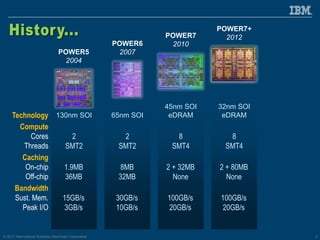
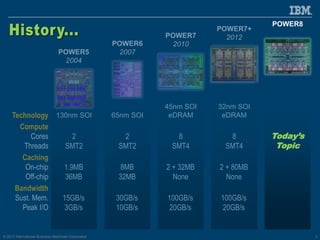
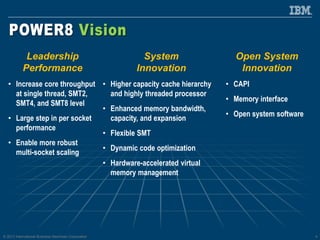
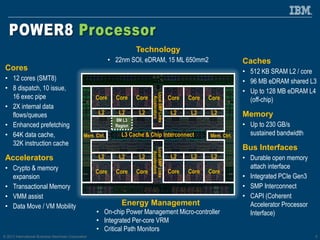
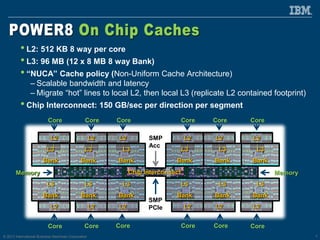
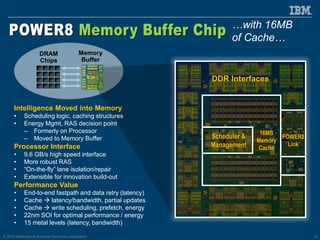
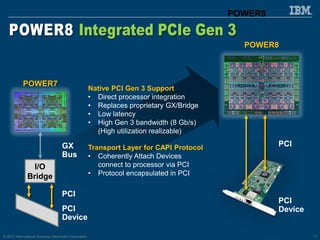
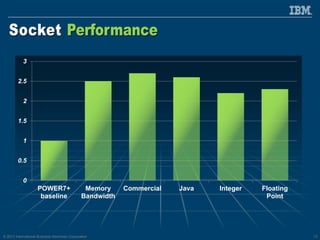
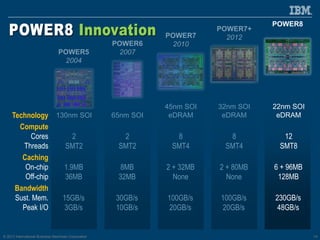
The document discusses the IBM Power8 processor's advancements in computing, emphasizing its increased core throughput, improved memory bandwidth, and enhanced multi-threading capabilities. It highlights features such as larger cache sizes, cutting-edge technology for system optimization, and strong enablement of big data analytics. Furthermore, it positions Power8 as a versatile platform suitable for various applications including cognitive computing and analytics, while fostering openness with system innovations and external accelerators.