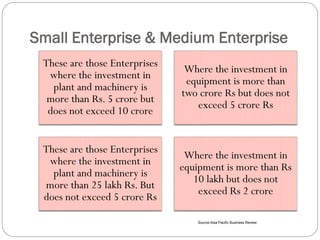
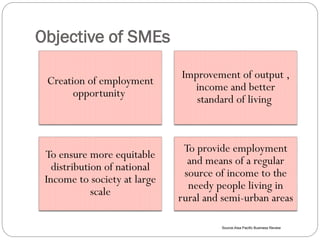
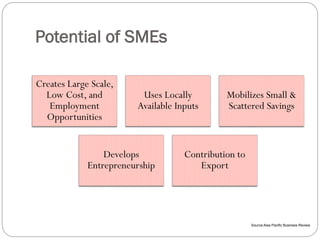
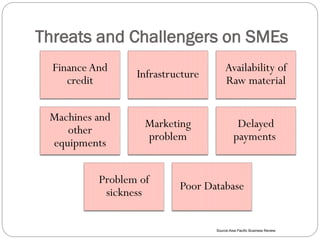
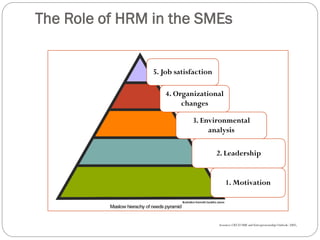
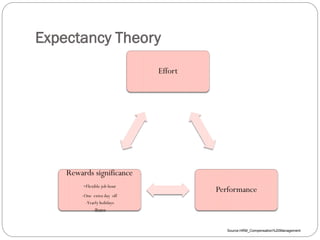
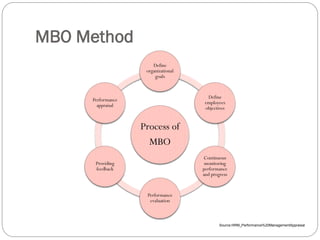
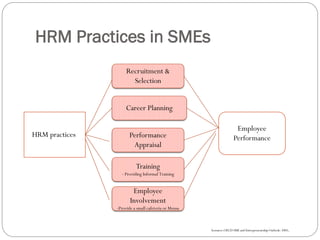
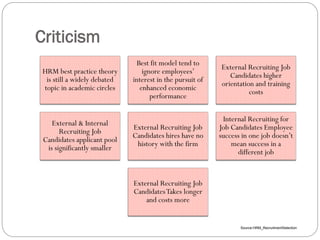
This document discusses human resource management practices in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It defines SMEs as having less than 250 employees in the EU and less than 500 in the US. The objectives of SMEs are creating employment, improving output and standards of living. SMEs contribute significantly to economies but face threats such as lack of financing, infrastructure and raw materials. Critical HRM goals in SMEs include labor productivity and quality. Common HRM practices in SMEs involve informal recruitment and training as well as employee involvement through cafeterias or events. Bangladesh has developed strong human resources and SMEs contribute greatly to its economy and employment.