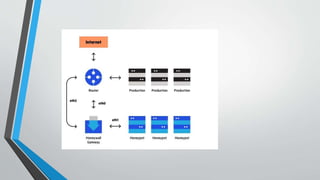
Honeypots are systems designed to be attacked to gather information about cyber attacks. They allow monitoring of the latest attack trends and where attacks originate. Different types of honeypots exist for various purposes like research, production environments, malware analysis, and email/database monitoring. Honeypots provide advantages like collecting high value data sets cost effectively with minimal resources, but also have disadvantages like limited visibility and risk of detection.