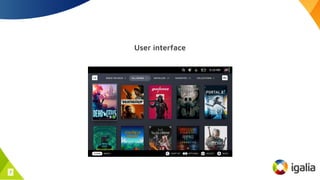
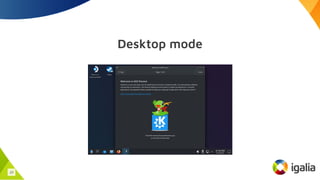
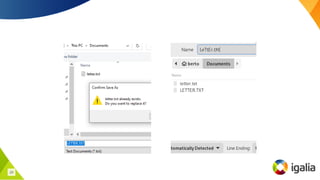
SteamOS, developed by Valve for the Steam Deck, is a Linux-based operating system that contributes to the Linux ecosystem through various improvements and custom features. It leverages tools like Proton to enable Windows game compatibility and introduces new Linux kernel features such as an improved futex API and case-insensitive filesystems. Overall, SteamOS fosters innovation and collaboration within the open-source community, benefiting both users and developers alike.