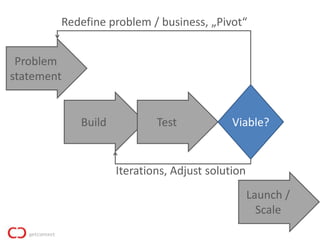
This document summarizes Manuel Koelman's talk on how pirates build products using lean startup principles. The key points are:
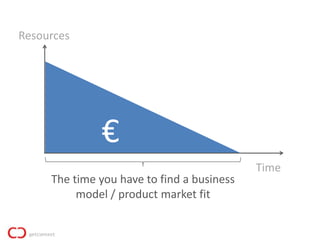
1) Startups face extreme uncertainty and most fail, usually because there are no customers rather than the product not working. Lean startup principles emphasize learning fast through experiments to reduce time to find a business model or product-market fit.
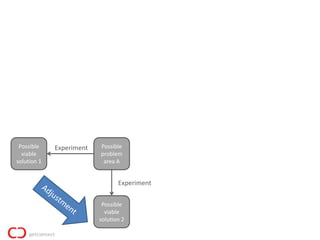
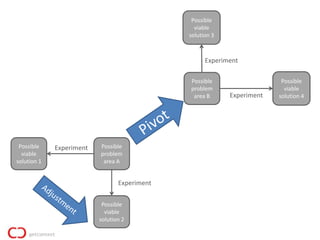
2) The lean startup process involves building a minimum viable product, testing it with customers, adjusting or pivoting based on feedback, and then repeating the process to make continuous progress. The goal is to validate problems and solutions as quickly as possible before running out of resources.
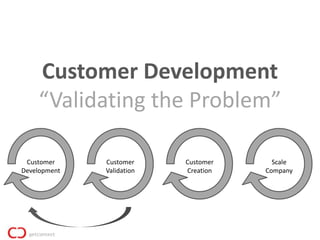
3) Customer development is key - get out of the house before coding to validate problems