HRM concepts explained
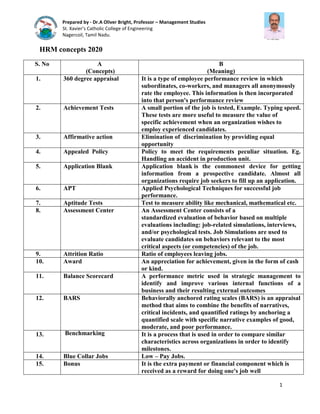
- 1. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 1 HRM concepts 2020 S. No A (Concepts) B (Meaning) 1. 360 degree appraisal It is a type of employee performance review in which subordinates, co-workers, and managers all anonymously rate the employee. This information is then incorporated into that person's performance review 2. Achievement Tests A small portion of the job is tested, Example. Typing speed. These tests are more useful to measure the value of specific achievement when an organization wishes to employ experienced candidates. 3. Affirmative action Elimination of discrimination by providing equal opportunity 4. Appealed Policy Policy to meet the requirements peculiar situation. Eg. Handling an accident in production unit. 5. Application Blank Application blank is the commonest device for getting information from a prospective candidate. Almost all organizations require job seekers to fill up an application. 6. APT Applied Psychological Techniques for successful job performance. 7. Aptitude Tests Test to measure ability like mechanical, mathematical etc. 8. Assessment Center An Assessment Center consists of a standardized evaluation of behavior based on multiple evaluations including: job-related simulations, interviews, and/or psychological tests. Job Simulations are used to evaluate candidates on behaviors relevant to the most critical aspects (or competencies) of the job. 9. Attrition Ratio Ratio of employees leaving jobs. 10. Award An appreciation for achievement, given in the form of cash or kind. 11. Balance Scorecard A performance metric used in strategic management to identify and improve various internal functions of a business and their resulting external outcomes 12. BARS Behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS) is an appraisal method that aims to combine the benefits of narratives, critical incidents, and quantified ratings by anchoring a quantified scale with specific narrative examples of good, moderate, and poor performance. 13. Benchmarking It is a process that is used in order to compare similar characteristics across organizations in order to identify milestones. 14. Blue Collar Jobs Low – Pay Jobs. 15. Bonus It is the extra payment or financial component which is received as a reward for doing one's job well
- 2. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 2 16. Brainstorming Finding a conclusion for a specific problem by gathering a list of ideas spontaneously contributed by its members. 17. Broadbanding It is defined as a strategy for salary structures that consolidate a large number of pay grades into a few "broad bands." In a broadband pay structure, the numbers of salary grades are consolidated into fewer, but broader, pay ranges 18. Business Game It is a 1- hour game which helps in the sharpening the management skills. It is being used in several institutes to provide the skills of management to professionals. 19. Career A general progression of an employee in his professional working. 20. Career Anchors Distinct pattern of self-perceived talents, attitudes, motives and values that guide and stabilize a person’s career after several years of real world experience and feedback. 21. Career Ladder The different stages an employee planning to grow in his career path. 22. Career management The process of designing and implementing goals, plans and strategies to enable the organization, to satisfy employee needs while allowing individuals to achieve their career goals 23. Career marriage Employment contract is a long–term contract like a marriage contract between bride and bridegroom. 24. Career success Individual’s capabilities for moving up in his or her career ladder with satisfaction. 25. Central Tendency Rate all their subordinates with an “average” score during performance appraisal. 26. Checklist A kind of informational job method used to minimize the failure by making up for potential limits of human memory and attention. It helps in keeping a track of all that is needed in completion of any given task in a very organized and structured manner. 27. Coaching It refers to counseling, guiding or instructing the learner about the short term job-related skills or long term career hazards. 28. Compensation It refers what an employee receives in exchange of his service. It includes payments like bonuses, profit sharing, overtime pay, recognition rewards and sales commission, etc 29. Compensation It is paid in the form of wages, salaries , special allowance and employee benefits 30. Competency mapping Identifying the competencies of all the employees. 31. Competitive Advantage Keeping ourselves competitive over others. 32. Comprehensive Interviews A selection device in which in-depth information about the candidate is obtained
- 3. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 3 33. CPM The critical path method (CPM) is a step-by-step project management technique for process planning that defines critical and non-critical tasks with the goal of preventing time-frame problems and process bottlenecks. 34. Creativity Training Training to develop the ability to think at their own and do new things successfully. 35. Critical incident method or technique A performance appraisal tool in which analyses the behavior of employee in certain events in which either he performed very well and the ones in which he could have done better. 36. Critical Incidents This method of Job Analysis focuses on identifying the critical incidents that distinguish satisfactory workers from unsatisfactory workers. This is based on the theory that certain tasks are crucial to satisfactory job performance, while others are not. 37. Cross- functional Members from different departments working together to define and implement changes and improvement 38. Cross-training It involves teaching an employee who was hired to perform one job function the skills required to perform other job function 39. Defence mechanism It is a way of behaving or thinking which is not conscious or deliberate and is an automatic reaction to unpleasant experiences or feelings such as anxiety and fear. 40. Dejobbing Broadening of the responsibilities of the company’s jobs and encouraging employees not to limit themselves to what’s on their job descriptions. 41. Demand Forecasting Forecast of the required manpower for a planed activity. 42. Demotions A permanent reassignment to a lower position than the employee had worked previously. 43. Discharge Due to poor performance 44. Disguised Grievance Recognition, affection, power, achievement etc unattended 45. Dismissal Termination initiated by the organization 46. Displacement It is a psychological defense mechanism in which negative feelings are transferred from the original source of the emotion to a less threatening person or object. 47. Diversity Training Training to make participants more aware of diversity issues in the workplace, their own beliefs on diversity, as well as provide skills to help them interact, collaborate and work more closely with people that have different qualities to their own 48. Downsizing It refers to the process of reducing the size of workforce by terminating the employment of employees 49. Dual career group or Dual career couple A marital couple where both partners are working professionals. Dual career group helps in achieving the psychological as well as financial satisfactions.
- 4. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 4 50. Dunlop's Model It states that the industrial relations system is really a social subsystem, and its actions are dependent on three factors: technology, the economy and the distribution of political power 51. Ergonomics It refers to the study of how people interact with their working environment and then adjusting that environment to improve efficiency by reducing the chance for injury, fatigue, discomfort and optimizing well-being and productivity. 52. ESOP An employee stock ownership plan (ESOP) is an employee benefit plan that provides a company’s workers with an ownership interest in the company. 53. Event Management It is the application of project management to the creation and development of large-scale events such as festivals, conferences, ceremonies, weddings, formal parties, concerts, or conventions. 54. Executive compensation It is the monetary and non-monetary benefits which are given to the senior management & executives of a company. Executive compensation includes salaries, perks, incentives, insurances etc 55. Executive Development Program Systematic process of learning and growth by which managerial personnel gain and apply 56. Exit Interview A survey that is conducted with an employee when he or she leaves the company 57. Explicit Knowledge Knowledge documented, applied and converted into product. 58. Extrinsic Rewards Tangible rewards given employees by managers, such as pay raises, bonuses, and benefits 59. Factual Grievance Legitimate expectations and aspirations not fulfilled 60. Fair Wages Fair Wages are minimum wage rates for specific occupations. They must be paid by contractors doing work for governments with fair wage policies. These policies generally apply to construction, trades and sometimes cleaning and security workers, and are often tied to union wage rates. 61. Fatigue It is a general term used to describe the feeling of being tired, drained or exhausted. It's a cumulative and gradual process that manifests in the form of tiredness, lack of energy, exhaustion and reductions in performance capacity. 62. Feedback A way of assessment of works done or processes and is an integral part of the HR department. Feedback is a way to understand the needs, requirements, performances etc of employees in an organization. 63. Focus of SHRM Model Plannned outcome and effects.
- 5. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 5 64. Forced choice It is a method of performance appraisal in which the rater has to make a forced choice between the available characteristics, about the employees in the form of a survey questionnaire. 65. Forced Ranking A controversial performance management tool which uses intense annual evaluations to identify the company's best and worst employees, using person to person comparison 66. Fringe benefits Refers to the extra benefits provided to employees in addition to the normal compensation paid in the form of wage or salary. Example. Company car, health insurance. 67. Functional Job Analysis (FJA) A method of job analysis that was developed by the Employment and Training Administration of the United States Department of Labor. FJA produces standardized occupational information specific to the performance of the work and the performer. 68. Gate hiring It is known as recruitment at factory gate. The practice of direct recruitment is followed usually to fill casual vacancies of unskilled or semi-skilled jobs 69. General Policy It reflects the philosophies and priorities of the top management in formulating the plans of the organizations growth. 70. Glass-ceiling effect Stopping the woman employee in promotions by gender discrimination 71. Golden Handshake A lump sum amount to the employees opting voluntary retirement 72. Graphic Rating Scale A type of performance appraisal method. In this method traits or behaviors that are important for effective performance are listed out and each employee is rated against these traits. 73. Graphology Study of hand-writing when employed to analyze their character. 74. Grievance It is a state of dissatisfaction when employees feel lack of justice and fair pay. 75. Hallo Error A mistake or bias that can occur in evaluating an individual's performance where they are consistently rated based on the evaluator's overall impression, rather than on their actual performance in various categories. 76. Horn Effect IT is a type of cognitive bias where a person's impression of another can substantially influence one's thoughts and feelings about that person. 77. HR Accounting It is a measurement of the cost and value of human resources to the organization. Economic value of employees. 78. HR Audit An examination and evaluation of policies, procedures and practices to determine the effectiveness of HRM
- 6. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 6 79. HR Planning Predicting of human resource requirements for a future period to avoid anticipated problems. 80. HR policy A type of standing plan that serves to guide subordinates in the execution of their tasks 81. HRIS Storing data and information for each individual employee to aid planning, decision making for external agencies. 82. HRM Acquisition, Development, Motivation and Maintenance of human resources. 83. HRP Determining HR requirements and plans and how to fulfill them. 84. Human capital It is an asset consisting of the knowledge and skills held by a person that can be used by an organization to achieve its goals. 85. Human Inventory/ Manpower Inventory Available human resources within the organization. 86. Imaginary Grievance Grievance due to wrong perceptions and no valid reason 87. Impact evaluation It provides information about the impacts produced by an intervention - positive and negative, intended and unintended, direct and indirect. 88. Implied Policy Inferred from the behavior of the organization. Example. Dress code 89. Imposed Policy Policy by external agencies like Govt. Example. Safety provisions as per govt. guidelines 90. In-basket test or In- basket exercise It is a test used by companies or governments in hiring and promoting employees. During the test, job applicants receive a number of mails, telephone calls, documents and memos. 91. Incentives Monetary benefits paid to workmen in lieu of their outstanding performance 92. Inclusive growth A longer term perspective focusing on productive employment 93. Induction or Orientation The process of familiarization with the organization and settling into the job. 94. Industrial Democracy It is an economic arrangement which involves workers making decisions, sharing responsibility and authority in the workplace 95. Integrity Test Test to predict more likely to steal from the employer 96. Intellectualization It is a defense mechanism where reasoning is used to block confrontation with an unconscious conflict and its associated emotional stress 97. Intelligence Tests Mental ability tests such as vocabulary, memory, verbal fluency etc. 98. Interest Tests Test to compare with interest of people in specific job
- 7. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 7 99. Interview It is a formal, in-depth conversation conducted to evaluate the acceptability of candidates for employment. 100. Intrinsic rewards Intangible that come from within the employee such as satisfaction of higher needs, esteem etc 101. IOSB Simulation Interactive Online Skill Building Simulation 102. Job Analysis Duties and requirements and relative importance of duties to given job. 103. Job Description Written statement of duties, responsibilities, required qualifications and reporting the relationships. 104. Job Design Organizing the tasks, duties and responsibilities into a unit of work so as to business objectives 105. Job Enlargement Horizontal loading of work in that the responsibilities increase at the same level only. 106. Job Enrichment Vertical job loading of jobs with the principles for enriching positions and giving employees more challenging work 107. Job Evaluation Evaluating relative value of each job. 108. Job Instruction Training (JIT) A form of simple on the job training where a new employee is trained step by step by a supervisor or an assigned coworker. This kind of training usually exists for jobs requiring manual skills such as factory workers 109. Job Rotation Employees are shifted between two or more assignments or jobs at regular intervals of time in order to expose them to all verticals of an organization 110. Job Specifications A statement in which explains the qualities required by people applying for the job. 111. Joint management councils Committees represented by the workers and management to discuss and give suggestions for improvement with regards to matters of mutual interest. 112. Knowledge management (KM) Process of creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization 113. Lay-off An indefinite separation of the employee from the pay roll due to factors beyond the control of the employer 114. Learning curve The relationship between the amount of learning and the time taken to learn is presented as a curve called learning curve. 115. Leniency It means the appraiser is lenient and is going “too easy” on the person they are rating. That means all scores will be very high. Like the halo effect, the leniency bias makes it challenging to know an employee's true pattern of strengths and weaknesses 116. Literacy Training Involves teaching employees things like reading, writing and problem-solving skills. It also indicates the training to educate about the company.
- 8. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 8 117. Living wage It is a socially-acceptable level of income that provides adequate coverage for basic necessities such as adequate food, shelter, child services, and healthcare 118. Logical Resistance This kind of resistance basically arises from the time people genuinely take to adapt and adjust to changes. 119. Management Position Description Questionnaire (MPDQ) A questionnaire used in human resource management for the purpose of analyzing management positions. It allows HR departments to establish training requirements, salary bands and job groupings for new posts. It has 208 items grouped in 13 categories 120. Management Training Need-based training imparted to executives at each level at the time of assuming the job. 121. Markov analysis The pattern of employees movements year after year such as promotion, retirement, transfer, exit etc is considered to make the probabilities. 122. MBE Management by exception (MBE) is a practice where only significant deviations from a budget or plan are brought to the attention of management. The idea behind it is that management's attention will be focused only on those areas in need of action. 123. MBO Management by objectives (MBO) is a strategic management model that aims to improve the performance of an organization by clearly defining objectives that are agreed to by both management and employees. 124. Mentoring Mentoring is the Employee training system under which a senior or more experienced person (the mentor) is assigned to act as an advisor, counselor, or guide to a junior or trainee 125. Metamorphosis Stage in socialization Metamorphosis Stage is the last stage (3rd stage) of socialization process in which a new employee changes himself/herself to adjust to the job, new groups or organization. 126. Minimum wages It is the minimum amount of remuneration that an employer is required to pay wage earners for the work performed during a given period, which cannot be reduced by collective agreement or an individual contract 127. Motivation A person‘s efforts are energized, directed and sustained towards attaining a goal. 128. Multi-skilling The training of a single employee in multiple skill-sets of different disciplines. 129. Narrative Appraisal It is also called an essay, is simply a written analysis of an employee's performance. It's one of the oldest appraisal methods. 130. Negative feedback Feedback regarding past behavior that did not yield desired results or ended up worsening the situation.
- 9. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 9 131. Negative feed-forward Message that helps the subject avoid a few unwanted behaviors. While the individuals have not necessarily committed such mistakes in the past, 132. Non-directive questionnaire/ Non- directive Interview Not having pre-arranged questions in such interview. Unstructured questionnaire. Interviewer asks questions whatever comes in his mind. 133. Online collaboration A technology that uses a collaboration software like ezTalks, Cloud Meeting etc. to allow a group of people to work together to achieve the same goal 134. Organization focus 3 Ps, People, Process, Performance. 135. Originated policy Established by top management to guide executive thinking at various levels. Example. Financial policy 136. Paired comparison. Method of evaluation in which each employee and job is compared with each other employee and job 137. Performance evaluation system A systematic way to examine how well an employee is performing in his or her job. 138. Performance Management System (PMS) A system to manage and improve the performance of the employees in the organization 139. Performance Orientation. It reflects the extent to which a community encourages and rewards innovation, high standards, excellence, and performance improvement 140. Performance Planning KPAs (Key Performance Analysis) and KRAs (Key Result Analysis). 141. Perquisites Benefits or amenities in cash or kind or money or money's worth and amenities which are not convertible in to money, provided by the employees at free of cost or at a concessional rate. It is considered as taxable. Example. Car, Cub membership, paid holiday, furnished house, stock option schemes etc. 142. Personality Tests A selection process employed to measure the personality characteristics of applicants that are related to future job performance 143. Personnel Management Focus on employer – employee relationship. 144. Personnel policies Number of actions that govern the relationship with employees in the attainment of organizational objectives. 145. PERT It is a project management planning tool used to calculate the amount of time it will take to realistically finish a project. PERT charts are tools used to plan tasks within a project - making it easier to schedule and coordinate team members accomplishing the work. 146. Plant council Joint councils applicable for central public sector undertakings.
- 10. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 10 147. Plateau Employee When employee reaches the last stage in his career he feels that no more career growth, his position is plateau. 148. Polygraph (Lie-detector) Tests By asking questions the physical changes of the body is examined 149. Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ) Position analysis questionnaire (PAQ) is a job analysis questionnaire that evaluates job skill level and basic characteristics of applicants for a set match of employment opportunity. PAQ was developed at Purdue University by McCormick, E.J., & Jeanneret, and Mecham in 1972. 150. Position Rotation A management approach, where employees are shifted between two or more assignments or jobs at regular intervals of time in order to expose them to all jobs of an organization to find the best fit job. 151. Positive feedback Feedback regarding past behavior that ended up producing desired results or impacted the desired outcome positively. 152. Positive feed-forward A prescriptive form of message that helps individuals achieves desired goals with a planned set of actions. 153. Preference Test An objective and standardized measure of sample behavior 154. Preliminary Interview Initial interview to identify the best applicants 155. Primacy Effect It is an involuntary mental bias; due to which a person retains information presented first more than the ones presented later on. 156. Projection A way of coping with one’s unwanted motives by shifting them to someone else. Blaming others. 157. Projective Tests These tests expect the candidates to interpret problems or situations based on their own motives, attitudes, values, etc 158. Promotion It refers to upward movement of an employee from his current job position to another that is higher is pay, responsibility and hierarchy within an organization. 159. Protégé relationship Senior-junior relationship in an organization for career guidance 160. 1Psychological Appraisal This method focuses on analyzing an employee's future performance rather than their past work. Qualified psychologists conduct a variety of tests (in-depth interviews, psychological tests, discussions, and more) to identify an employee's emotional, intellectual, and other related traits. 161. Psychological Bond An individual’s beliefs regarding the terms and condition of a reciprocal exchange agreement between that person and another party. 162. Psychological Resistance This resistance occurs purely due to mental and psychological factors. 163. Ramification It refers the integration strategy of training and
- 11. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 11 development program with the formulation and execution in job. 164. Rationalization A defense mechanism which substitutes an acceptable conscious motive for an unacceptable unconscious motive. 165. Realistic Job preview A selection device that allows job candidates to learn negative as well as positive information about the job and organization 166. Recency Effect Tendency to remember and recollect the things, experiences or gifts/ items which have been given to that person recently. In other words, people remember the things which have been said or described in the end, at the start. 167. Recruitment Process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating to apply for the job in the organization. 168. Refresher Training or Retraining A training program designed for the old or existing employees of an organization, with a purpose to acquaint them with the new skills, methods, and processes required for improving their performance on the jobs. 169. Regression It is a defense mechanism proposed by Anna Freud whereby the ego reverts to an earlier stage of development usually in response to stressful situations. 170. Reject error Rejecting the right person 171. Repression A mental process by which a person pushes down the information of the anxiety-arousing situation into the unconscious mind or simply tries to forget. 172. Resistance The action taken by individuals and groups when they perceive that a change that is occurring as a threat to them 173. Re-skilling It means changing the skill set or updating the essential skill to keep the employees more productive. 174. Rest-pause and Rest-pause Training It is an intensity extending method that's long been praised for its strength and hypertrophy (muscle power) benefits. It's where you perform an exercise to technical failure. This "rest period" is typically 15-30 seconds after continuous work. Rest-pause Training a method for hypertrophy (muscle power) benefits. This training helps to maximize sleep, while minimizing stress, to aid recovery 175. Retraining It is training given to long-term employees of an organization to make them equipped with the future needs of the organization. Retraining helps in developing employees and preventing them from being obsolete for the job requirements. Retraining is also done during job rotation
- 12. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 12 176. Retrenchment Termination of employment due to economic reason 177. Reverse brainstorming A technique that builds on our natural ability to more easily see problems than solutions, ie finding problems that could fail. 178. Reward Incentive plan to reinforce the desirable behavior of workers or employers and in return for their service to the organization 179. Select error Selecting the wrong person 180. Selection Identify and hire those with a greater likelihood of success in a job. 181. Self development Taking steps to make self better such as by learning new skills or overcoming bad habits. 182. Self-control or self- management It means a personal desire to improve through an individual's attempt 183. Sensitivity Training A type of group training that focuses on members to develop a better awareness of group dynamics and their roles in the group and inter-personal skill. 184. Separation Cessation of service of agreement with the organization. 185. Shop Councils In every Industrial establishment employing 500 or more workmen, the employer shall constitute a shop council. Shop council represents each department or a shop in a unit. Each shop council consists of an equal number of representatives from both employer and employees. 186. Simulation A training and feedback method in which learners practice tasks and processes in lifelike circumstances using models or virtual reality, with feedback from observers, peers, actor-patients, and video cameras to assist improvement in skills 187. Simulation Tests This test is to observe the candidate perform the actual job in a controlled environment. 188. Skill Inventory Available Human skills within the organization. 189. Skills training It is designed to provide employees with the targeted training they need to gain the knowledge and abilities necessary to fulfill the specific requirements of their job positions 190. Socialization Socialization is a process of adaptation, adjustment, making arrangements for setting one employee in the organizational environment. 191. Sociological Resistance This resistance relates not to individuals but rather to the common values and customs of groups. 192. Specific Policy Refers specific issues in line with general policy. Example.
- 13. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 13 Rewarding the employees. 193. Stereotyping Generalizing behavior based on place, province etc in rating the employees 194. Strategic Human Resources Strategies for organizational sustenance and growth. 195. Stress interview A technique that deliberately places the job candidate in a stressful situation to observe how the candidate reacts during the job interview. 196. Structured Interview It is a formal interview (e.g. a job interview) in which the interviewer asks a standard set of questions in a standardized order within the time allotted. 197. Succession Planning The process of ensuring suitable supply of successors for current and future senior or key jobs arising from business strategy. 198. Supply Forecasting Projection of the future supply of the manpower. 199. T group Training or Leaderless Training T-Group (Training Group) training is a training approach based on experiential learning and involving small, unstructured groups in which participants learn from their own interactions and evolving group dynamics, about interpersonal relationships, group dynamics and leadership. 200. Tacit Knowledge Knowledge embedded in individuals 201. Talent Management Talent management is an organization's commitment to recruit, hire, retain, and develop the most talented and superior employees available in the job market. 202. Team rewards Any formal incentives provided to a work team or at least one of its individual team members for team performance. 203. Team Training A process that empowers teams to improve decision making, problem solving, and team-development skills. 204. Telecommuting Telecommuting is a work arrangement that enables a staff member to work at home from another off-site location for all or part of the regular workweek 205. Test Examination, evaluation, observation, or trial used to determine and document capabilities, characteristics, effectiveness, reliability and suitability. It is the process of differentiating between applicants in order to identify and hire those with a greater likelihood of success in a job. 206. Training A process of learning a sequence of programmed behavior 207. Training Multiplier Effect Come down to the employee level and train them to the required level. 208. Training Multiplier-effect Replicating own core competency and creating an entire team of individuals who perform at high levels 209. Training needs assessment Training Needs Analysis is the process in which the
- 14. Prepared by - Dr.A Oliver Bright, Professor – Management Studies St. Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu. 14 (TNA) company identifies training and development needs of its employees so that they can do their job effectively 210. Transactional analysis (TA) Psycho-analytic theory and method of therapy wherein social transactions are analyzed to determine the ego state of the patient (whether parent-like, childlike, or adult-like) as a basis for understanding behavior. 211. Transfer A movement of an employee between equivalent positions at periodical intervals is called transfer. Transfers may be either organization-initiated or employee- initiated. 212. Transformation Training Training the employees from the conventional skills to acquire the new required skill for the organization 213. Unit councils Joint councils for manufacturing and mining units 214. Unsolicited Applicants It is a group of Applicants who have applied without any advertisement or requirement from the company. 215. Vestibule training A situation used by a manufacturing business, less than ten trainees would be supervised by one skilled trainer, and the training provided simulates on the job training without compromising production speed or quality. 216. VRS Retirement proposal from the employee. 217. Walk-In interview It is defined as a condition wherein a person (who may be a customer, a new employee, a prospective employee who has come for an interview etc) reaches the respective office or place without any prior appointment 218. Weighted application blank A weighted application blank (WAB) is an approach to collecting and scoring background information from job applicants. It involves scoring applicant background in a quantitative manner based on the proven "best responses" to each application item. 219. Works committee A committee formed as per the Industrial Dispute Act 1947 which consists of equal number of employee representatives and management representatives for any establishment having 100 or more workers. 220. Write-in Interview Interviewing the candidates who applied for job as casual applicants (applications received without any advertisements or invitations).