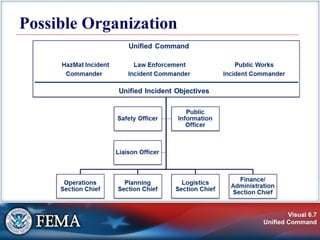
This document provides an overview of unified command. It defines unified command as consisting of incident commanders from different jurisdictions operating together under a single command structure. The benefits of unified command include a shared understanding of priorities, a single set of objectives, collaborative strategies, improved information flow, less duplication of efforts, and better resource utilization. Key features include a single integrated organization, co-located facilities, one set of objectives and plans, and an integrated general staff. The document outlines potential barriers to implementing unified command and strategies for making it work effectively.