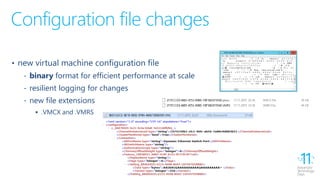
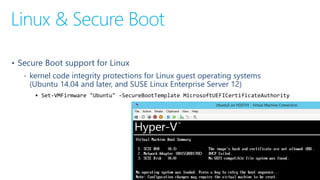
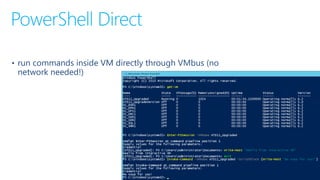
The document summarizes new features in the next version of Hyper-V including improved Hyper-V Manager, ability to dynamically resize VM memory and add/remove network adapters while running, support for Linux secure boot, production checkpoints, cluster upgrades without downtime, PowerShell direct on VMs, and other resiliency and container improvements. It also discusses VM versioning and manual upgrades being required when moving to new versions.