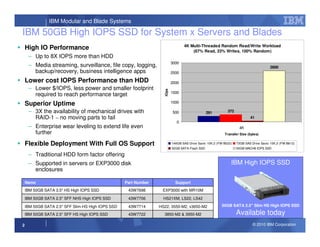
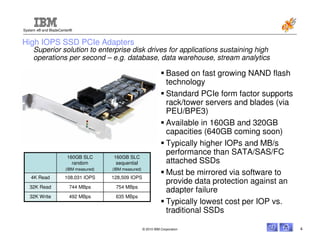
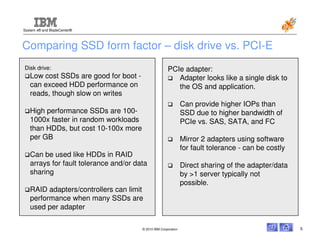
This document discusses the use of solid state drives (SSDs) in servers to improve performance, reduce costs, and increase reliability compared to spinning hard disk drives (HDDs). It summarizes three main uses of SSDs: 1) replacing boot disks to speed up applications, 2) replacing disks in high input/output systems, and 3) using SSDs as a fast virtual memory paging device. It then provides details on IBM's 50GB high input/output SSD options for servers and blades, and 160GB/320GB PCIe SSD adapters that provide even higher performance than SATA/SAS attached SSDs.