1) The document outlines steps for conducting a behavioral event interview (BEI) to identify competencies through individual and team analysis of interview transcripts.
2) Analysts work in pairs to read, identify, underline, note, and code competencies in transcripts using their own abbreviations and themes with competency dictionaries as a reference.
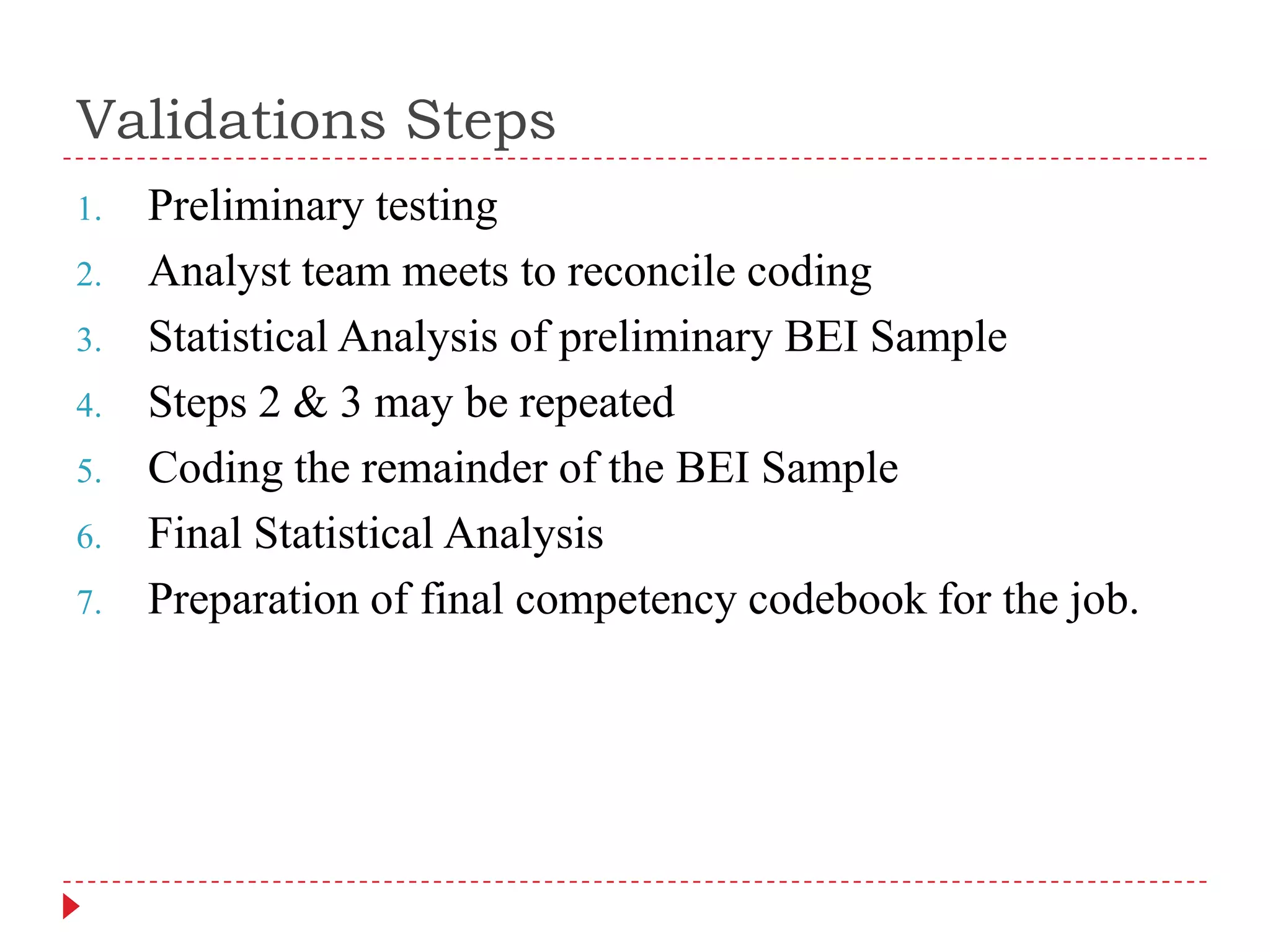
3) The team then discusses themes found, defines positive/negative competencies, and consolidates competencies into the smallest number of clusters while validating findings through preliminary testing and statistical analysis.