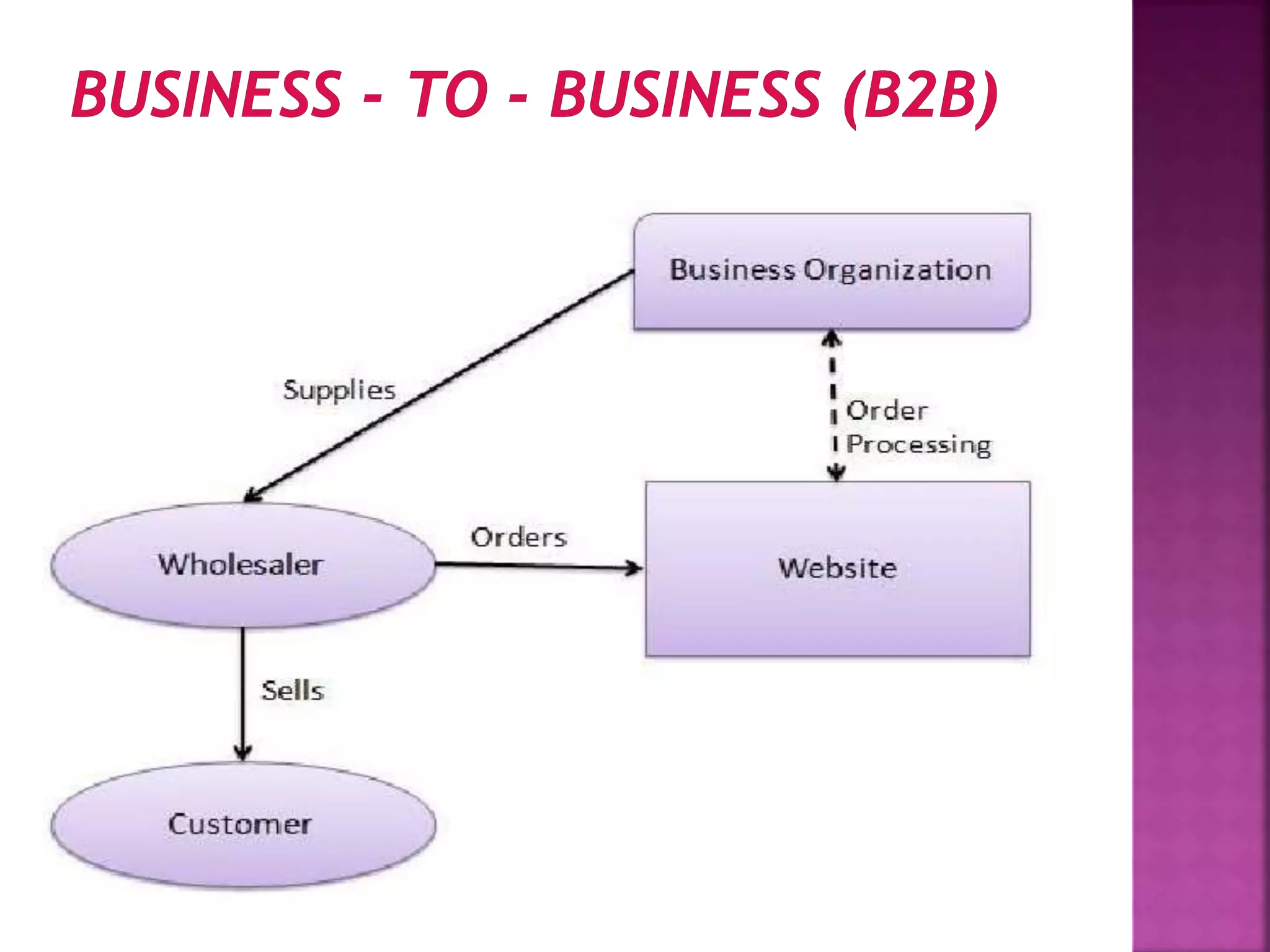
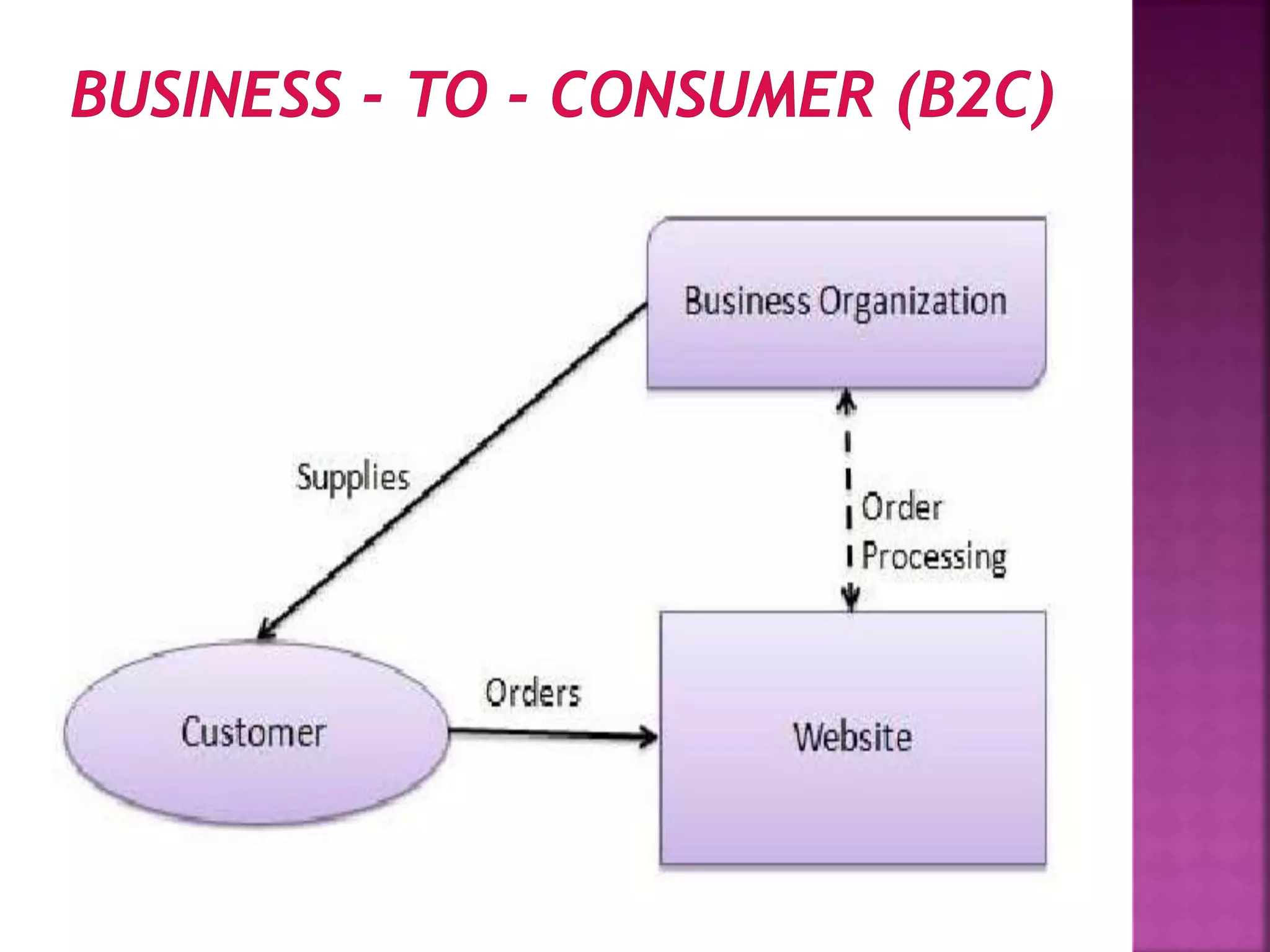
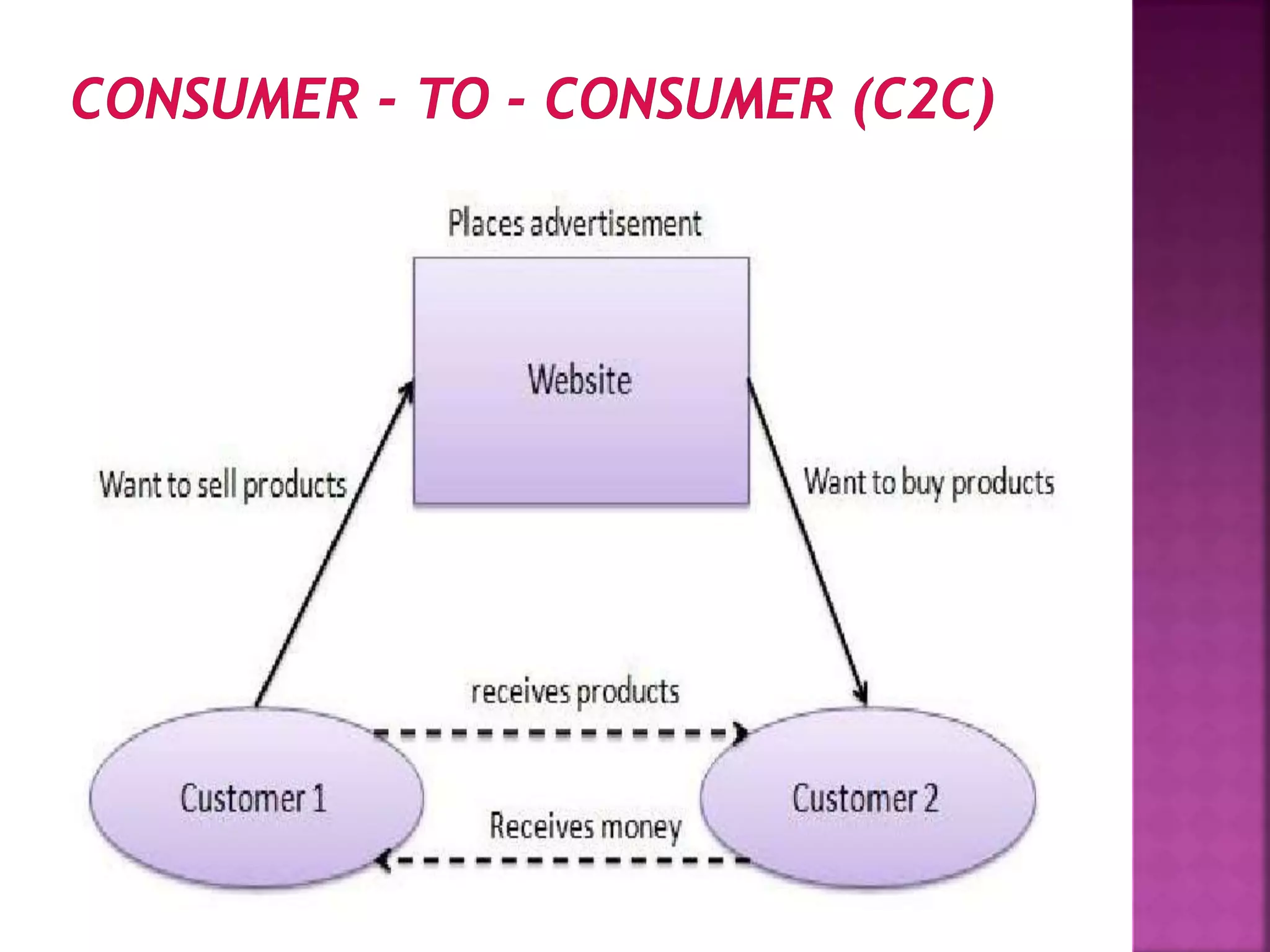
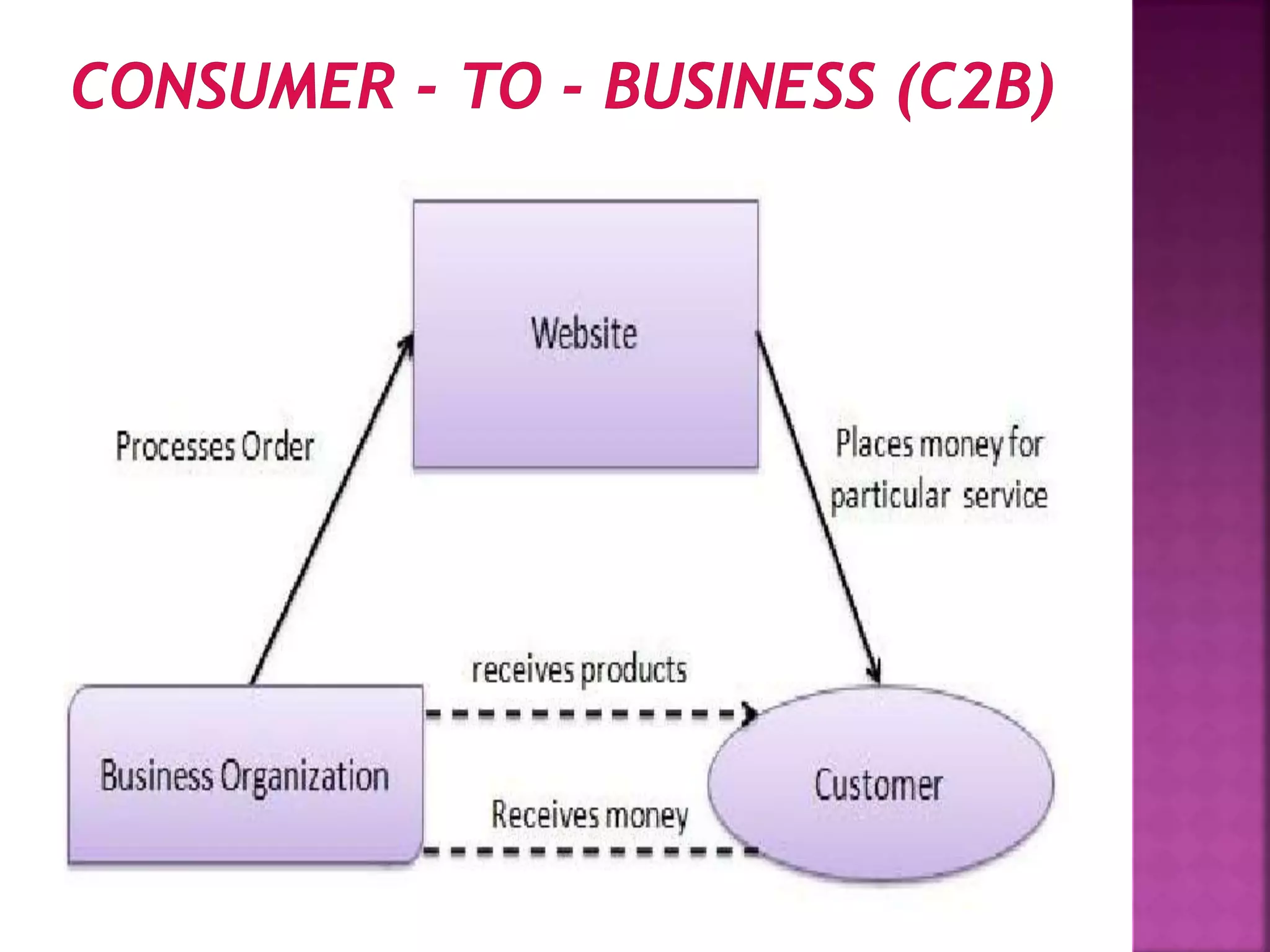
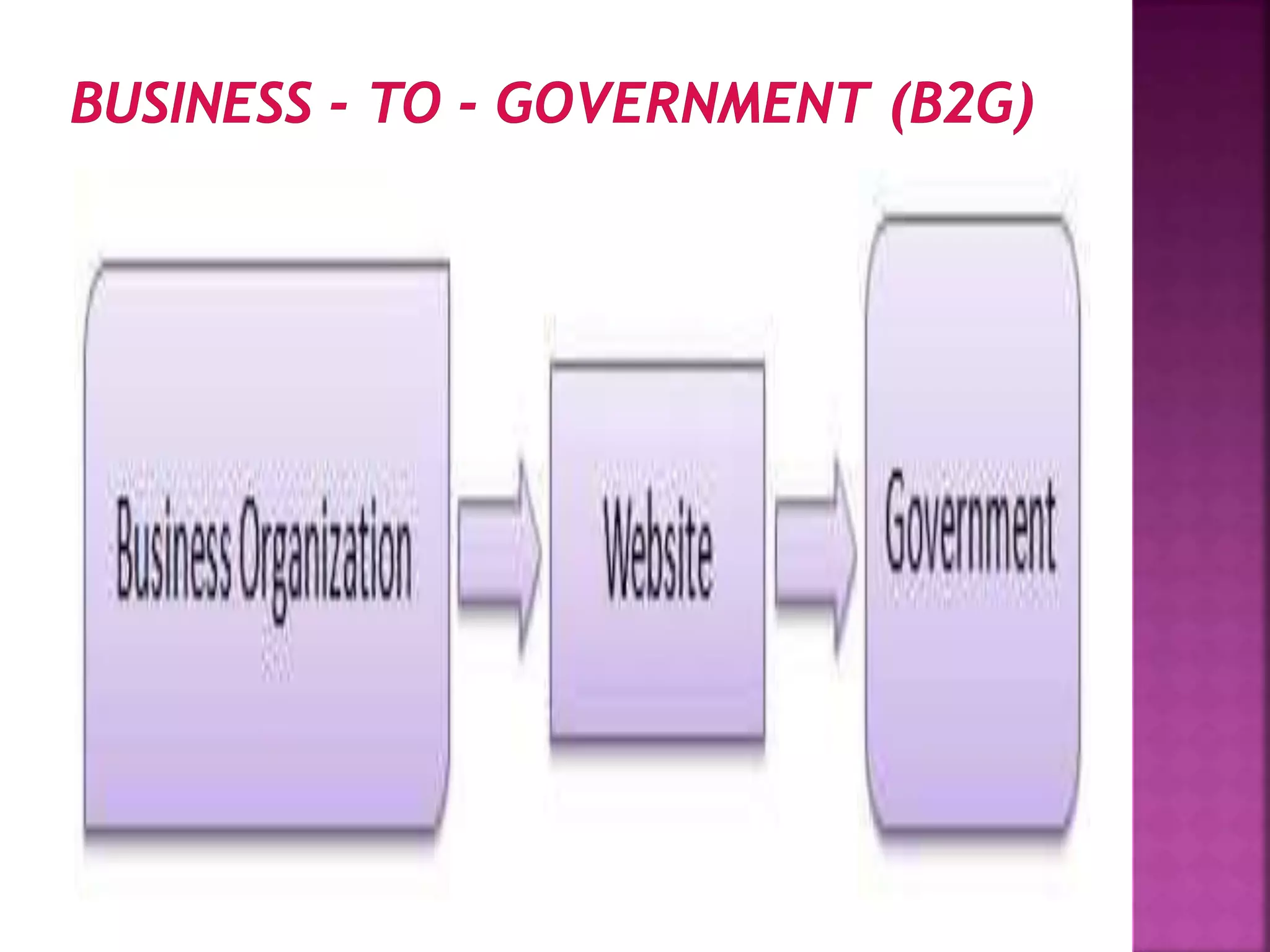
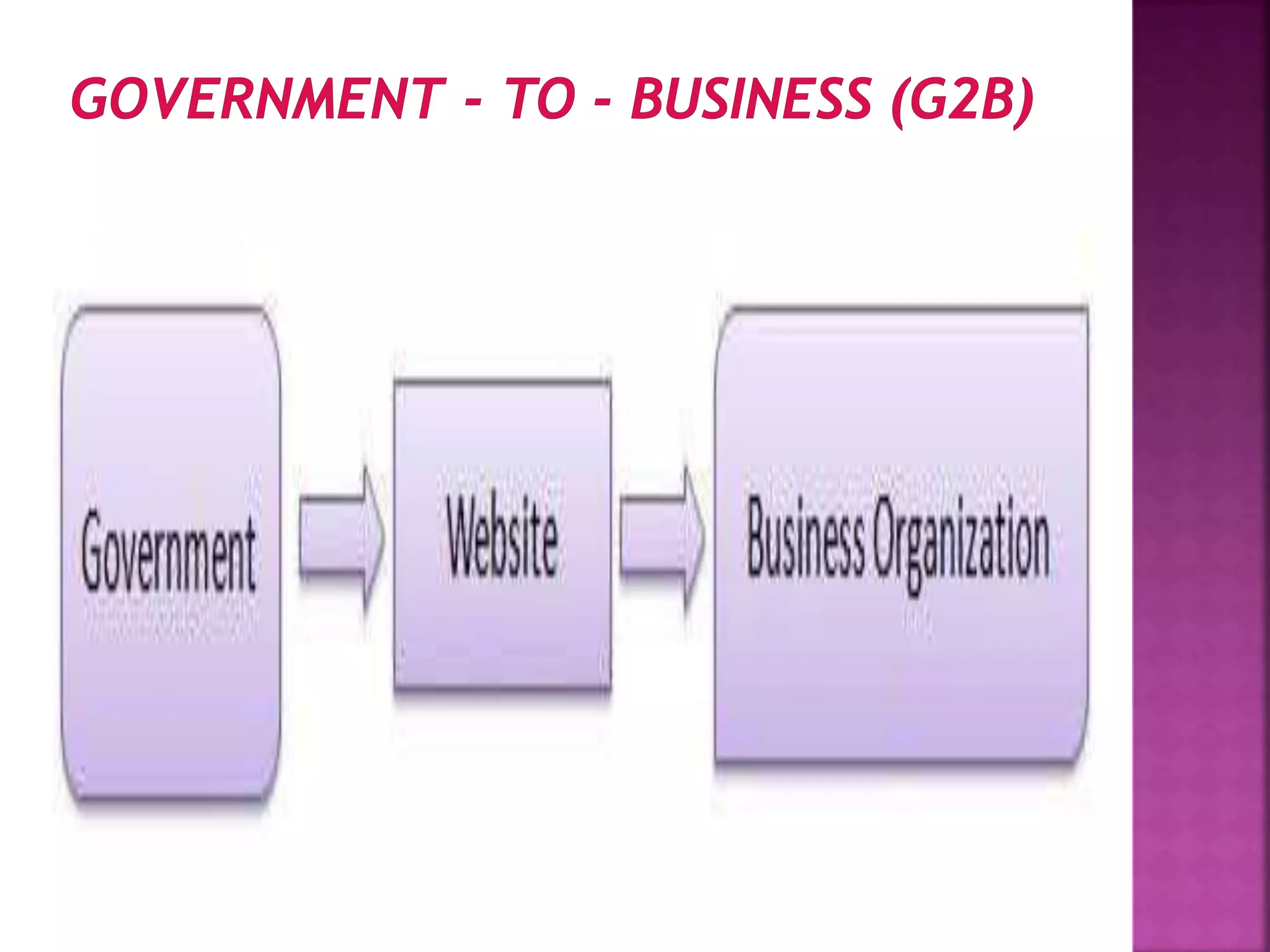
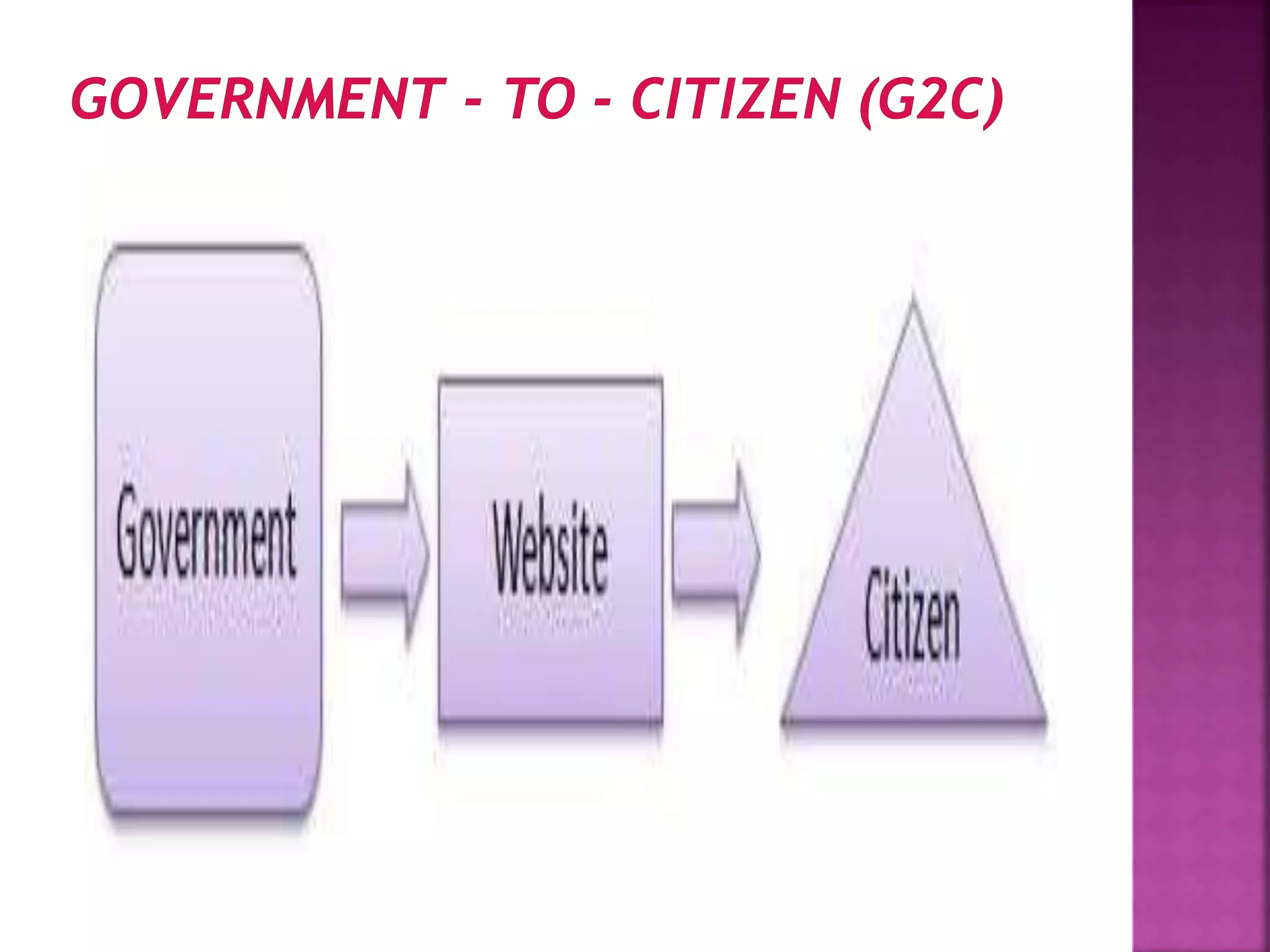
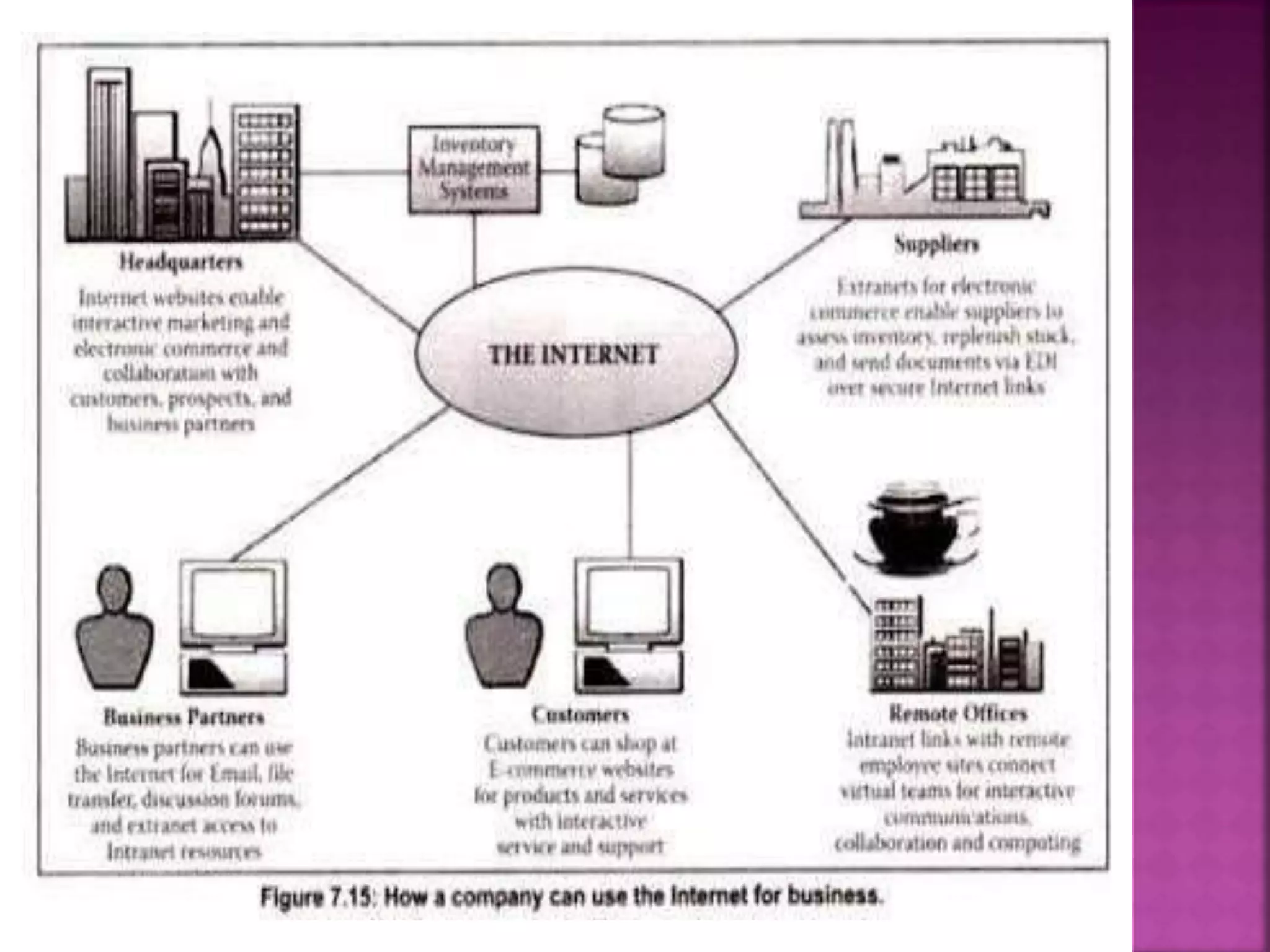
The document provides an overview of e-commerce and the internet. It defines e-commerce as conducting business electronically using electronic devices and networks. The internet is described as a worldwide collection of computer networks connected to each other. Key topics covered include definitions of e-commerce, benefits and challenges of e-commerce, the evolution and services of the internet, building websites, e-marketing, electronic payments, security issues, and encryption.