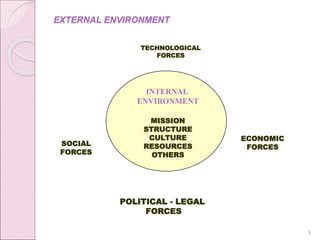
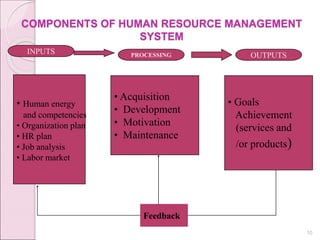
This document provides an overview of human resource management (HRM). It discusses what HRM is, its importance because people are critical to achieving organizational goals, and its major functions such as planning, recruitment, selection, and development. The document also examines the historical development of HRM from personnel management to its modern strategic focus. Key movements discussed include scientific management, human relations, human behaviorism, and organizational development.