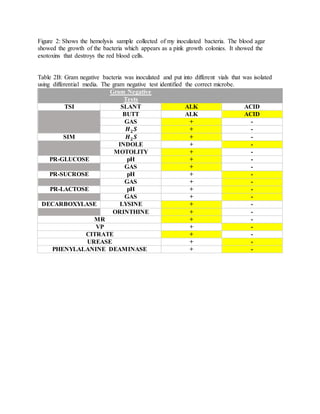
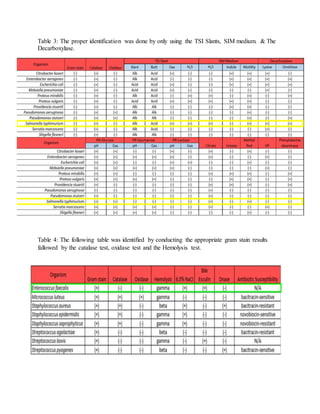
This document summarizes a student laboratory experiment to identify two unknown bacterial strains, one gram-positive and one gram-negative, through a series of biochemical tests over two weeks. The student's gram-positive strain was identified as Enterococcus faecalis and the gram-negative strain as Salmonella typhimurium based on results from tests including gram staining, catalase, oxidase, hemolytic activity, salt tolerance, bile-esculin hydrolysis, DNase production, and sugar fermentation patterns. A variety of selective and differential media were used to isolate and characterize the bacteria through observation of colony morphology and biochemical reactions.