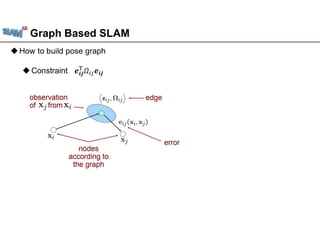
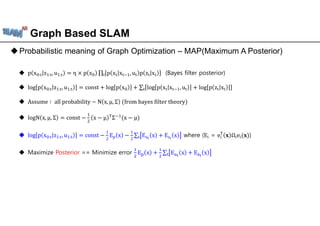
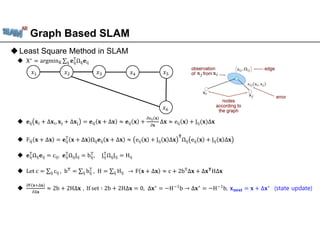
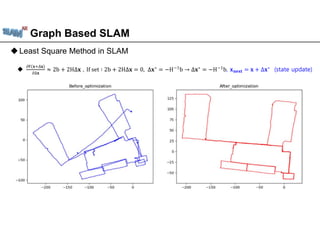
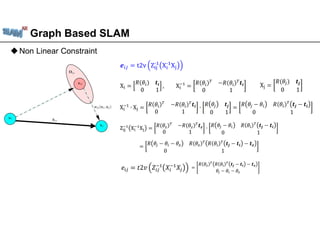
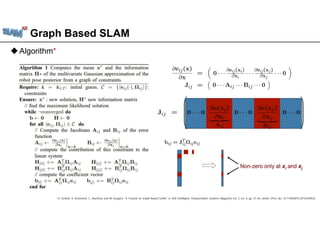
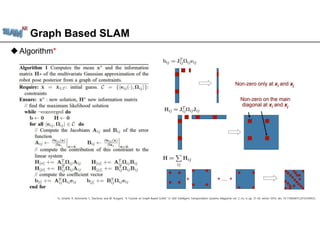
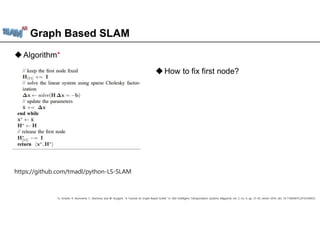
The document discusses graph-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), detailing its modeling through a graph where nodes represent the robot's pose and edges signify spatial constraints. It covers the process of building pose graphs using methods such as odometry and iterative closest point (ICP), followed by optimizations using least squares for error minimization. The text also mentions key algorithms and offers references for further reading on the subject.

![Graph Based SLAM
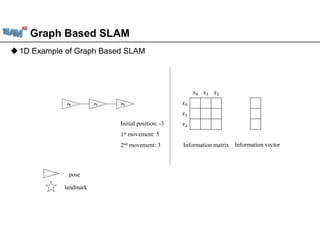
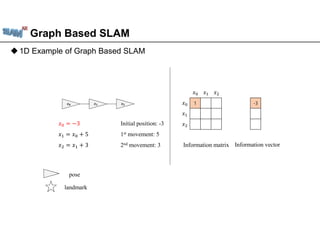
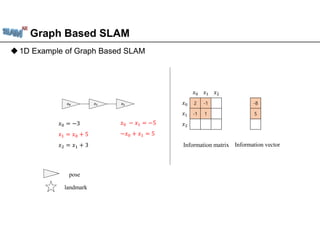
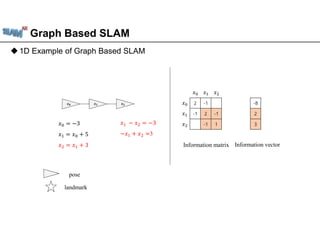
1D Example of Graph Based SLAM
pose
landmark
𝒙𝟎 𝒙𝟏 𝒙𝟐
𝑥 𝑥 𝑥
𝑥 2 -1 0
𝑥 -1 2 -1
𝑥 0 -1 1
-8
2
3
Information vector
𝑥 = −3
𝑥 = 𝑥 + 5
𝑥 = 𝑥 + 3
𝝁 = 𝛀 𝟏
𝝃
[𝑥 𝑥 𝑥 ] = −3 2 5
Information matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphbasedslamusingposegraph-240814183225-e36ee6cd/85/huongdanGraph-Based-SLAM-Using-Pose-Graph-pdf-7-320.jpg)