Healthcare Quarterly Vol.16 No.1
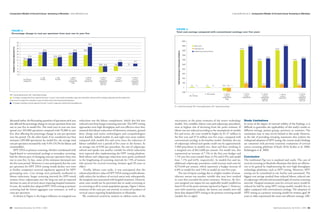
- 1. Comparative Models of Cervical Cancer Screening in Manitoba Linda DeRiviere et al. Linda DeRiviere et al. Comparative Models of Cervical Cancer Screening in Manitoba Figure 4. Figure 3. Total cost savings compared with conventional cytology over five years Percentage change in cost per specimen from year one to year five 20000 40 33.2 18,531.8 18,330.8 35 18000 Labour costs Change in Cost per Specimen (%) 30 Colposcopy cost 16,549.7 16,550.0 24.4 24.0 19.0 16000 25 Lengthening screening intervals Total Cost Savings (in Thousands of Dollars) 20 19.6 18.9 14000 15 13.3 13.8 15.5 12,888.2 12,848.4 10 10.3 12000 11,985.8 11,985.7 7.2 4.7 5 -10.9 -9.4 -5.6 0 10000 0 -5 8000 -10 6000 - 15 1- 2 - LBC 3 - LBC 4 - LBC for 5 - HPV for 6 - HPV for 7 - HPV for 8 - HPV for 4000 Conventional ThinPrep SurePath primary primary primary primary primary cytology (CC) testing & HPV testing & LBC testing & LBC testing & CC testing & CC triage implement implement 1,702.7 2000 1,702 over 5 yrs over 5 yrs 784.6 784.6 43.5 0 0 43.5 00 -954.6 -1,303.1 0 0 -2000 HPV = human papillomavirus; LBC = liquid-based cytology. 2- 3 - LBC SurePath 4 - LBC for 5 - HPV for 6 - HPV for 7 - HPV for 8 - HPV for LBC, ThinPrep primary primary primary primary primary = % change in average total cost per specimen from year 1 to year 5: costs include consumables; wage costs and benefits; and fee tariffs for cytology, colposcopy and other related visits. testing & HPV testing & LBC testing & LBC testing & CC testing & CC triage implement implement Costs are net of savings from a decrease in cases of cervical cancer. Costs exclude capital equipment. over 5 yrs over 5 yrs = % change in laboratory cost per specimen from year 1 to year 5: wage costs, benefits and consumables only. CC = conventional cytology; HPV = human papillomavirus; LBC = liquid-based cytology. discussed earlier, the fluctuating quantities of specimens each year reductions was the labour complement, which also fed into uncertainty in the point estimates of the newer technology Study Limitations also affected the percentage change in cost per specimen from year reduced costs from longer screening intervals. The HPV testing models. Two variables, labour costs and colposcopy procedures, In terms of the degree of external validity of the findings, it is one to year five in model five. The total costs in year one were approaches were high throughput and cost-effective since they were at highest risk of deviating from the point estimate. If difficult to generalize the applicability of this study’s results to spread over 205,000 specimens compared with 95,000 in year assumed that labour reductions of laboratory assistants, general labour was not reduced according to the assumptions in models different settings, patient groups, provinces or countries. The five, thus affecting the percentage change in cost per specimen duty, charge and senior technologists and cytopathologists five and seven, the costs would be higher by $1.37 million in conclusions may or may not be limited to this study. However, over the period. On the other hand, if we considered year four were feasible. Indeed models six and eight were more realistic the first year and $7.0 million over five years, compared with at the risk of providing sweeping statements that endorse the estimates (205,000 specimens) for model five, the average total compared with models five and seven since the reduction of conventional cytology in the baseline model. Similarly, the rate widespread adoption of HPV testing, the current study’s findings cost per specimen increased by only 9.4% (10.3% for labour and labour unfolded over a period of five years in the former. At of colposcopy referral and uptake could vary by approximately are consistent with previous economic evaluations of cervical consumables). an average cost of $104 per procedure, the rate of colposcopy 5,900 procedures in models two, three and four, resulting in cancer screening platforms (Chuck 2010; Krahn et al. 2008; HPV DNA as primary screening, whether coordinated with referral and uptake was another variable for which reductions a marginal cost of $613,600 per annum. For model two, this Kulasingam et al. 2009). liquid-based or conventional cytology as secondary screening, were expected after implementing the HPV testing platform. represented an increase of 7.5% in the first year budget and had the slowest pace of changing costs per specimen from year Both labour and colposcopy reductions were partly attributed 7.1% over five years (model three: 6.3% and 6.9%; and model Conclusion one to year five. In fact, some of the estimates decreased over to the lengthening of screening intervals for 73% of women four: 7.1% and 6.6%, respectively). In models five and six, The traditional Pap test is outdated and costly. The case of the five-year period. Moreover, it was anticipated that the costs who present for cervical screening (women aged 30 years or additional colposcopy procedures could increase total costs by cervical screening in Manitoba illustrates that there are efficien- per specimen for HPV DNA testing would decline over time older). $276,640 per annum, which represents a budget increase of cies to be gained by implementing the new high-throughput as further companies received regulatory approval for HPV Finally, labour costs aside, it was anticipated that the 6.0% in model five and 5.0% in model six over five years. technology platforms, such as HPV testing. Moreover, HPV genotyping tests. Cost savings were primarily attributed to enhanced predictive value of HPV DNA testing would substan- The rate of repeat cytology due to a higher number of unsat- testing can be centralized in one facility and automated. The labour reductions, longer screening intervals for HPV-tested tially reduce the incidence of cervical cancer and, subsequently, isfactory smears was another variable that may have resulted biggest cost savings resulted from reduced labour, reduced rate women, fewer colposcopies over the long run and an expected the marginal costs associated with hospital treatment. However, in costs that exceeded the point estimates. However, the five- of colposcopy referrals and increased length of routine screening decrease in cases of cervical cancer requiring hospital treatment. some cases would not be prevented due to under-screening or year marginal cost impact for any applicable model totalled less intervals. Hospital treatment costs for cervical cancer would be In sum, the models that adopted HPV DNA testing as primary no screening at all in certain population groups. Figure 5 shows than 0.5% of the point estimate reported in Figure 1. However, reduced by half by using HPV testing models (models five to screening had the lowest aggregate cost estimates, as well as estimates of the costs per case averted, in terms of incidence of even with sensitivity analysis, the lowest cost models were still eight) compared with conventional cytology. The adoption of costs per specimen. cervical cancer requiring hospitalization in Manitoba. those that adopted HPV testing as the primary screening model HPV testing as a primary screening model for women aged 30 As shown in Figure 4, the largest influence on marginal cost We conducted sensitivity analysis to address some of the (models five to eight). years or older represented the most cost-efficient strategy. LBC 84 Healthcare Quarterly Vol.16 No.1 2013 Healthcare Quarterly Vol.16 No.1 2013 85
