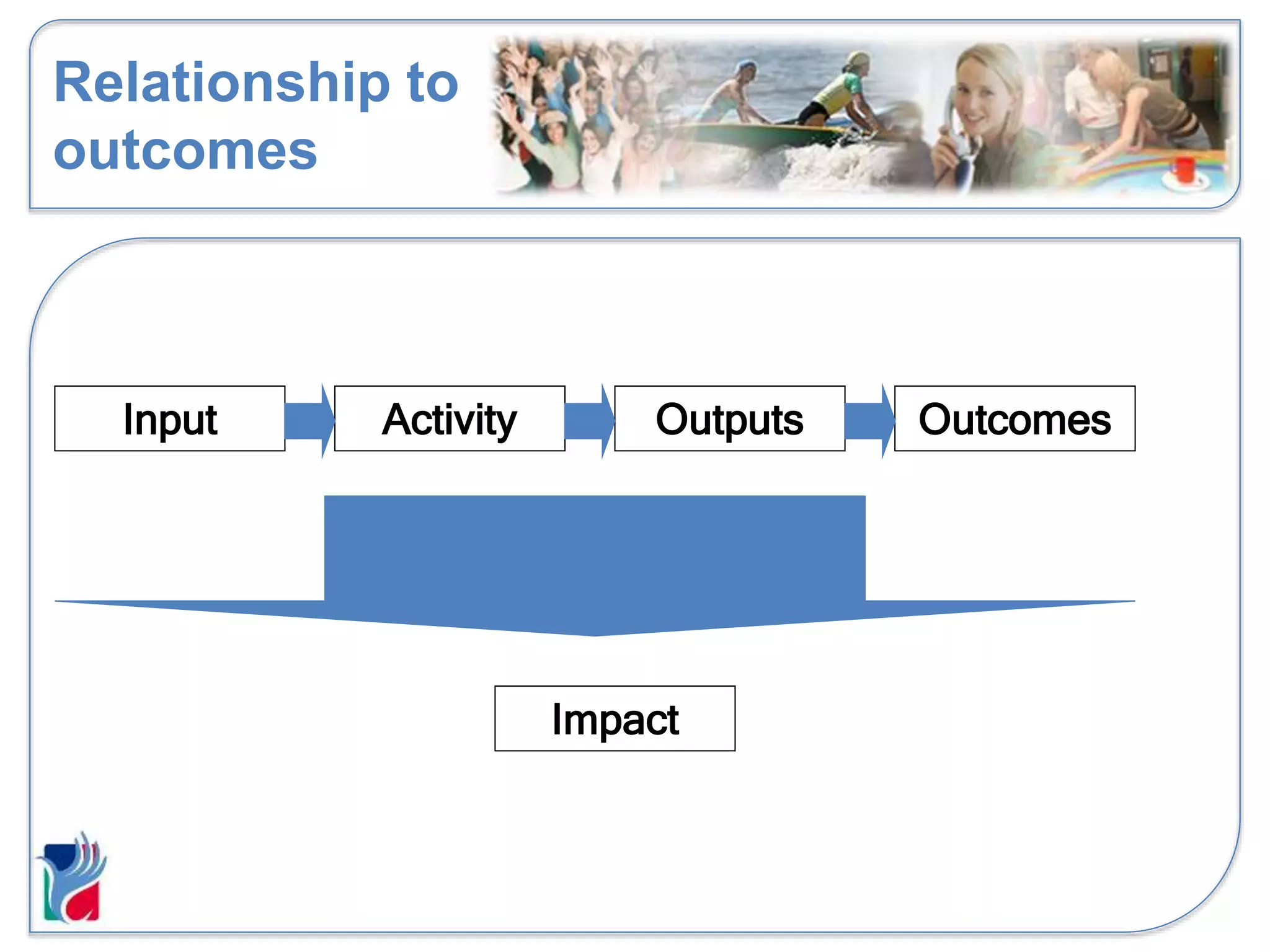
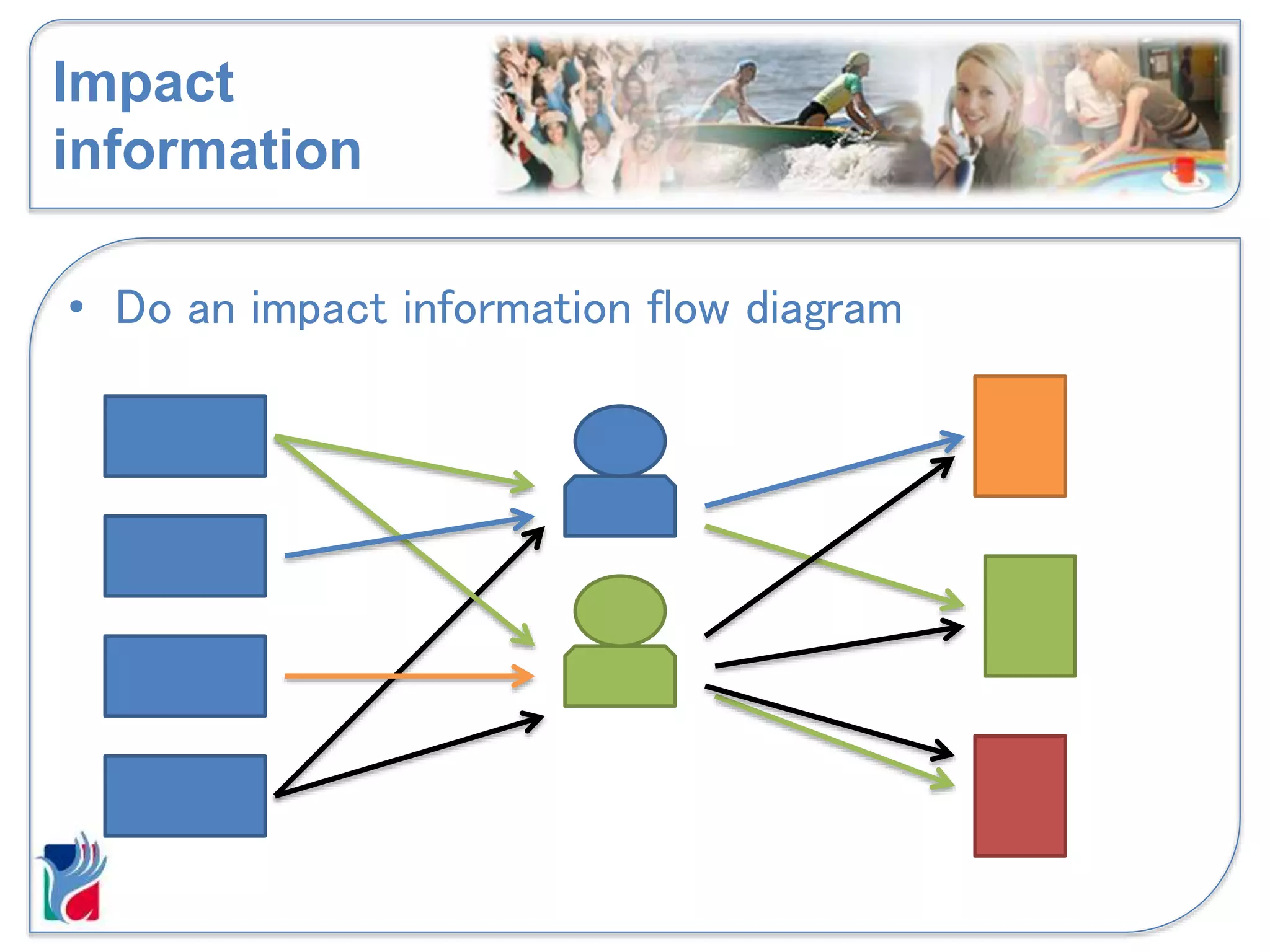
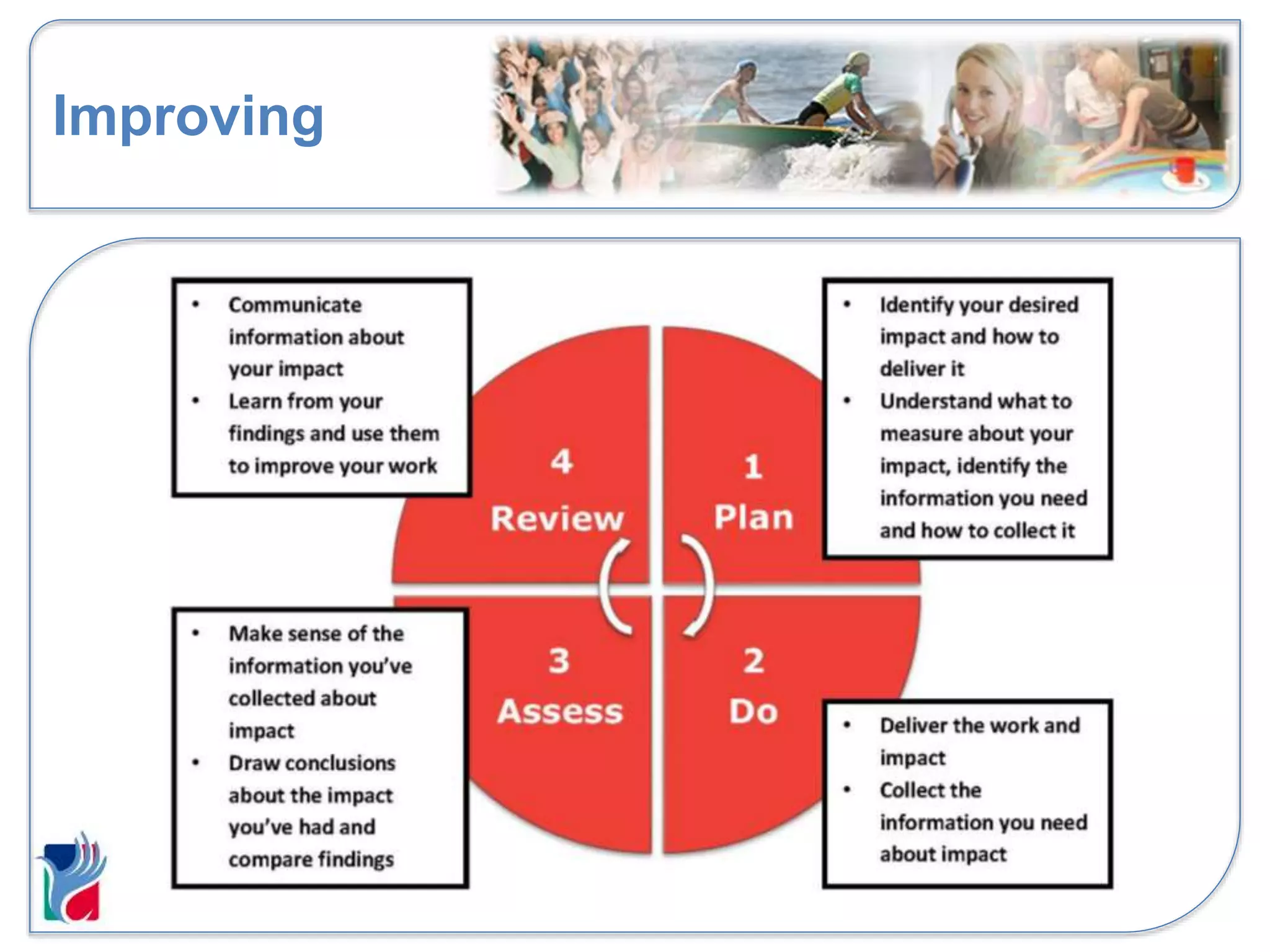
The document discusses impact reporting and how to make annual reports effective for organizations. It defines impact as the difference an organization makes and how the world would look without the organization. Impact can be both positive and negative, planned or unplanned, and affect various stakeholder groups. When reporting impact, organizations should consider their purpose, involve stakeholders, use proportionate methods, consider both qualitative and quantitative data, and be transparent. The annual report is one way to communicate impact information to critical audiences, and the information provided should be relevant, reliable, and help those audiences make decisions.