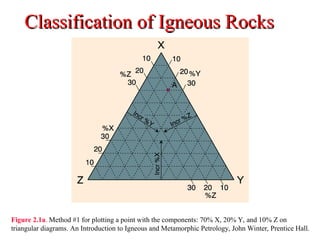
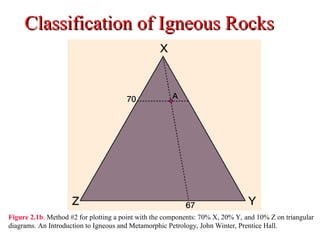
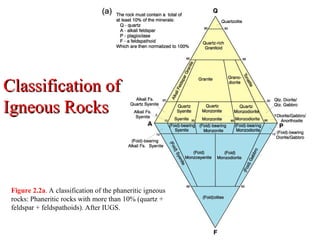
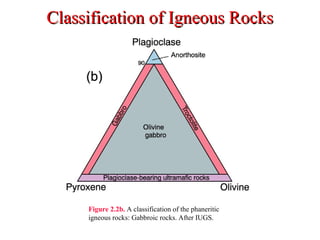
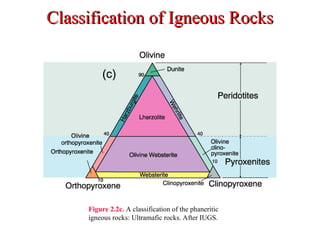
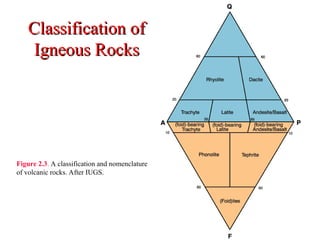
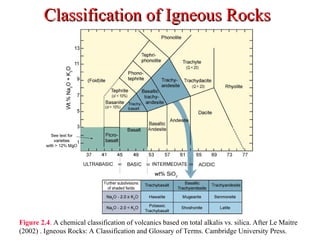
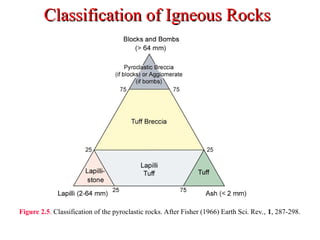
The document provides an overview of the classification of igneous rocks, detailing their textures and grain sizes. Various classification methods are illustrated using triangular diagrams, and specific types of rocks are categorized based on composition and texture, including phaneritic and volcanic rocks. Additionally, it references key figures and sources for deeper understanding of the classifications discussed.