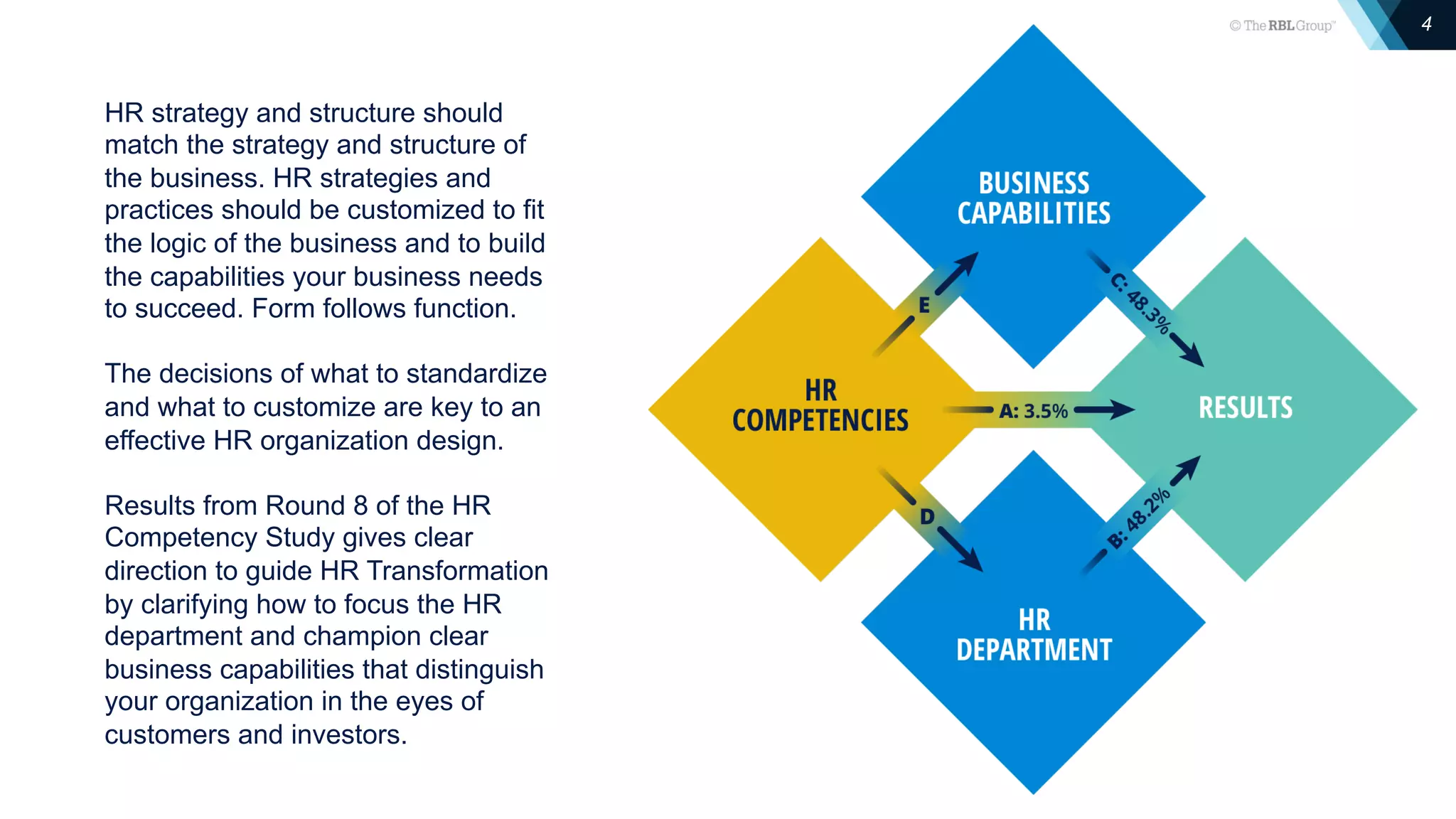
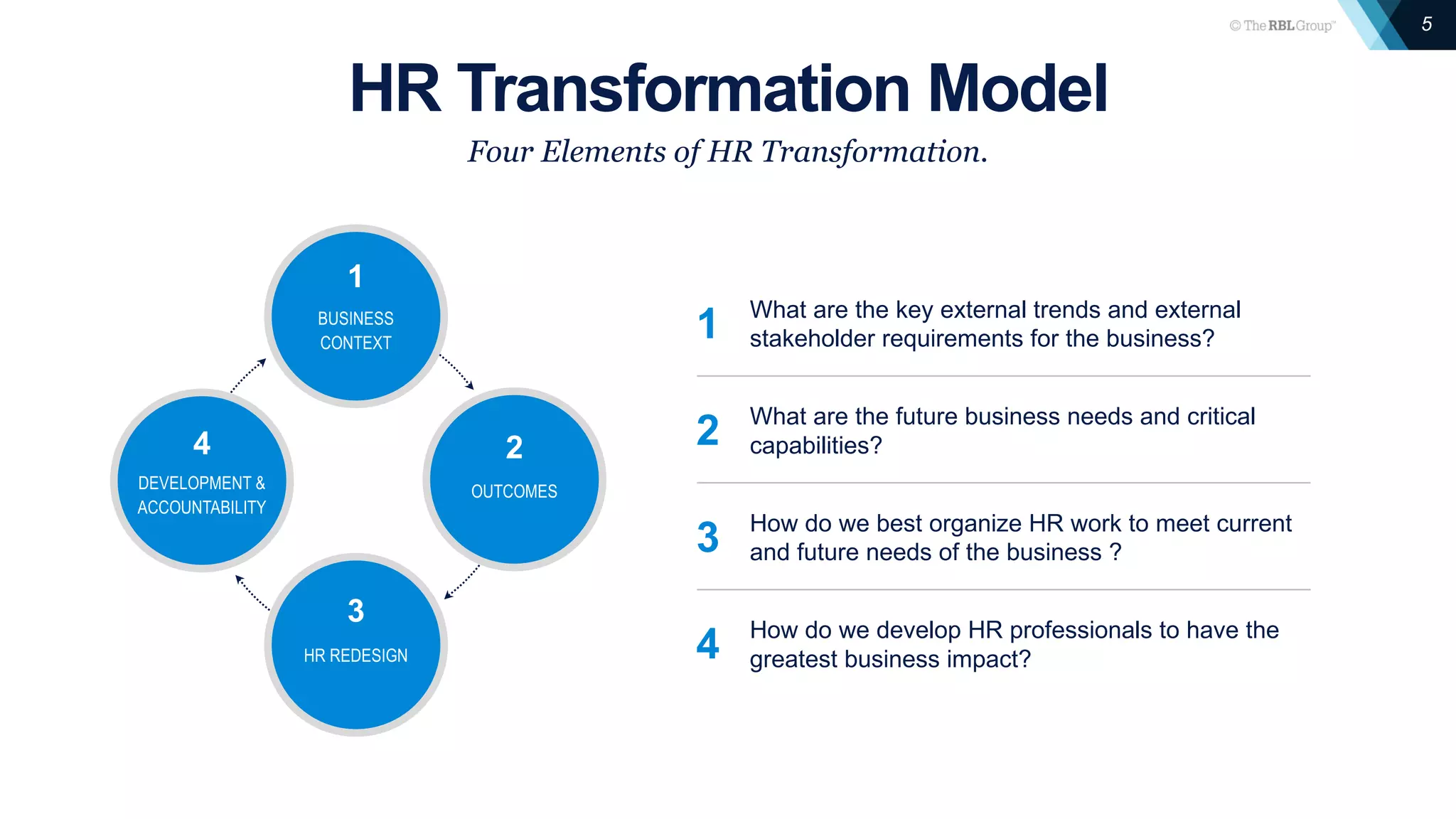
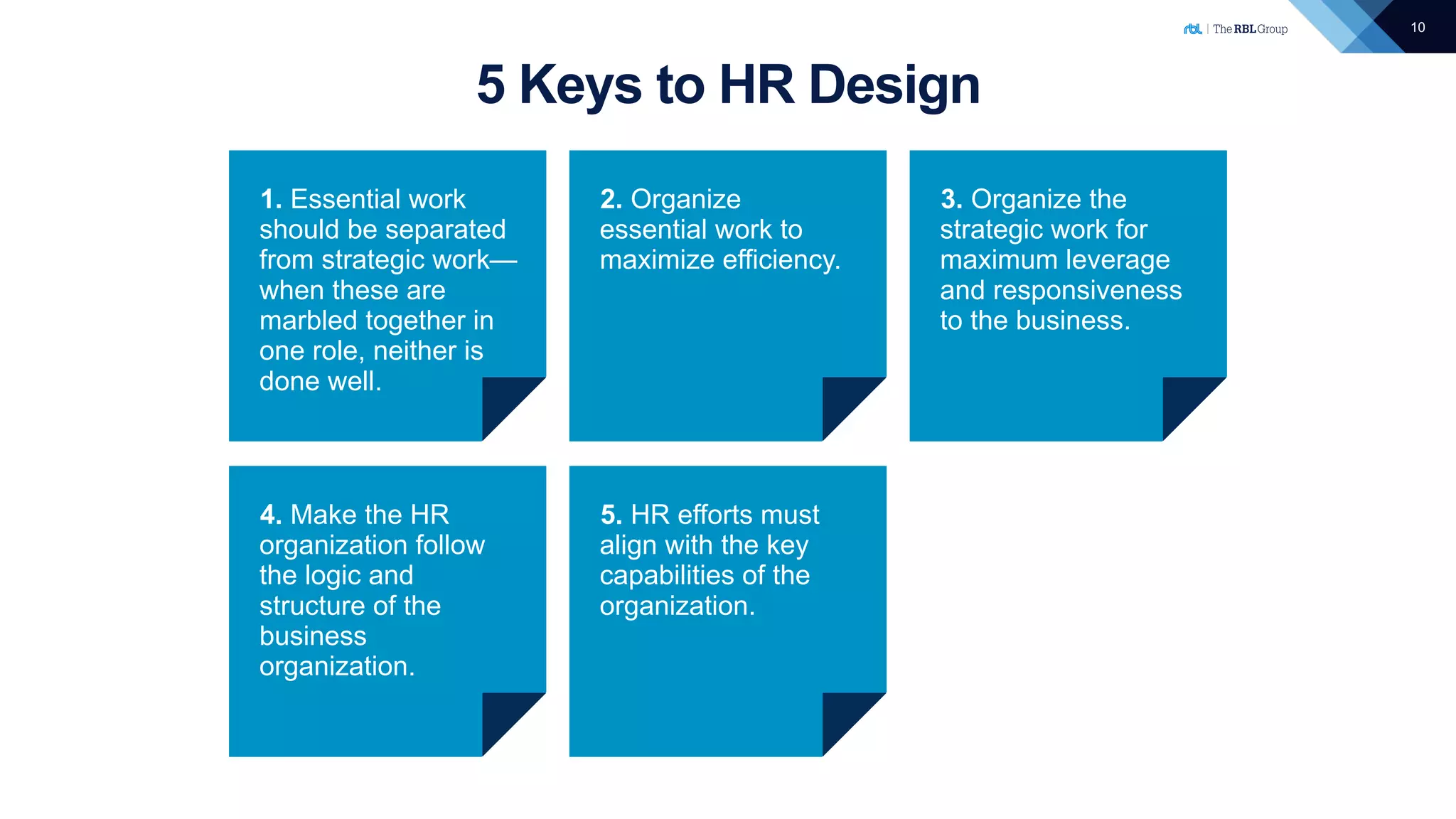
The document outlines the principles of HR transformation, emphasizing the alignment of HR strategies and practices with business needs to enhance organizational value. It details a four-element model for effective HR transformation, including understanding external trends, identifying business capability needs, organizing HR work, and developing HR professionals. Key to success is separating essential work from strategic work and ensuring HR efforts support the organization's key capabilities for improved efficiency and effectiveness.