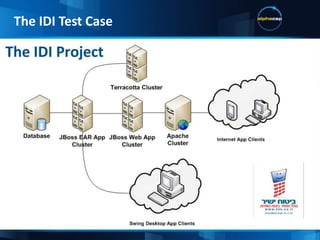
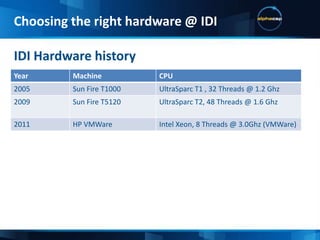
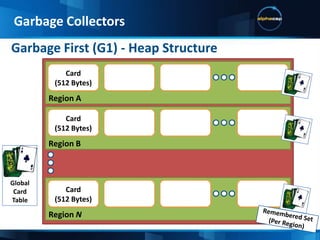
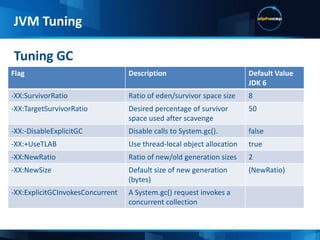
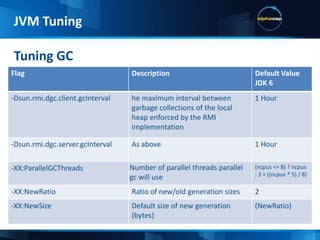
This document discusses JVM tuning and garbage collection. It provides an overview of key JVM flags and garbage collection strategies. It also describes the IDI test case which includes a swing desktop client, wicket web application, mobile web app in development, multiple application servers and frameworks. Hardware choices like CPU architecture and memory are important considerations for performance. The ideal configuration depends on the application's needs in terms of computational intensity and concurrency.