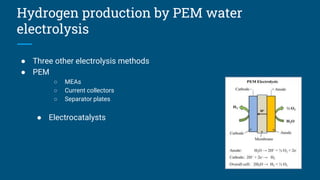
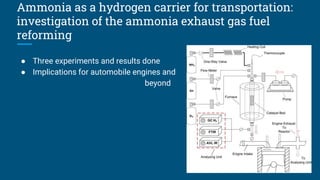
The document reviews research on using hydrogen and ammonia for clean and renewable energy. It discusses using hydrogen and ammonia to power transportation and electricity generation as alternatives to fossil fuels in order to mitigate climate change. It summarizes several studies on using ammonia for power production through electrolysis and fuel cells. It concludes that hydrogen and ammonia show potential as sustainable energy carriers but require further research and infrastructure investments to be implemented widely.