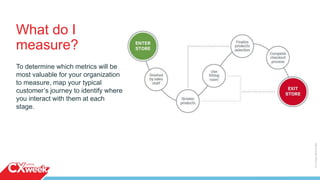
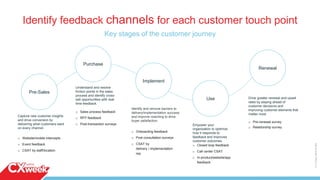
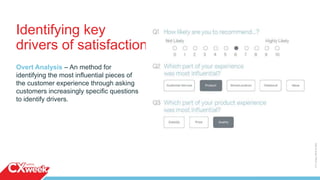
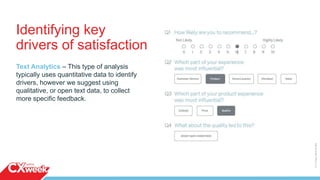
The document outlines a four-day webinar series on executing a customer experience (CX) program, covering building a CX vision, execution strategies, cultural changes, and communicating results. It emphasizes the importance of mapping customer journeys, selecting appropriate metrics, and utilizing feedback channels to enhance customer satisfaction. Additionally, the importance of iterating processes and taking action based on insights is highlighted, alongside practical advice for implementing these strategies effectively.