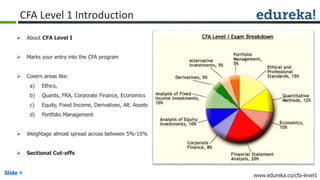
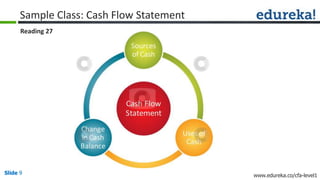
This document provides an overview of a presentation on how to crack the CFA Level 1 exam. The presentation covers an introduction to the CFA Level 1 exam, who should take it, how to prepare, and a sample class on reading cash flow statements. It is presented by Ankur Kulshrestha and Amit Parakh, who have extensive experience in CFA training and corporate finance. The presentation promotes Edureka's upcoming refresher course for the CFA Level 1 exam, which will provide 50 hours of live online classes over 8 weekends to help students prepare.