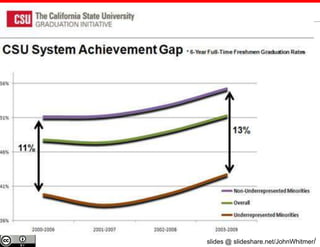
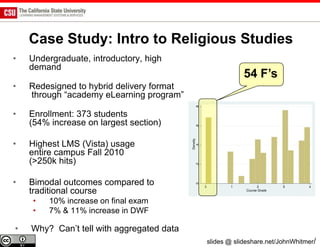
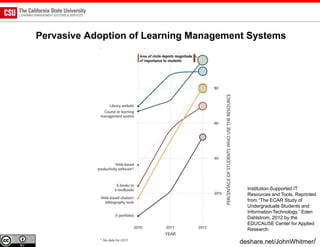
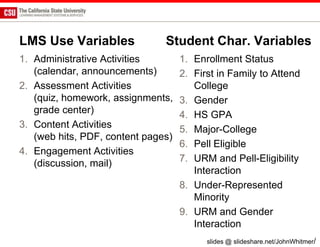
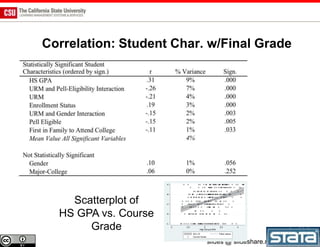
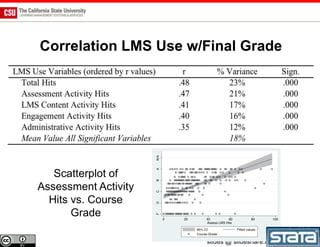
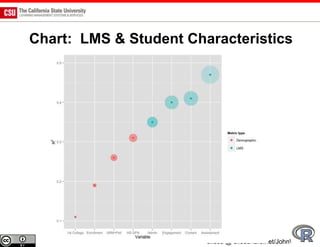
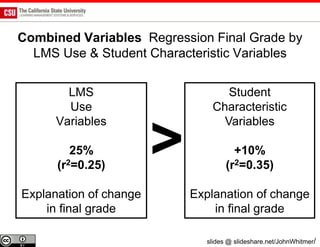
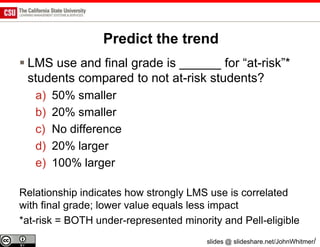
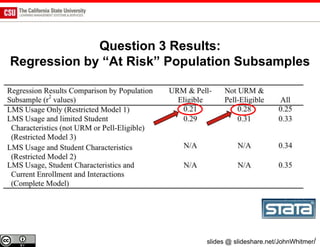
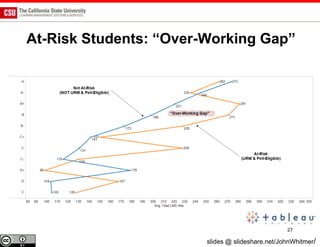
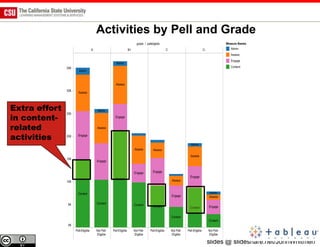
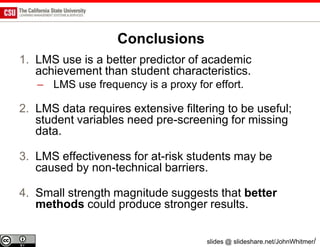
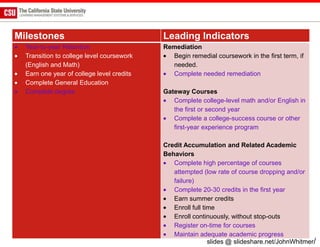
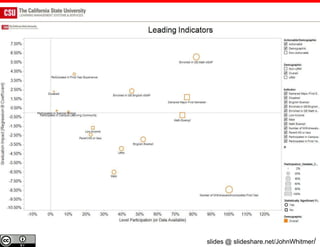
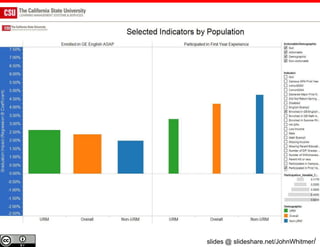
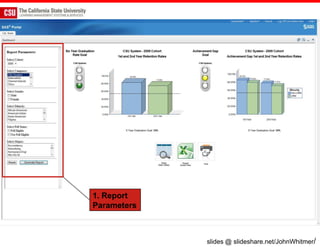
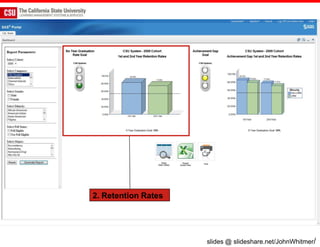
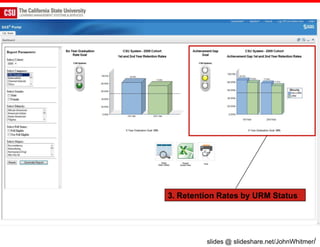
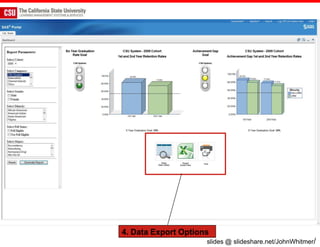
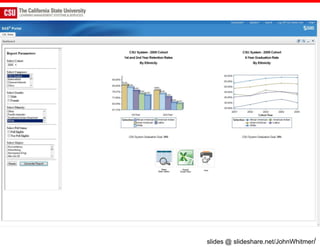
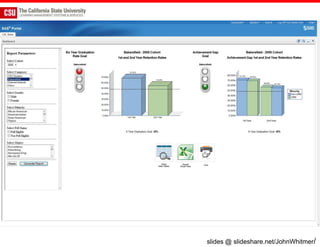
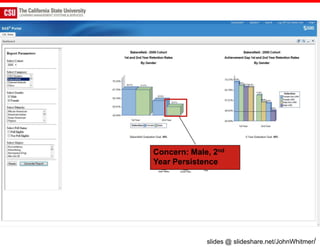
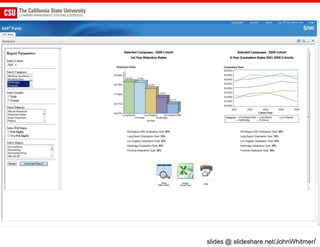
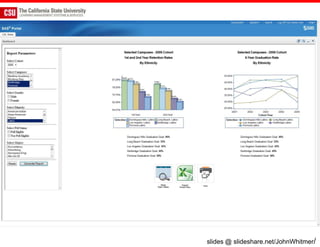
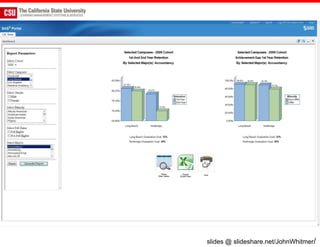
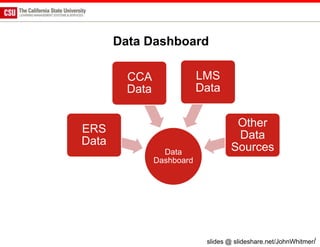
The document discusses the use of learning analytics and a data dashboard to improve student achievements at California State University, highlighting the importance of data-driven decision making for early intervention. It presents a case study from Chico State and outlines various strategies, milestones, and metrics to track academic progress and retention rates. Key findings suggest that LMS usage is a stronger predictor of academic success than traditional student characteristics, which may point to new opportunities for supporting at-risk students.