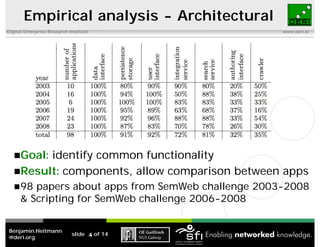
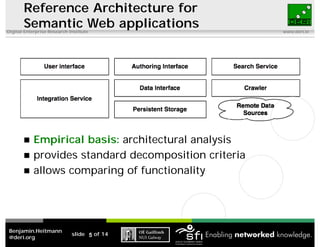
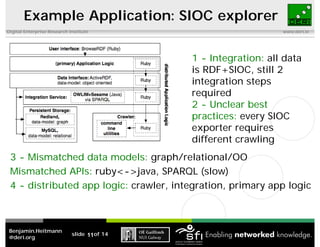
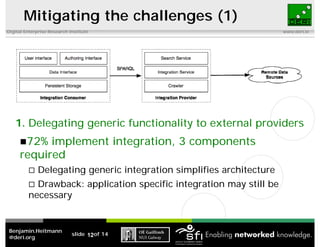
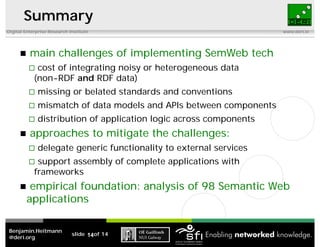
This document discusses the challenges of implementing semantic web technologies based on an empirical analysis of 98 applications, highlighting issues such as integrating noisy data, missing standards, and mismatched data models. It presents a reference architecture and offers approaches to mitigate these challenges, including delegating functionality to external services and using frameworks for application assembly. The findings aim to support real-world adoption of semantic web technologies by outlining common obstacles and potential solutions.