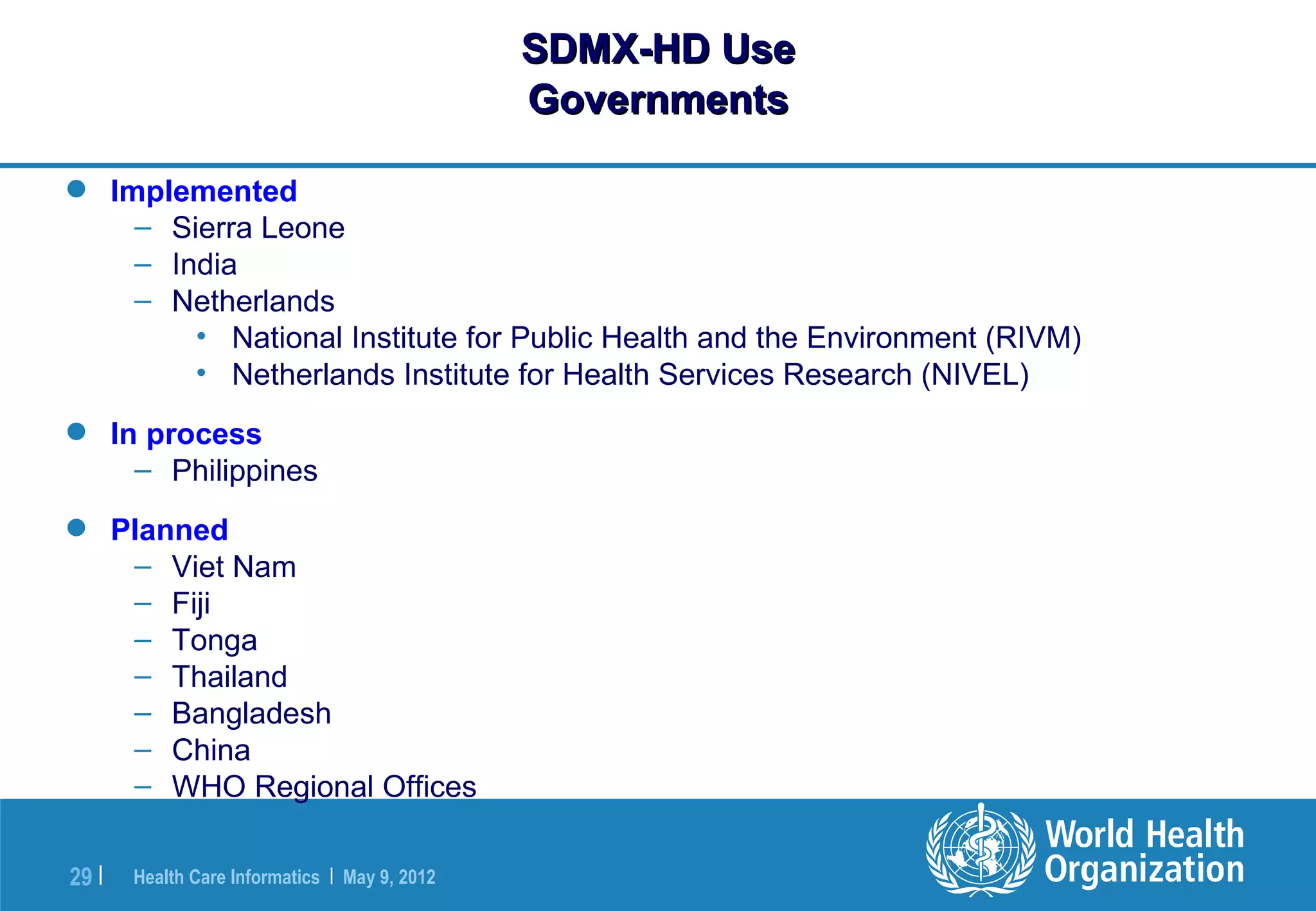
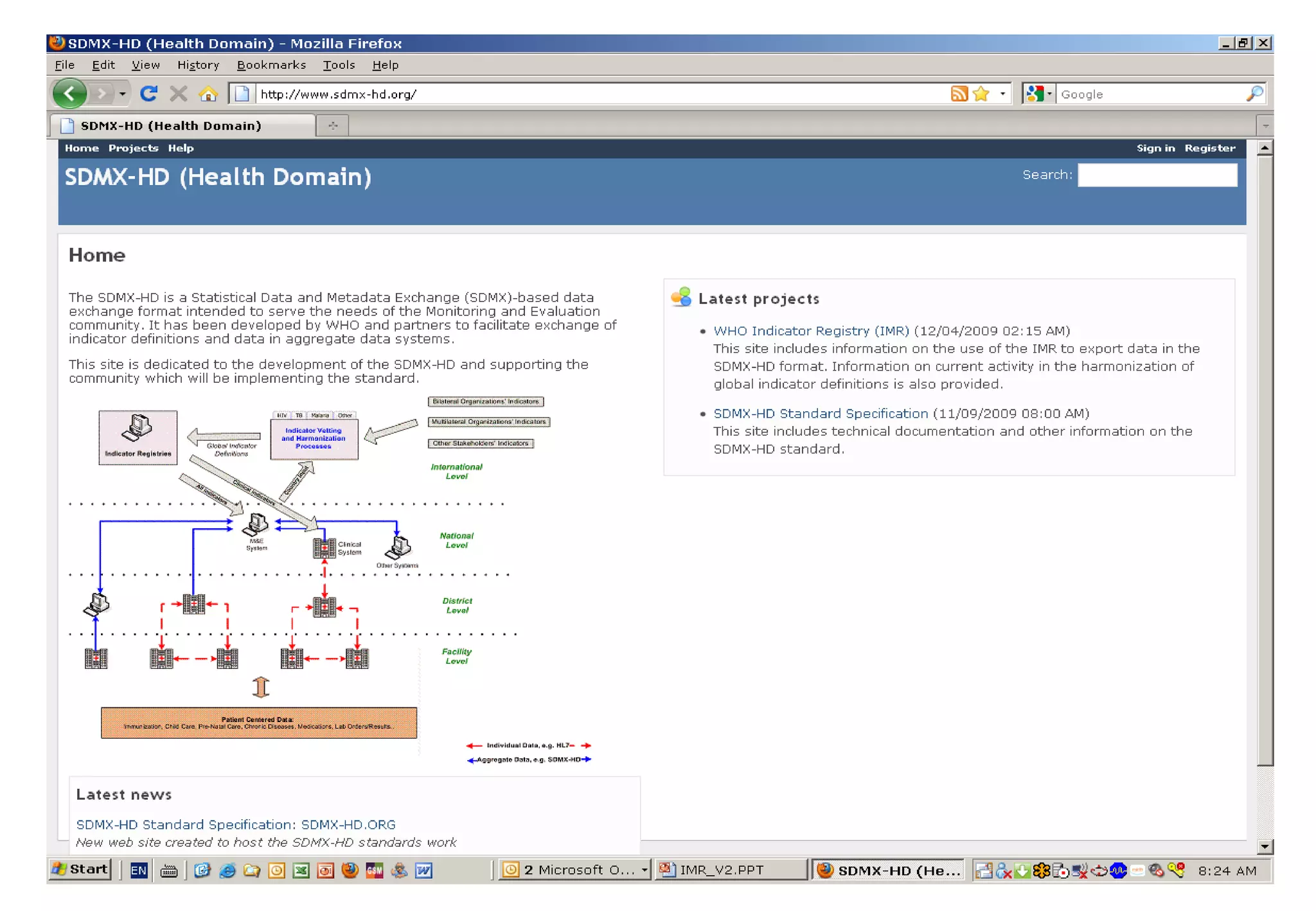
The document outlines the WHO Indicator and Measurement Registry (IMR) and the Statistical Data and Metadata Exchange (SDMX) specifically for health, aiming to improve the interoperability of summary data in healthcare. It identifies issues related to varying definitions, insufficient metadata, and lack of standardized formats, proposing solutions through the IMR and SDMX-HD data exchange format. The initiatives aim to harmonize indicator definitions and enhance global data management in health monitoring and evaluation.