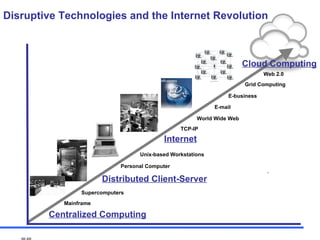
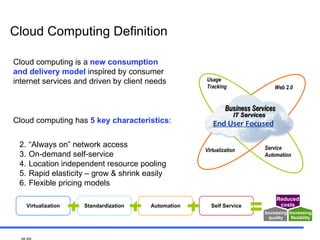
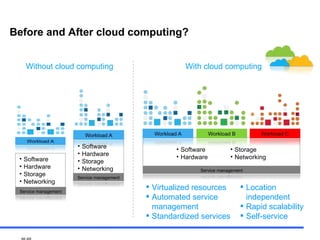
The document discusses the rise of cloud computing and its impact on IT infrastructure. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources and data storage over the internet and has five key characteristics: on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. The adoption of cloud computing is changing the cost structure of IT and allowing businesses to be more agile while maintaining security and privacy. Clients want to leverage cloud computing to transform their business operations and deliver new services efficiently.
![Cloud Computing: Da Teoria para a Prática Cezar Taurion Gerente de Novas Tecnologias/Technical Evangelist [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cezartaurion-110828141429-phpapp02/75/IBM-Seminario-Computacao-em-Nuvem-1-2048.jpg)










![Obrigado! Mais informações: www.ibm.com /cloud-computing www.ibm.com/developerworks/cloud www.computingonclouds.wordpress.com www.ibm.com/developerworks/blogs/page/ctaurion [email_address] @twitter, Facebook, Linkedin, BranchOut](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cezartaurion-110828141429-phpapp02/85/IBM-Seminario-Computacao-em-Nuvem-16-320.jpg)