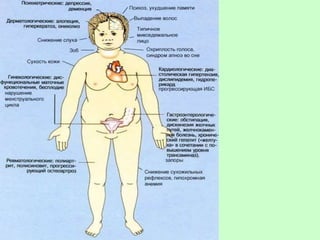
Hormonal drugs are used to treat hypo- and hyperthyroidism. For hypothyroidism, drugs include levothyroxine sodium and liothyronine, which supplement thyroid hormones. For hyperthyroidism, drugs like mercazolil inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis or radioactive iodine can destroy thyroid follicle cells. A constant iodine supply is necessary for normal thyroid hormone synthesis, so iodized salt is commonly used to prevent iodine deficiency. Levothyroxine sodium is the drug of choice for hypothyroidism replacement therapy and mercazolil works by blocking peroxidase to inhibit thyroid hormone production for hyperthyroidism treatment.