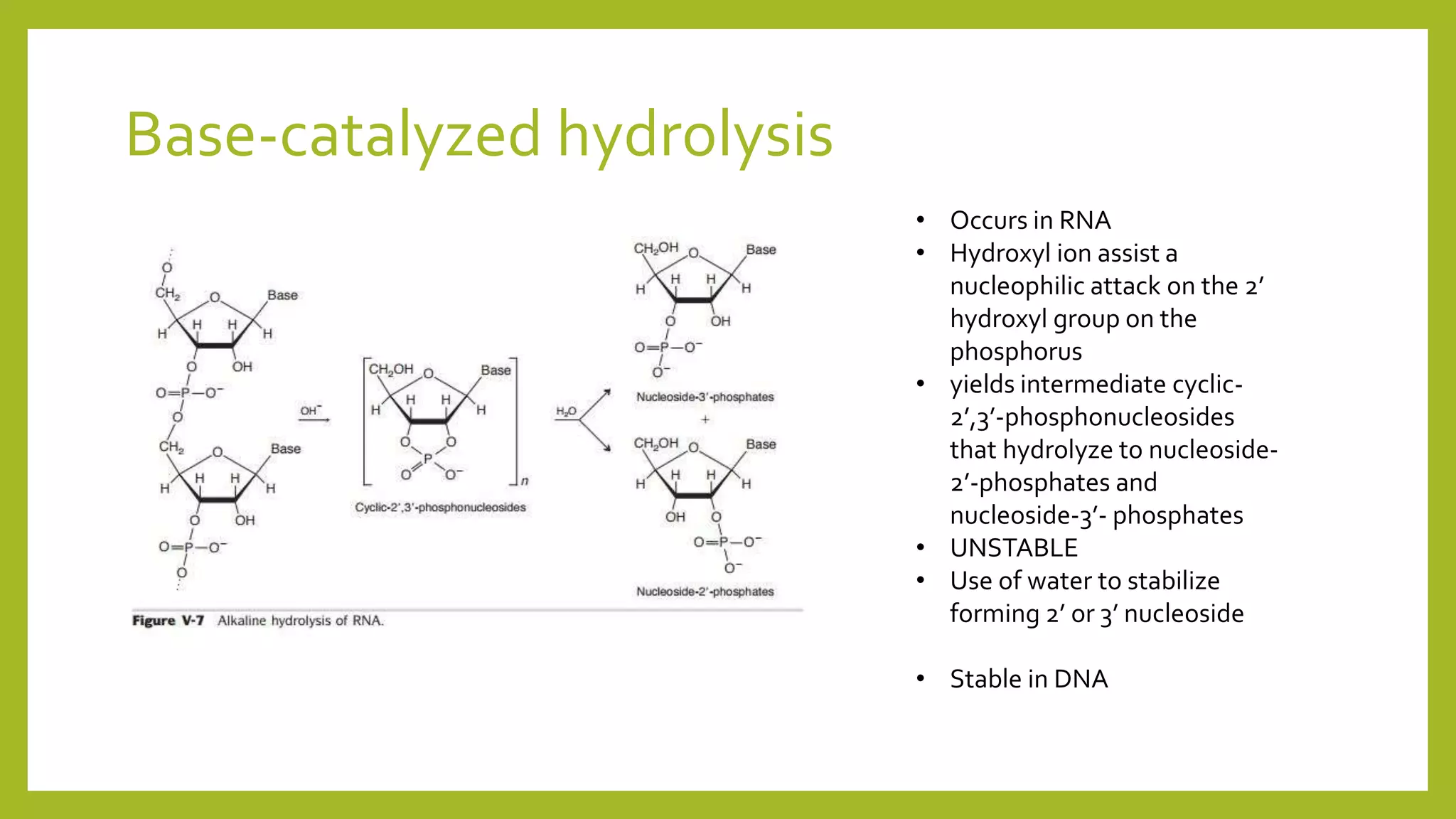
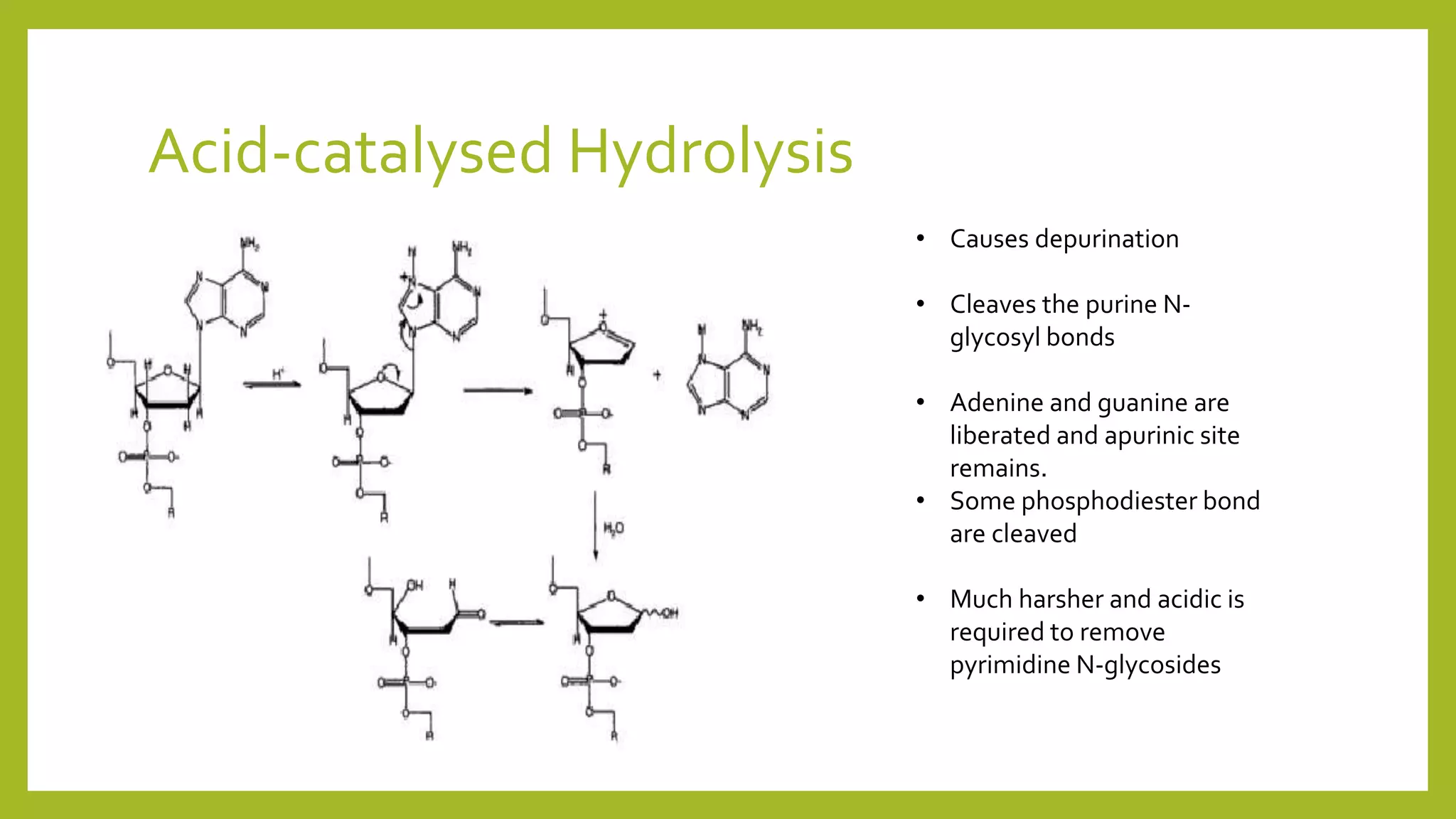
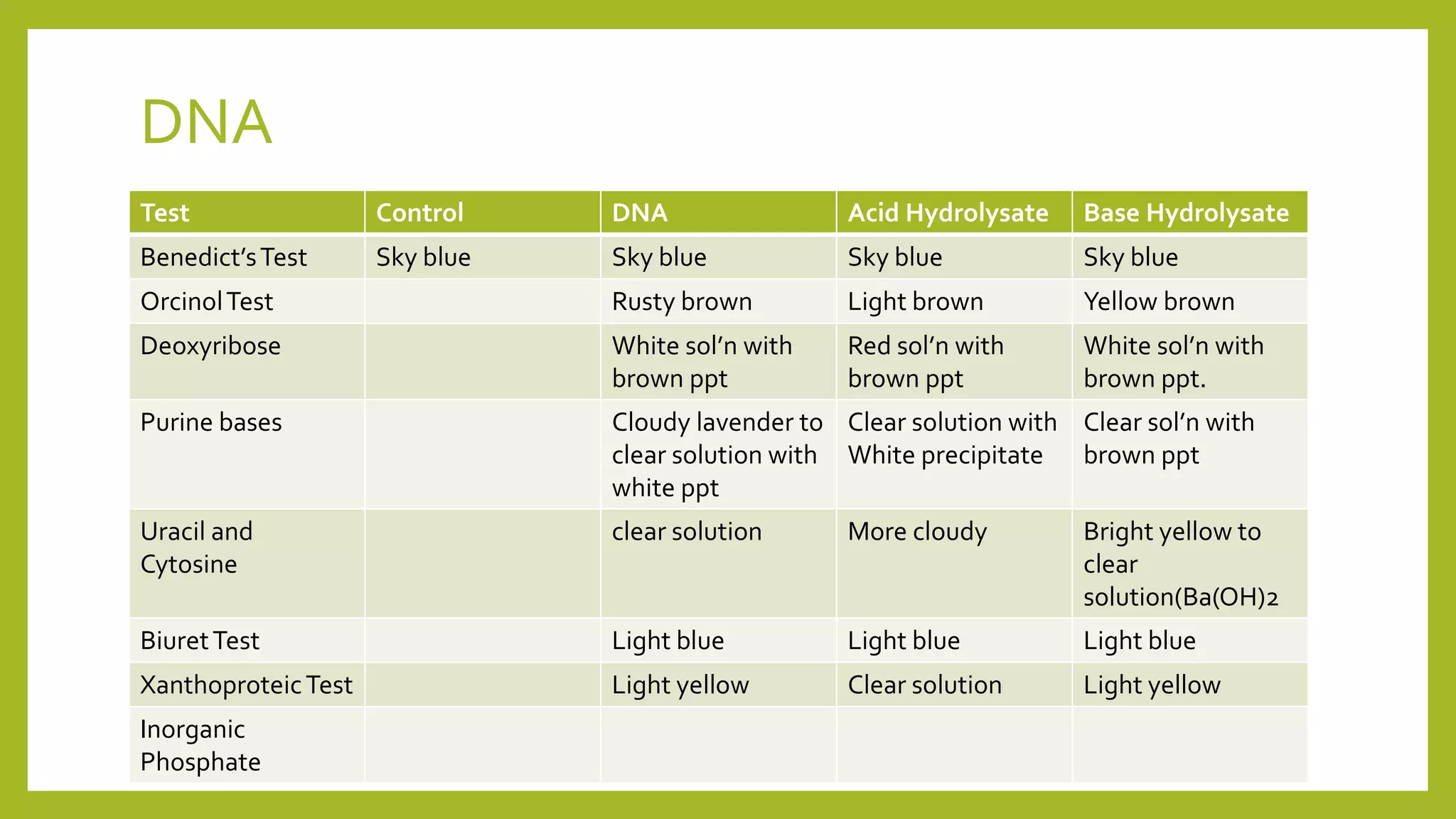
This document describes the hydrolysis of nucleic acids through acid-catalyzed and base-catalyzed hydrolysis. It provides objectives, theories, and results of qualitative tests performed on DNA and RNA samples and their hydrolysates. Base-catalyzed hydrolysis occurs only in RNA, yielding nucleosides, while DNA remains stable. Acid hydrolysis yields purine and pyrimidine bases and phosphoric acid. Though errors were made, the experiments helped understand nucleic acid hydrolysis and how to differentiate hydrolyzed and unhydrolyzed nucleic acids using qualitative tests.