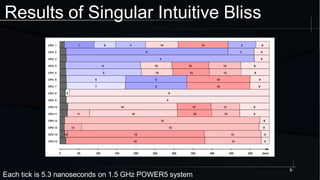
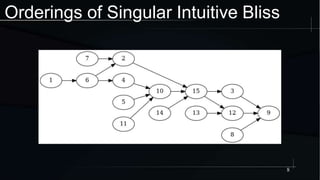
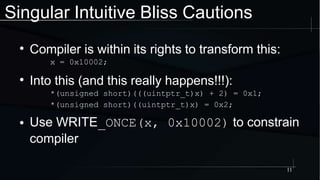
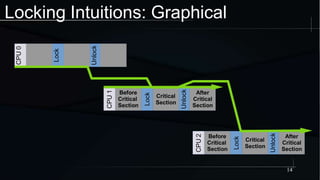
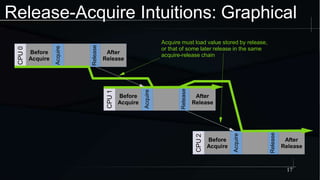
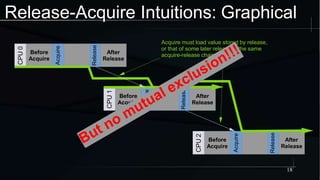
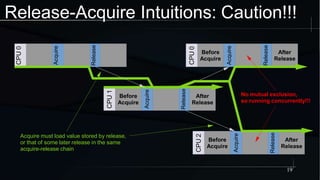
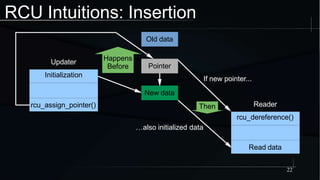
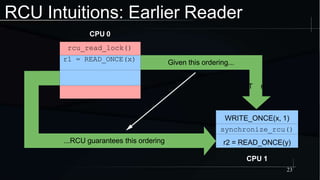
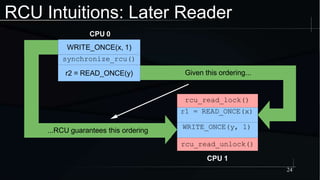
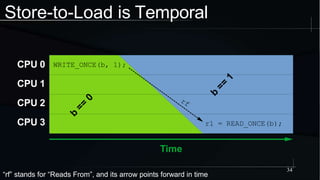
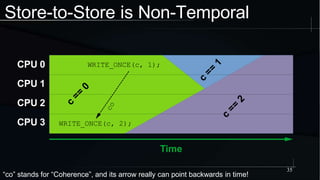
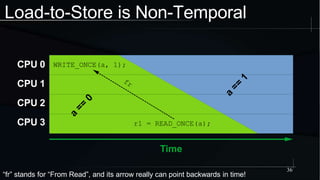
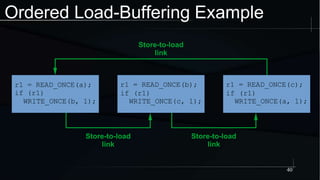
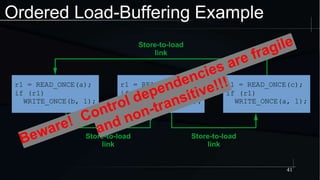
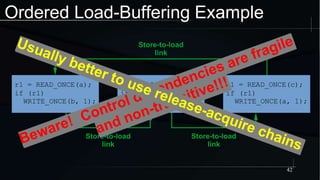
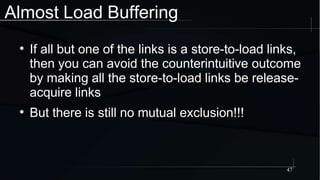
The document discusses advanced concepts in memory ordering, focusing on different types of intuitions such as transitive, locking, release-acquire, and RCU (Read-Copy-Update) within multi-threaded programming. Cautions regarding compiler optimization and the importance of memory model rules of thumb are highlighted, emphasizing techniques like using 'write_once' and 'read_once' for safe variable access. It concludes with recommendations for using well-defined patterns and primitives to manage memory ordering effectively in concurrent programming environments.