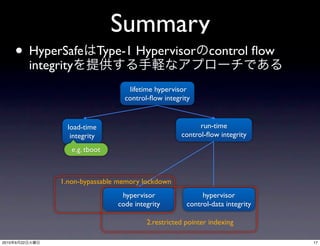
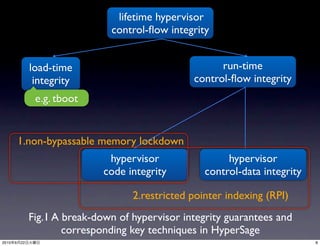
This paper proposes HyperSafe, which provides lifetime control flow integrity for the hypervisor through two techniques: 1) non-bypassable memory lockdown of hypervisor code and control data, and 2) restricted pointer indexing to allow only valid control transfers. It implements these techniques in a type-1 hypervisor using LLVM for pointer analysis and enforcement with restricted pointer indexing. This aims to prevent attacks against the hypervisor, such as VM escapes or installation of a hypervisor rootkit.


![Approach a secure hypervisor
• [seL4, SOSP’09]
•
• Microkernel
•
• TPM&TXT measured launch
•
•
2010 6 22 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypersafeintro-100622085115-phpapp02/85/Hypersafe-Introducing-in-japanese-by-third-party-3-320.jpg)

![cf).Control Flow Integrity [Abadi et.al. , CCS’05]
•
• SFI primitive
• jmp call src/dst
• programming return-oriented
2010 6 22 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypersafeintro-100622085115-phpapp02/85/Hypersafe-Introducing-in-japanese-by-third-party-5-320.jpg)



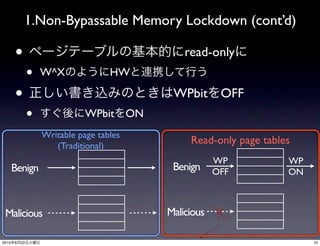

![2.Restricted Pointer Indexing (cont’d)
• control data
• call/ret, jmp src/dst
• static analysis CFG(Call Flow Graph)
• CFG Target Table
Call Site i Call Site i Target Table i
eax Callee j eax Callee j
func_j func_j: func_j func_j:
call *%eax | call *%eax |
Ri: ... ... | Ri: ... ... Target Table j |
[esp] | [esp] |
Ri Ri
ret ret
(a) Traditional indirection call (b) New indirection call
2010 6 22 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypersafeintro-100622085115-phpapp02/85/Hypersafe-Introducing-in-japanese-by-third-party-12-320.jpg)



![Related Work
•
• seL4[Klein et al, SOSP’09],WIT[Akritidis et al, IEEE
S&P’08],KLEE[Cadar et al, OSDI’08]
• OS or
• SIM[Sharif et al, CCS’09] SecVisor[Seshadri,et al, ’07]SBCFI
[Petroni et al,CCS’07]
• Trusted Computing
• TrustVisor[McCune et al, Oakland’10], Flicker[McCune et
al,Eurosys’08],Pioneer[Seshadri et al, SOSP’05]
2010 6 22 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypersafeintro-100622085115-phpapp02/85/Hypersafe-Introducing-in-japanese-by-third-party-16-320.jpg)