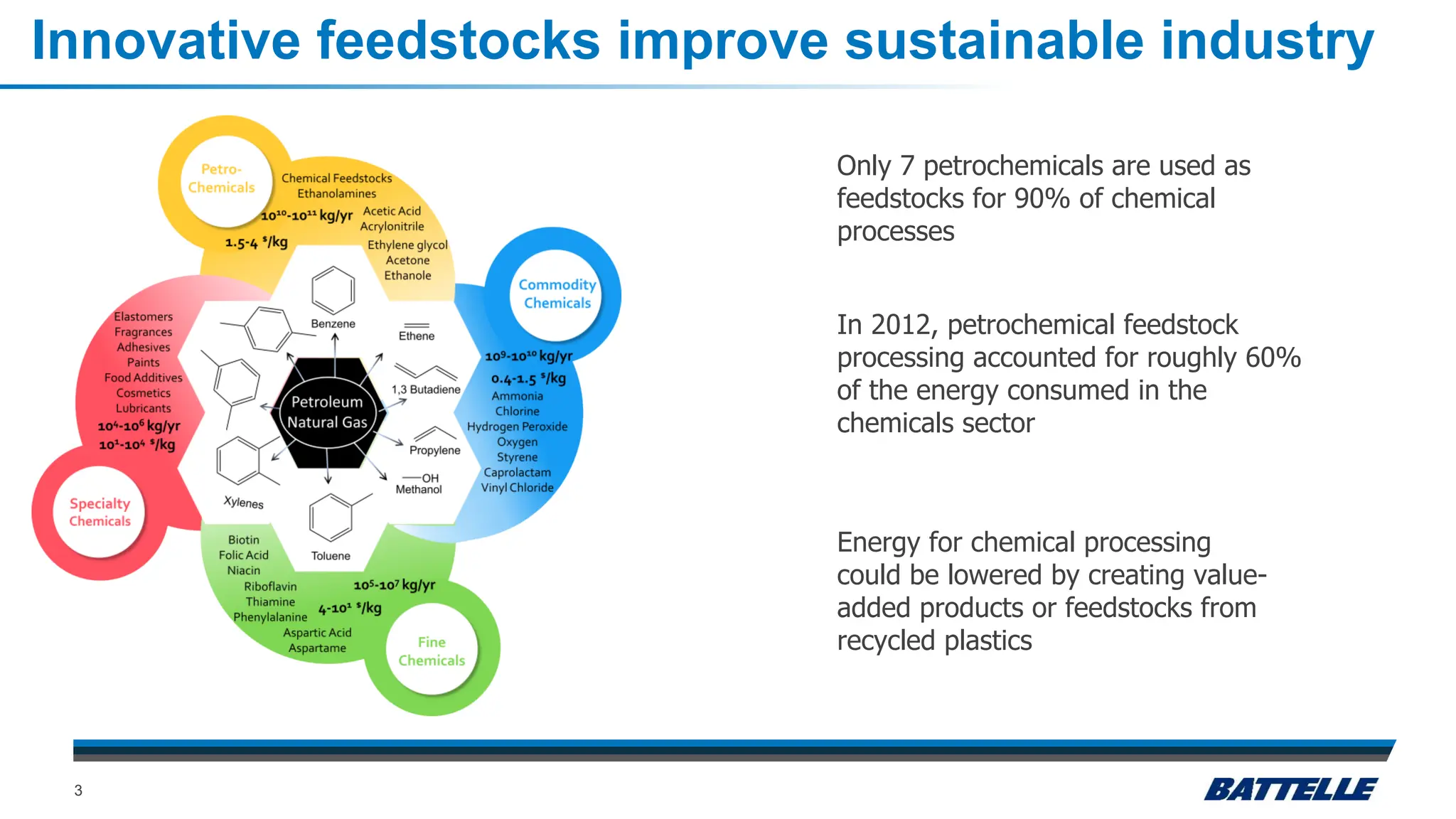
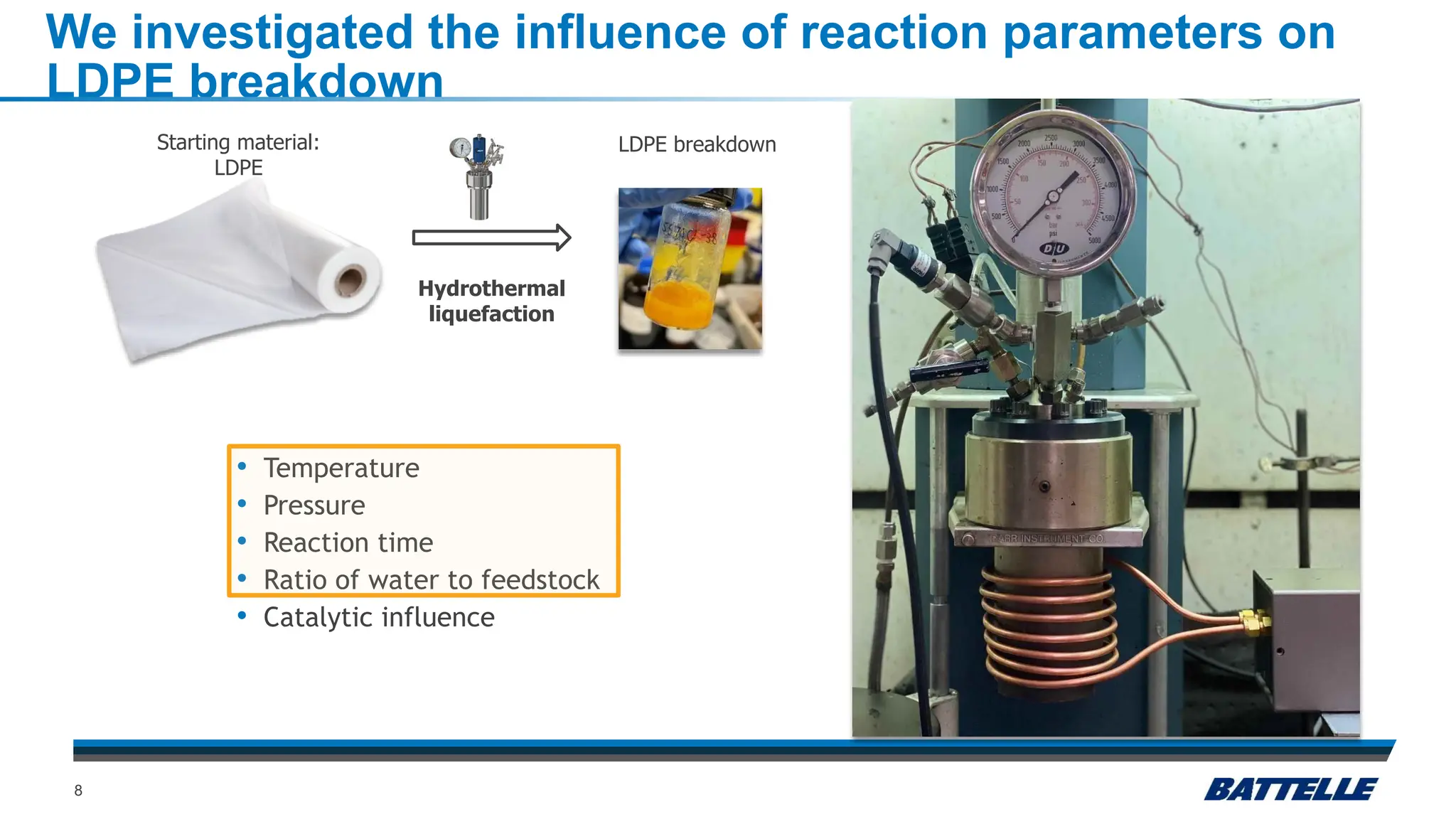
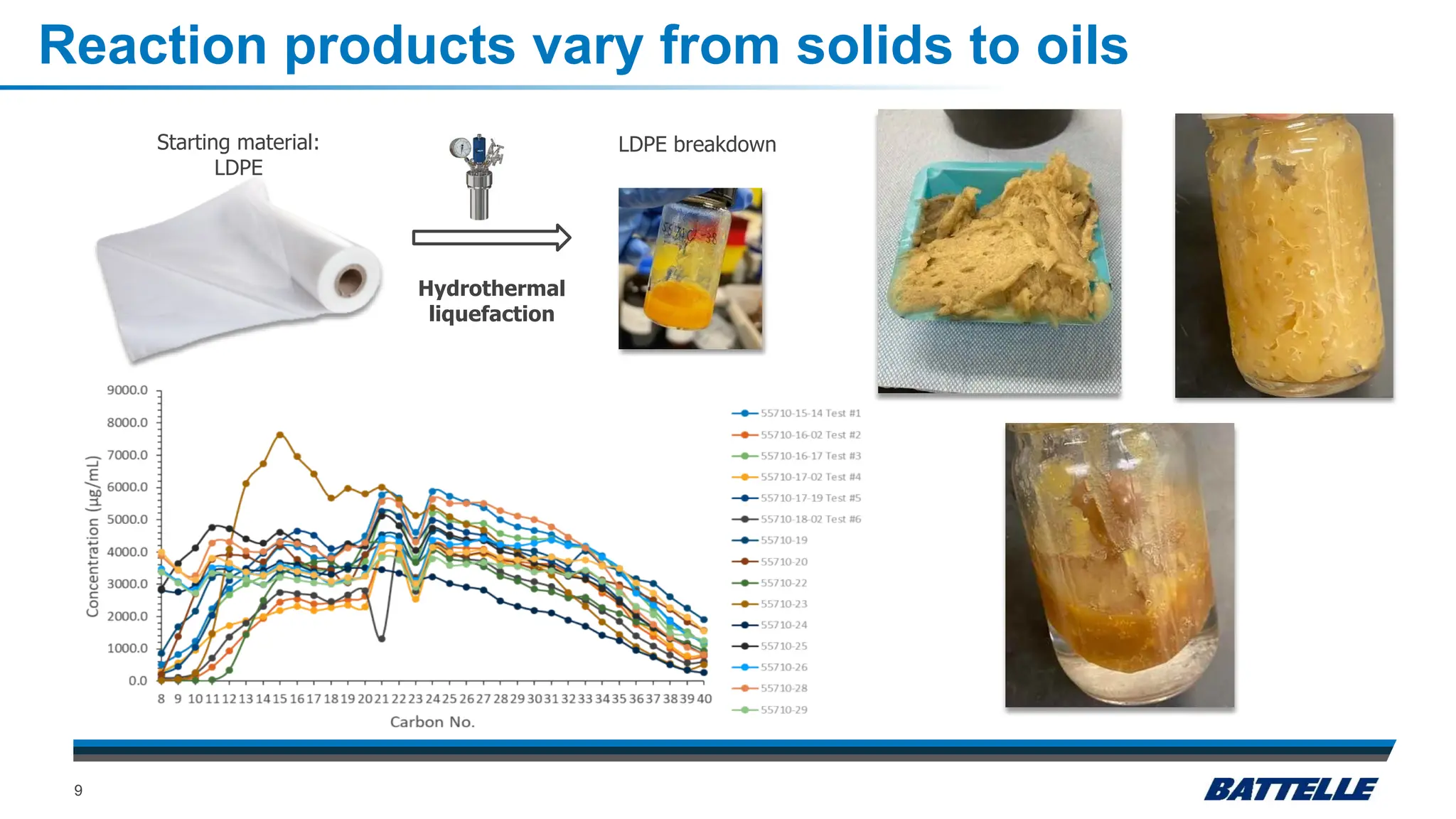
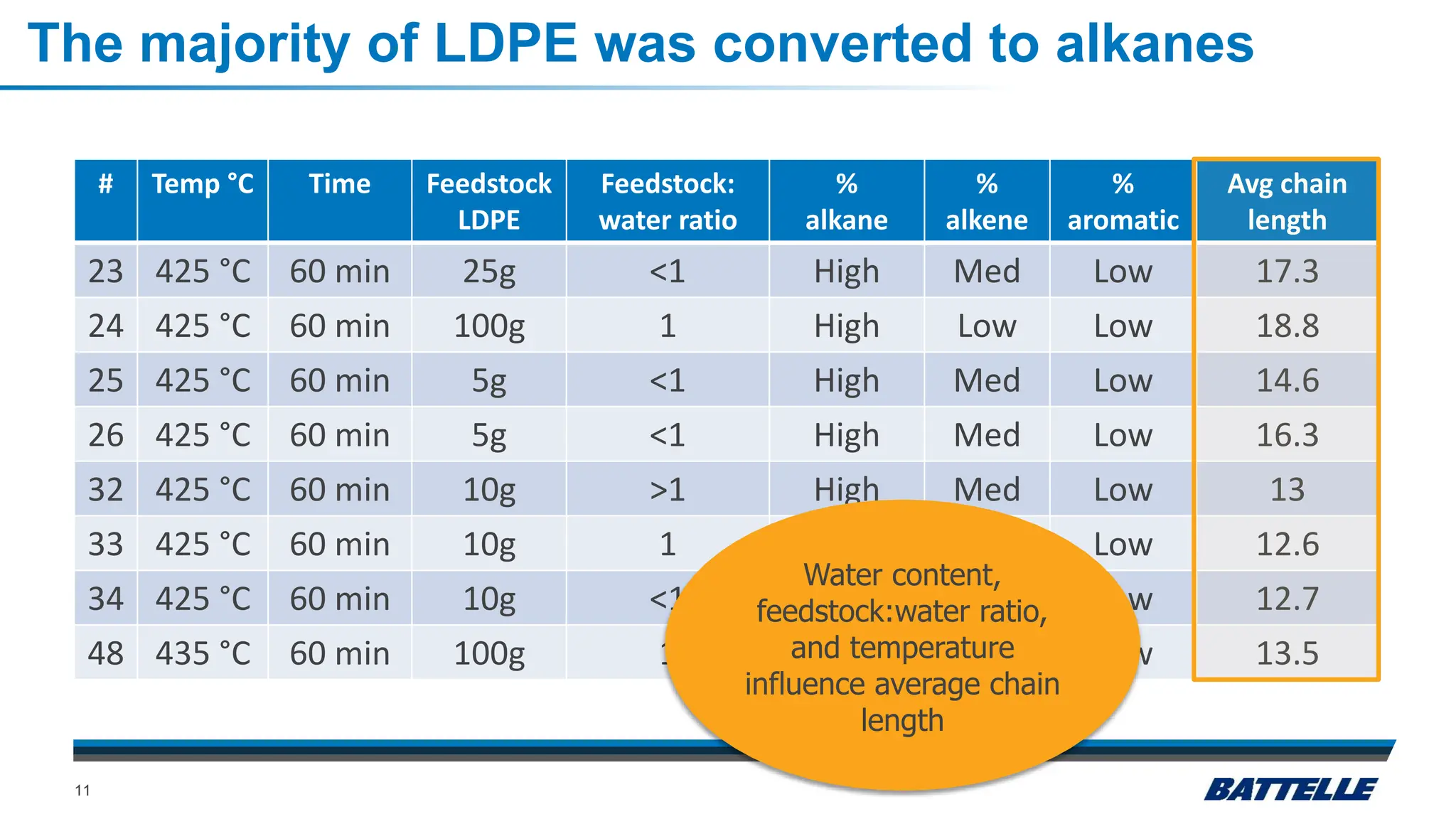
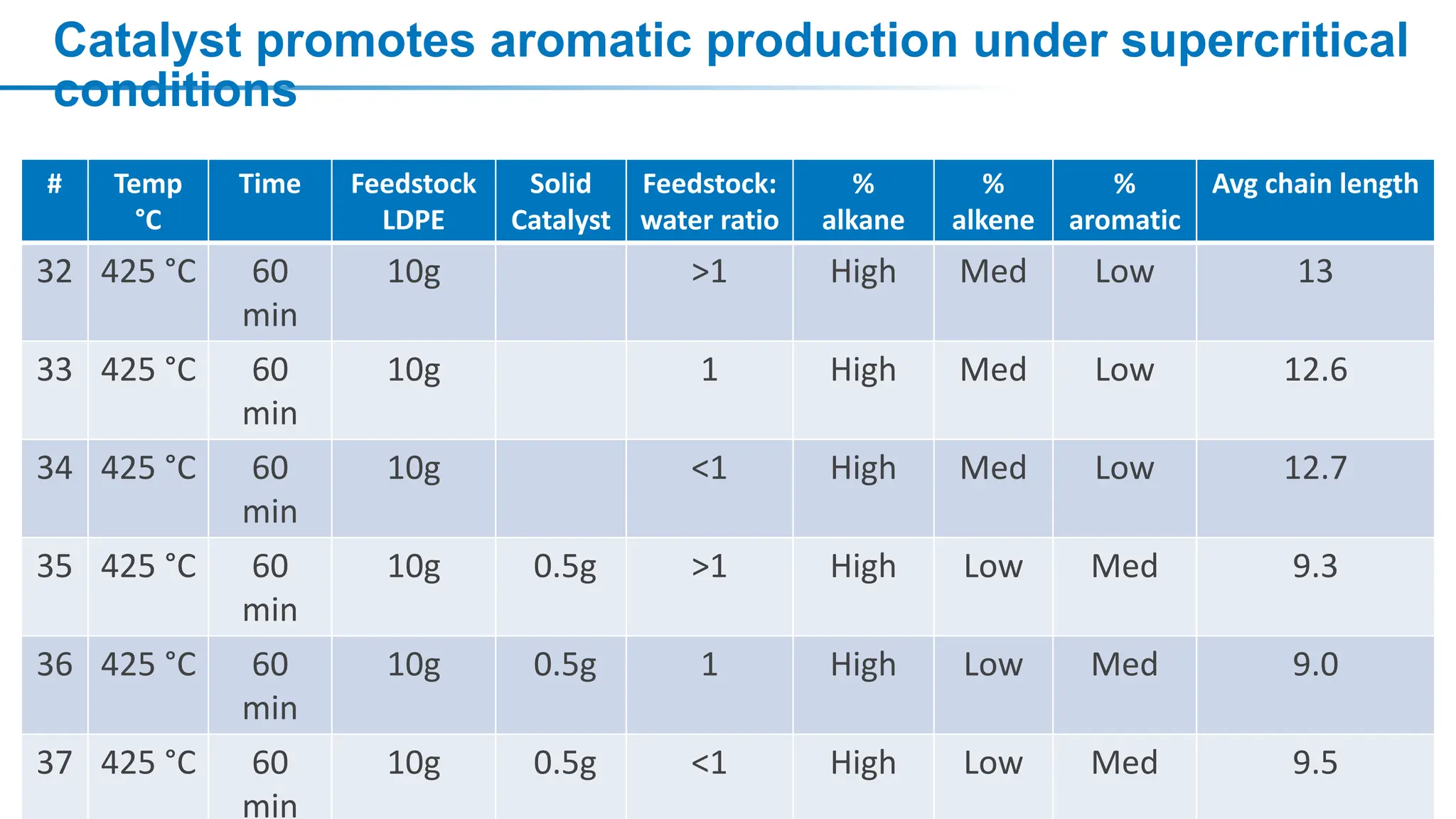
The document discusses hydrothermal liquefaction as a method for enhancing plastic circularity and reducing plastic pollution. It highlights the effectiveness of hydrothermal liquefaction in breaking down various plastics, particularly low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and how reaction parameters and catalysts can influence the production of valuable byproducts. The findings suggest that optimizing these parameters could lead to improved recycling and energy recovery from plastic waste.