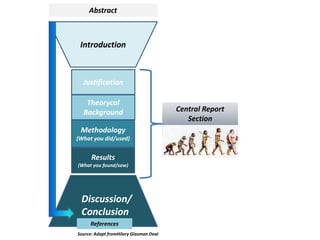
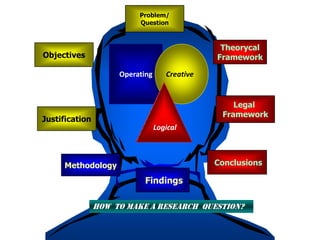
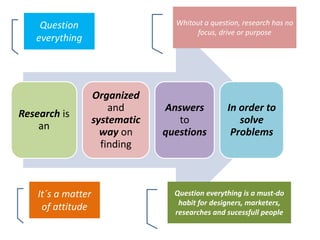
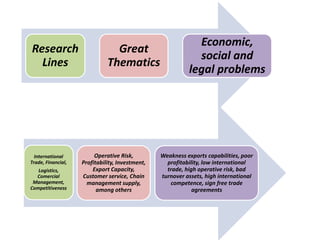
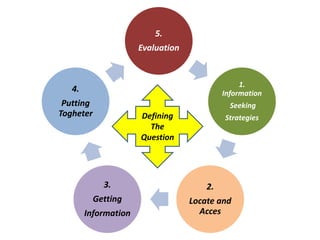
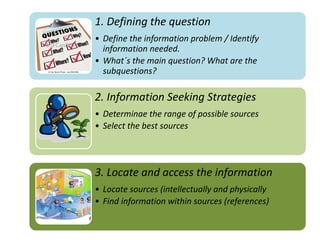
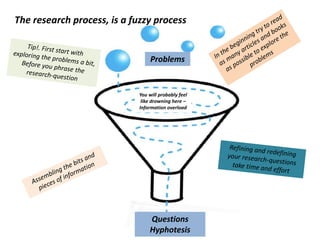
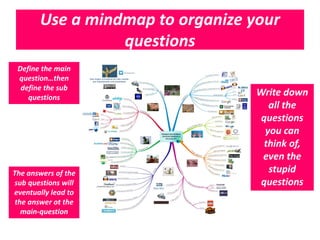
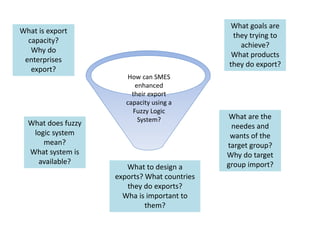
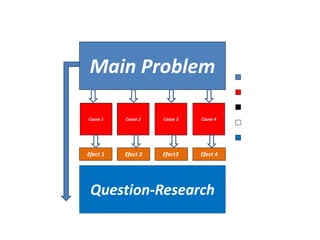
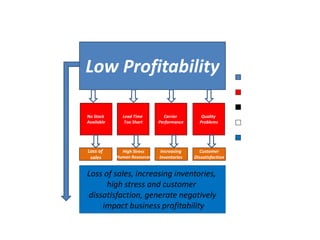
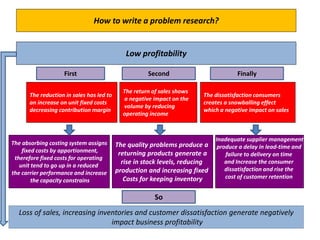
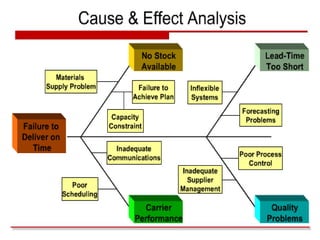
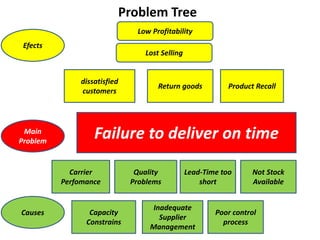
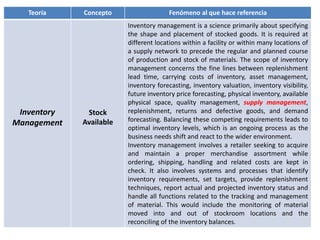
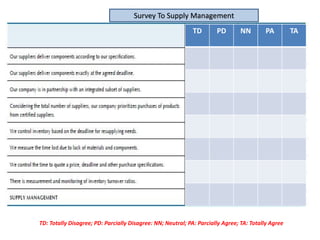
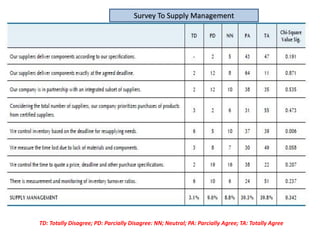
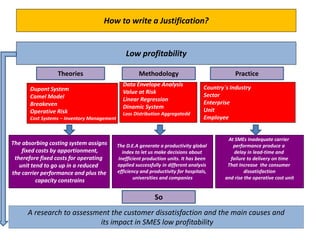
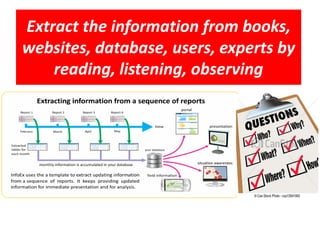
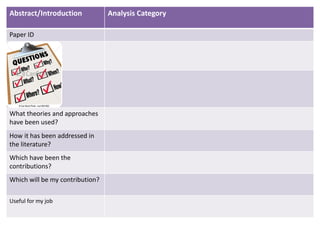
The document provides guidance on how to develop a research question. It outlines the typical structure of a research process, including defining the question, seeking information from various sources, analyzing the collected information, and evaluating whether the question was answered. It emphasizes starting with a broad question and identifying sub-questions to focus the research. Tips are provided for each step, such as using a mind map to organize questions, taking notes from sources, and thinking of ways to communicate results. The overall process is described as iterative, with the ability to redefine the question if initial information does not provide an answer.