The document is an introductory guide to MariaDB, covering key concepts such as SQL, the history of MariaDB, and practical applications in a virtual event led by IBM's Tony Pearson. It outlines installation steps, how to manage users and databases, and provides examples of SQL commands for creating and manipulating data within a MariaDB environment. Prominent users of MariaDB are mentioned, alongside a comparison with MySQL, highlighting its community development and commercial support features.







![Launch the MariaDB server as
a background service
[tony ~]# systemctl start mariadb.service
[tony ~]# systemctl enable mariadb.service
[tony ~]$ systemctl status mariadb.service
● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.2.33 database server
Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d
└─migrated-from-my.cnf-settings.conf
Active: active (running) since
Wed 2020-09-30 03:45:30 MST
All of the examples will use Red Hat
Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
Systemctl is used to start and stop
background services
• start – run MariaDB server now
• enable – run MariaDB every
time you boot your system
• status – check if MariaDB is
running or stopped
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-11-320.jpg)
![Login as “root” user until we
create other users
[tony ~]$ mysql -u root -p -h localhost
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands
end with ; or g.
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB
Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear
the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> quit
Bye
[tony ~]$
The mysql client will
connect to the MariaDB background
service on port 3306
-u <user> -p (Log in as root, and
prompt for the password)
-h <ip address> (we will use localhost)
Once you are in, you will see new prompt
MariaDB [(database)]>
h show commands available
c cancel the current statement
W show warning messages
q get out, “quit” or “exit” also work
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-12-320.jpg)
![Explore the system databases
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.02 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> use mysql;
Database changed
MariaDB [mysql]>
MariaDB Relational Database
Management System (RDBMS) uses
system databases
You can see these databases already
exist with show databases statement
The use command changes the prompt to
that database, and allows commands on
tables within that database
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-13-320.jpg)
![Explore the system databases
MariaDB [(mysql)]> show tables;
| Tables_in_mysql |
+---------------------------+
| . . . |
| user |
| . . . |
MariaDB [mysql]> select user, host from user;
+---------+-----------+
| user | host |
+---------+-----------+
| root | % |
| root | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | ::1 |
| root | localhost |
+---------+-----------+
The show tables command is a
quick way to list all of the tables in
a database
The mysql database has about 30
tables including one called user
The select statement can display
information in the user and host
columns of the user table
While I only have one root user,
you can see I have four entries in
the table
13(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-14-320.jpg)

![Create a new database and
administrator user privileges
MariaDB [mysql]> create database hrdb
character set utf8;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec)
MariaDB [mysql]> create user hradmin
identified by ‘SafeW0rd’;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
MariaDB [mysql]> grant all privileges
on hrdb.* to 'hradmin'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [mysql]> grant file on *.* to
'hradmin'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Create a new database called hrdb for
Human Resources team
Create user hradmin as the database
administrator and sets the password
Grant privileges so that the administrator
can create tables in this database and
perform maintenance activities
• ‘hradmin’@’%’ allows remote access
Grant FILE allows hradmin to read and
write CSV files to/from database data
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-16-320.jpg)
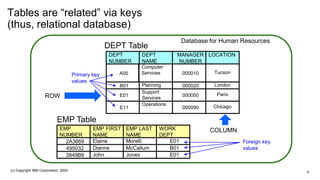
![Create tables for the
departments and employees
[tony ~]$ mysql -u hradmin -pSafeW0rd
hrdb
MariaDB [hrdb]> create table dept (
-> deptnum char(3) primary key,
-> deptname varchar(50),
-> manager integer,
-> location varchar(50));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
MariaDB [hrdb]> create table emp (
-> empnum char(6) primary key,
-> empfirst varchar(50),
-> emplast varchar(50),
-> workdept char(3));
Switching to the newly created hrdb
database with new user hradmin
We will create two tables:
• Dept – a list of all of the departments
• Emp – a list of all of the employees
For long commands, if it does not see the
semicolon (;) it will prompt you to continue
with an arrow →
Make a mistake? Just enter c to cancel
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-17-320.jpg)
![Display table schema for the
departments and employees
MariaDB [hrdb]> describe dept; describe emp;
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| deptnum | char(3) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| deptname | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| manager | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| location | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| empnum | char(6) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| empfirst | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| emplast | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| workdept | char(3) | YES | | NULL | |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
The describe command will
display the table definitions
The deptnum and empnum
columns are primary keys, so
they must contain a unique
value in every row
Columns that can have NULL
as value are considered
optional
You can specify a default for
any field if you like
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-18-320.jpg)
![Create tables for the
departments and employees
MariaDB [hrdb]> insert into dept values
-> ('A00', 'Computer Services', 000010, 'Tucson’),
-> ('B01', 'Planning', 000020, 'London’),
-> ('E01', 'Support Services', 000050, 'Paris’),
-> ('E11', 'Operations', 000090, 'Chicago');
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
MariaDB [hrdb]> insert into emp values
-> ('2A3669', 'Elaine', 'Morelli', 'E01’),
-> ('495032', 'Diane', 'McCallum', 'B01’),
-> ('3849B9', 'John', 'Jones', 'E01');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
We can now enter data into
these tables using INSERT
Note that CHAR and
VARCHAR require
quotation marks, but
INTEGER columns do not
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-19-320.jpg)
![Scenarios that require
changes to the data in tables
MariaDB [hrdb]> update emp set
emplast='Franklin' where empnum='495032';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.13 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
MariaDB [hrdb]> delete from emp where
workdept='E01';
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.07 sec)
MariaDB [hrdb]> delete from dept where
deptnum='E01';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Here are two typical examples of database
operations that the Human Resources
department might encounter
1. Diane McCallum changes her last name
2. Dept E01 is terminated
The UDPATE command can change one or
more columns
The DELETE command can remove one or
more rows, including the entire table!
The WHERE determines which rows are to be
processed for this request
19(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-20-320.jpg)
![Display table schema for the
departments and employees
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from dept;
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
| deptnum | deptname | manager | location |
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
| A00 | Computer Services | 10 | Tucson |
| B01 | Planning | 20 | London |
| E01 | Support Services | 50 | Paris |
| E11 | Operations | 90 | Chicago |
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from emp limit 1;
+--------+----------+---------+----------+
| empnum | empfirst | emplast | workdept |
+--------+----------+---------+----------+
| 2A3669 | Elaine | Morelli | E01 |
+--------+----------+---------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The SELECT command will
display the table values
The asterisk (*) indicates all
columns, we have only four
columns in each table so they
can fit on the screen
If you just want to see the first
few rows, just use LIMIT
keyword
20(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-21-320.jpg)
![Sorting by a different column
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from dept order by
location;
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
| deptnum | deptname | manager | location |
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
| E11 | Operations | 90 | Chicago |
| B01 | Planning | 20 | London |
| A00 | Computer Services | 10 | Tucson |
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from dept order by
deptname DESC;
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
| deptnum | deptname | manager | location |
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
| B01 | Planning | 20 | London |
| E11 | Operations | 90 | Chicago |
| A00 | Computer Services | 10 | Tucson |
+---------+-------------------+---------+----------+
By default, rows are displayed in
ascending primary key order
The ORDER BY command can
specify one or more columns to
use for sorting in different order
The ASC and DESC keywords
can determine which direction to
sort by
Combine with LIMIT 10 to
generate a “Top 10” list
21(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-22-320.jpg)
![Joining data from two tables,
the INNER join
MariaDB [hrdb]> select dept.deptnum,
emp.empnum from dept inner join emp on
dept.deptnum=emp.workdept;
MariaDB [hrdb]> select d.deptnum, e.empnum
from dept d inner join emp e on
d.deptnum=e.workdept;
MariaDB [hrdb]> select d.deptnum, e.empnum
from dept d, emp e where
d.deptnum=e.workdept;
+---------+--------+
| deptnum | empnum |
+---------+--------+
| B01 | 495032 |
+---------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The most common is an INNER join
The first statement is standard SQL
Abbreviations with “dept d” / “emp e”
MariaDB also supports this using
SELECT / WHERE clause
B01
495032
A01
E11
519832
22(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-23-320.jpg)
![Grouping into categories and
counting the number in each
COUNT(*) – number of rows in this
category
GROUP BY – use workdept as the
category
Note that you can change the heading
using
• count(*) AS headcount
HAVING – similar to WHERE but for
calculated values
MariaDB [hrdb]> select workdept, count(*) from
emp group by workdept;
+----------+----------+
| workdept | count(*) |
+----------+----------+
| A00 | 3 |
| B01 | 2 |
| C01 | 4 |
| D41 | 2 |
+----------+----------+
MariaDB [hrdb]> select workdept, count(*) as
headcount from emp group by workdept having
headcount>2;
+----------+-----------+
| workdept | headcount |
+----------+-----------+
| A00 | 3 |
| C01 | 4 |
+----------+-----------+
23(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-24-320.jpg)
![Tables versus Views
Key differences?
A copy of the table is independent,
any changes to the table are not
reflected back to the original table
** GOOD FOR TESTING **
Any changes to the view are applied
to the original table
** SINGLE POINT OF TRUTH**
The mysqldump utility can backup
individual tables, but not individual
views. Backup entire database will
re-define the view for you.
MariaDB [hrdb]> create table teamC01 select *
from emp where workdept='C01';
MariaDB [hrdb]> create view showC01 as select
* from emp where workdept='C01';
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from teamC01;
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from showC01;
+--------+----------+----------+----------+
| empnum | empfirst | emplast | workdept |
+--------+----------+----------+----------+
| 098765 | Karen | Eastern | C01 |
| 456789 | Ulrich | Trenton | C01 |
| 519823 | Frank | Smith | C01 |
| 987654 | Lisa | Franklin | C01 |
+--------+----------+----------+----------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
24(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-25-320.jpg)
![Exporting database data to
CSV files
Comma-Separated Variables (CSV)
You can choose your delimiter:
• 0x2c – ASCII code for comma
• 0x09 – ASCII code for tab (→)
• 0x7c – ASCII code for pipe (|)
For character strings, surround them
with quotation marks
• 0x22 – code for double quote
• 0x27 – code for single quote
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from dept INTO OUTFILE
‘/tmp/dept.csv' fields terminated by 0x2c
optionally enclosed by 0x22;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.04 sec)
MariaDB [hrdb]> quit
Bye
[tony ~]$ cat /tmp/dept.csv
"A00","Computer Services",10,"Tucson"
"B01","Planning",20,"London"
"E11","Operations",90,"Chicago"
25(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-26-320.jpg)
![Importing CSV files into
databases
You can add data to databases
by importing from CSV files
Specify the delimiter and
quotation marks to expect
Add “IGNORE 1 LINES” if the
incoming CSV file has a
header line
MariaDB [hrdb]> LOAD DATA INFILE ‘/tmp/dept2.csv'
into table dept fields terminated by 0x2c
optionally enclosed by 0x22;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: 3 Deleted: 0 Skipped: 0 Warnings: 0
MariaDB [hrdb]> select * from dept;
+---------+-------------------+---------+-------------+
| deptnum | deptname | manager | location |
+---------+-------------------+---------+-------------+
| A00 | Computer Services | 10 | Tucson |
| B01 | Planning | 20 | London |
| C01 | Manufacturing | 30 | Los Angeles |
| D41 | Engineering | 40 | New York |
| E11 | Operations | 90 | Chicago |
| F21 | Marketing | 50 | Atlanta |
+---------+-------------------+---------+-------------+
26(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-27-320.jpg)
![Backing up and recovering
databases
[tony ~]$ mysqldump -u hradmin -pSafeW0rd hrdb > hrdb_dump.sql
[tony ~]$ mysqldump -u hradmin -pSafeW0rd hrdb dept > dept_table.sql
[tony ~]$ mysql -u hradmin -pSafeW0rd
MariaDB [(none)]> use hrdb;
Database changed
MariaDB [hrdb]> source hrdb_dump.sql
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 6 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 14 rows affected (0.00 sec)
27
The mysqldump utility is able to backup an
entire database, or selected tables
The output is an SQL file, all the statements
you need to re-generate the tables
Can be used to export database to another
RDBMS like IBM Db2 or to a test database
The SOURCE command can read the SQL
statements to create tables and insert data
(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-28-320.jpg)


![Notices and disclaimers
— Information concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the
suppliers of those products, their published announcements or other
publicly available sources. IBM has not tested those products about this
publication and cannot confirm the accuracy of performance,
compatibility or any other claims related to non-IBM products. Questions
on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the
suppliers of those products. IBM does not warrant the quality of any
third-party products, or the ability of any such third-party products to
interoperate with IBM’s products. IBM expressly disclaims all
warranties, expressed or implied, including but not limited to, the
implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a purpose.
— The provision of the information contained herein is not intended to, and
does not, grant any right or license under any IBM patents, copyrights,
trademarks or other intellectual property right.
— IBM, the IBM logo, ibm.com and [names of other referenced IBM
products and services used in the presentation] are trademarks of
International Business Machines Corporation, registered in many
jurisdictions worldwide. Other product and service names might
be trademarks of IBM or other companies. A current list of IBM
trademarks is available on the Web at "Copyright and trademark
information" at: www.ibm.com/legal/copytrade.shtml
(c) Copyright IBM Corporation, 2020 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l203326-intro-mariadb-techu2020-v9-201104231642/85/L203326-intro-maria-db-techu2020-v9-32-320.jpg)
