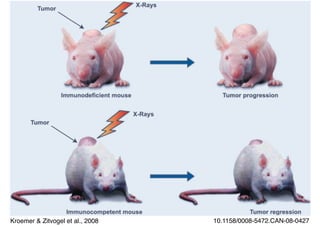
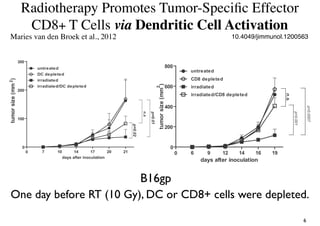
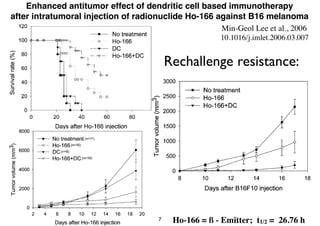
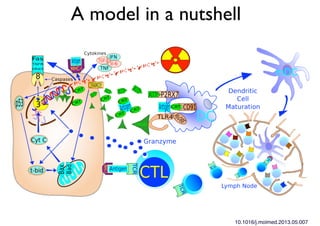
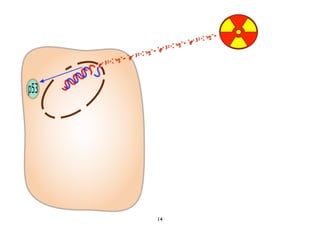
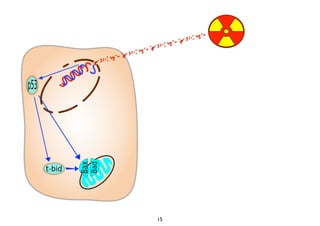
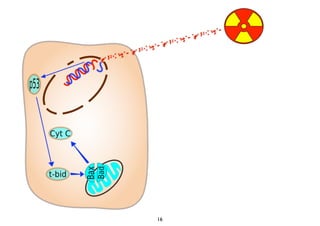
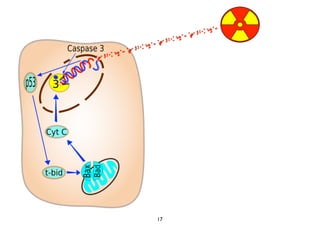
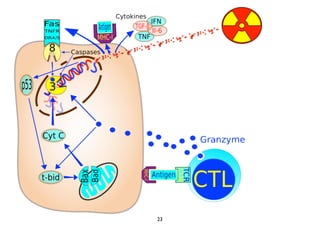
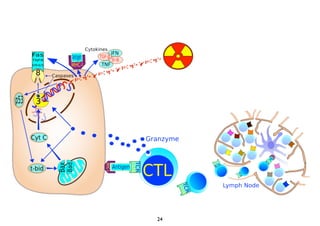
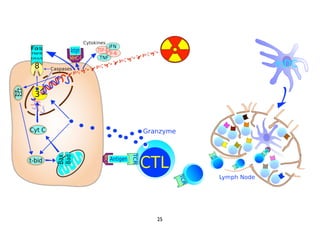
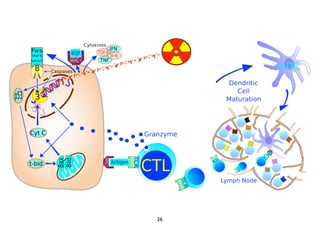
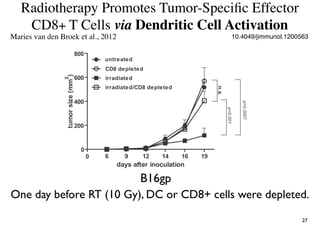
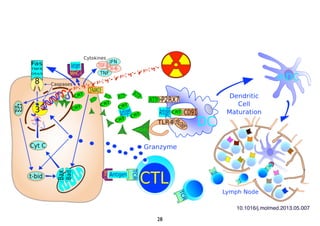
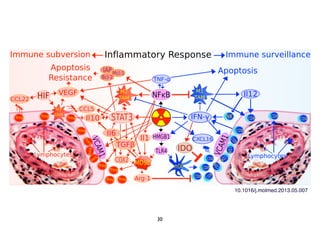
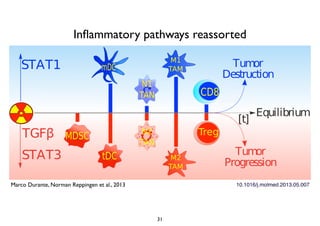
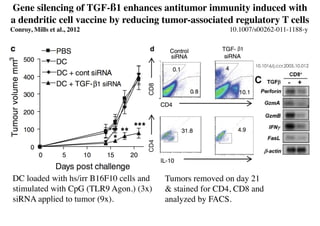
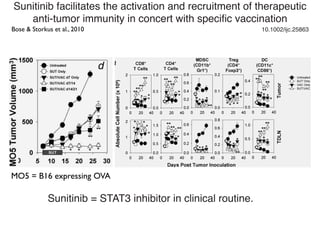
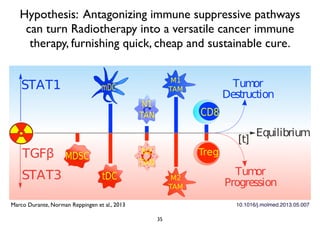
Radiotherapy can enhance the immune system's ability to fight cancer in several ways:
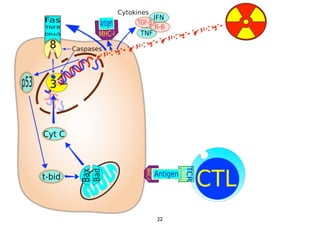
1) Radiation can activate dendritic cells to promote tumor-specific CD8+ T cells.
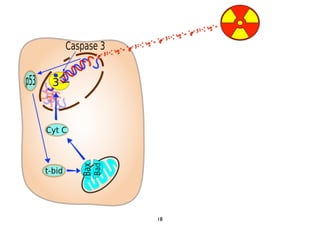
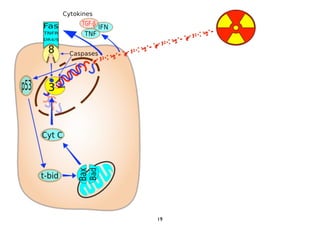
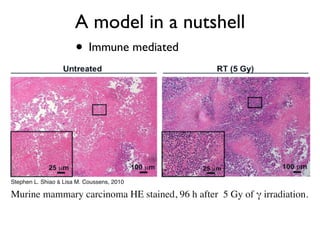
2) Both cell-intrinsic and immune-mediated mechanisms contribute to the anti-tumor effects of radiation.
3) Breaking immune suppression, such as blocking TGF-ß or STAT3, can increase the success of radiotherapy and immunotherapy combinations by turning radiation into a versatile cancer immune therapy.