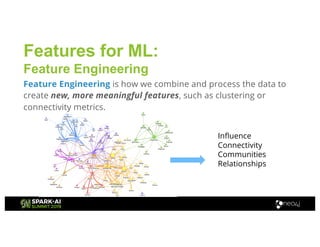
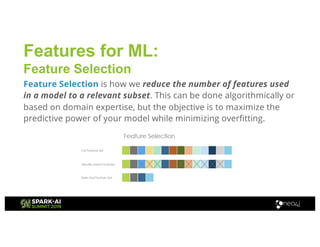
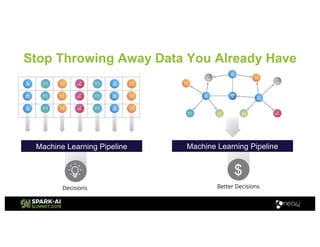
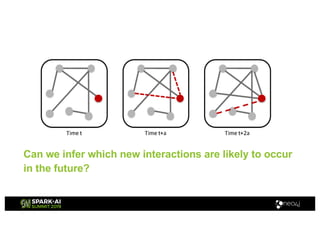
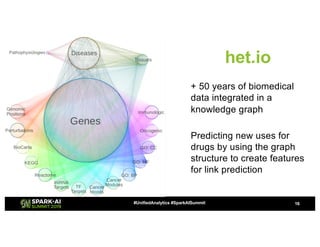
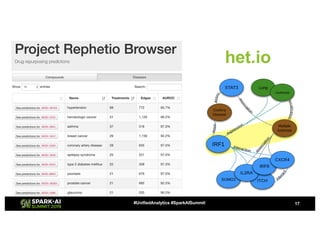
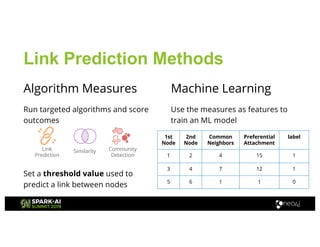
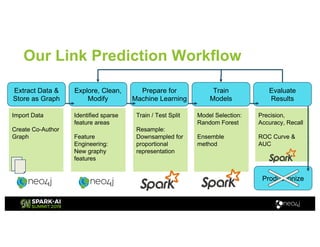
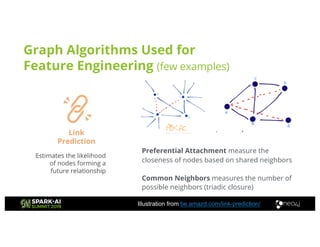
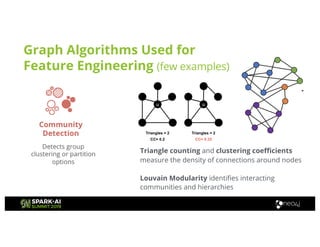
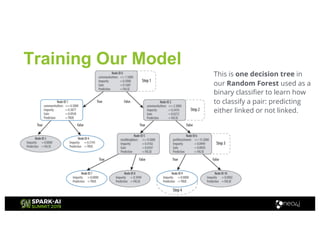
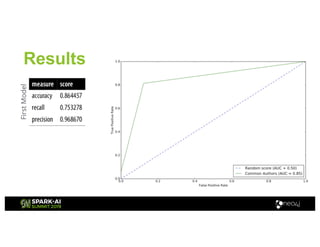
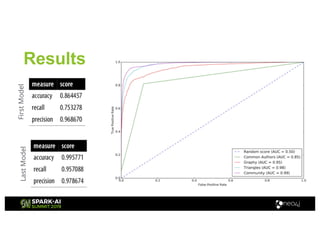
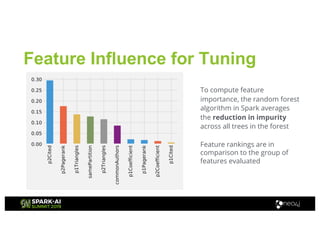
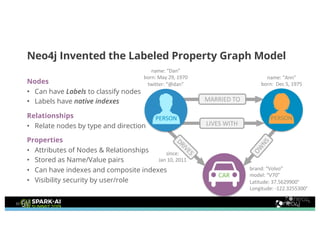
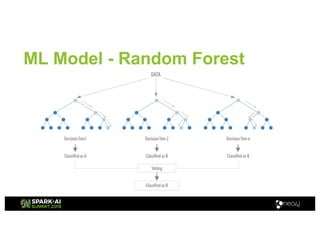
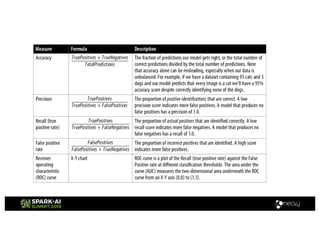
Amy Hodler from Neo4j presented on improving machine learning predictions through graph analytics at the Spark AI Summit. The discussion focused on link prediction, feature extraction, feature engineering, and using graph structures for predictive modeling. Key techniques included community detection, co-authorship graphs, and the application of random forest classifiers for evaluating collaboration predictions.