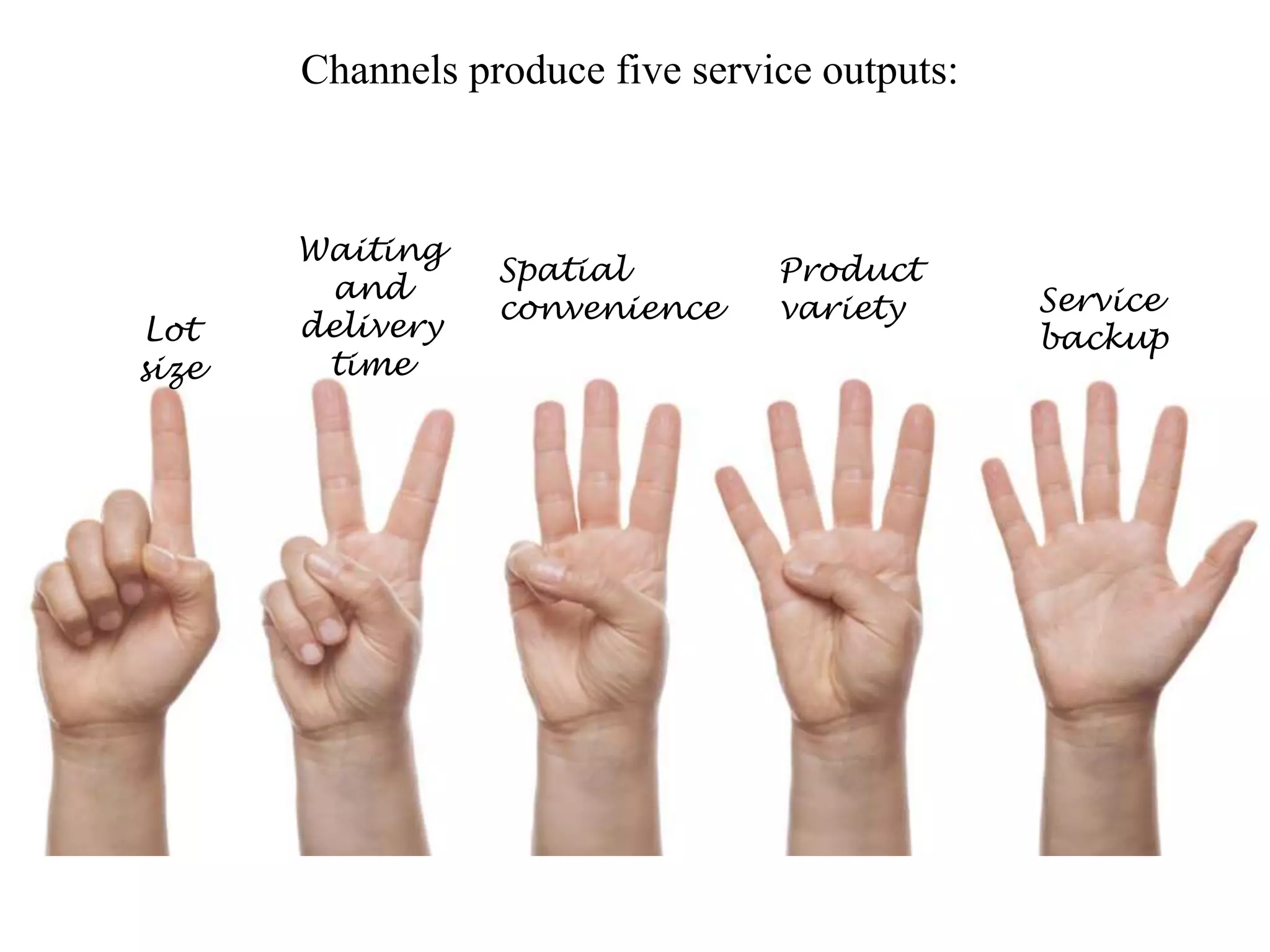
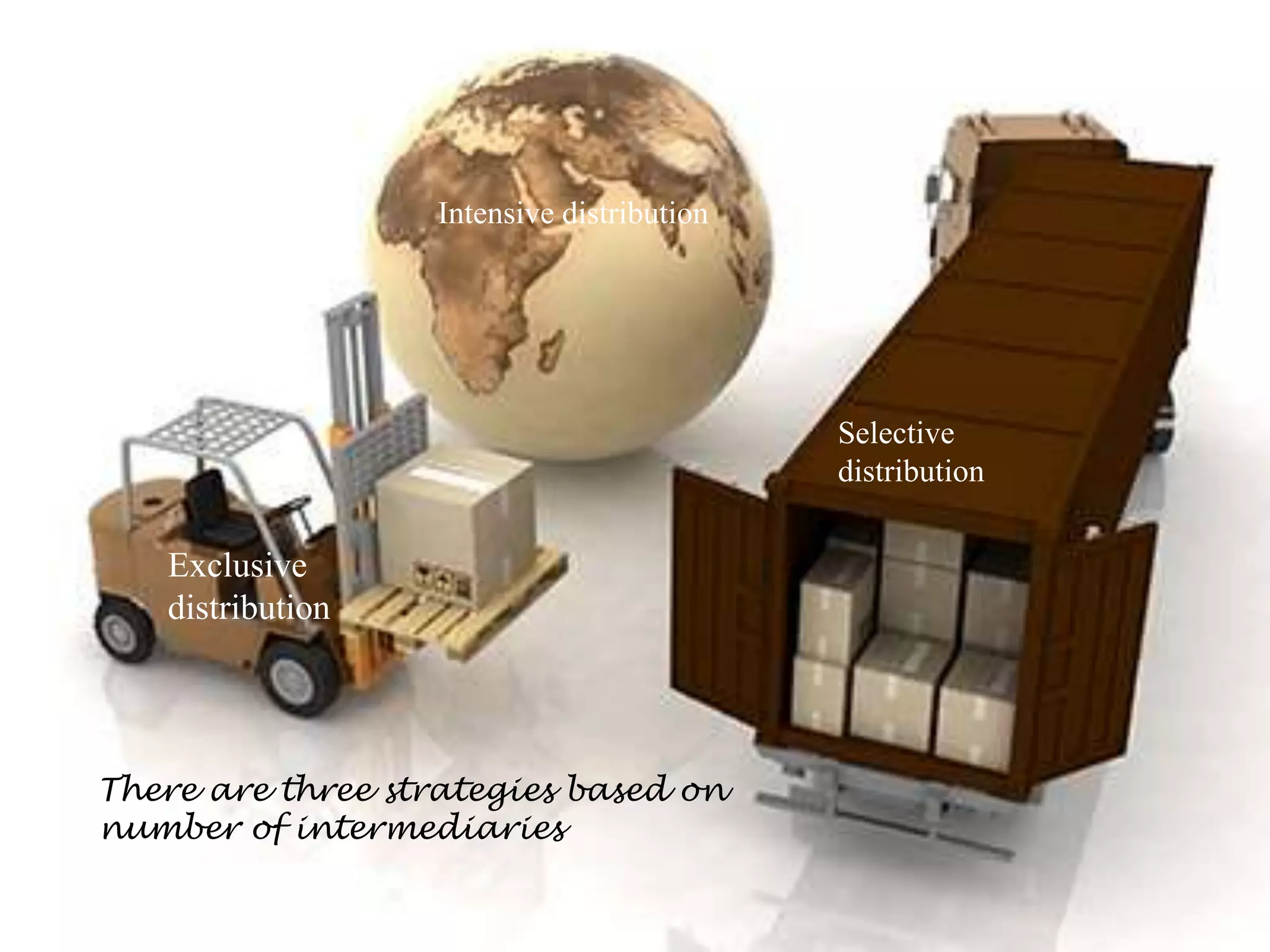
This document discusses designing and managing integrated marketing channels. It states that marketers should analyze customer needs, establish channel objectives and constraints, and identify and evaluate major channel alternatives. It notes that channels produce five service outputs: lot size, waiting and delivery time, spatial convenience, product variety, and service backup. Objectives and constraints vary based on market segments, product characteristics, and the larger environment. When identifying alternatives, each channel has unique strengths and weaknesses, and alternatives differ in types of intermediaries, number of intermediaries, and terms and responsibilities. Evaluation of alternatives considers the different levels of sales and costs each will produce.