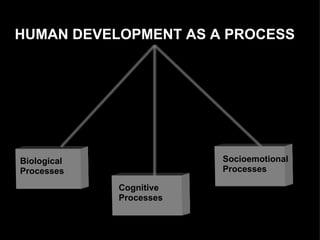
Human development is concerned with advancing human well-being rather than just economic growth. It aims to enlarge people's choices and capabilities through pursuing human rights and freedoms. The objective of human development is to create an environment where people can enjoy long, healthy lives. Human development occurs through biological, cognitive, and socioemotional processes across the life span from prenatal to late adulthood periods. Key issues in human development include social progress, economics, efficiency, equity, participation, freedom, and human security.