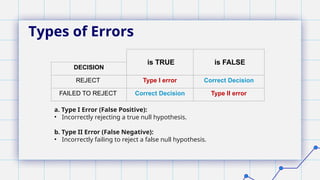
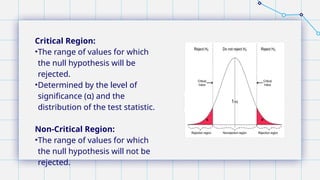
The document provides an overview of hypothesis testing in statistics, covering essential concepts such as types of hypotheses, probability errors, regions of rejection, and levels of significance. It explains the difference between the null and alternative hypotheses, the implications of type I and type II errors, and discusses the commonly used significance levels. Additionally, it highlights the role of tabular values in determining cutoff points for rejecting hypotheses.