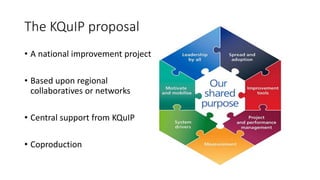
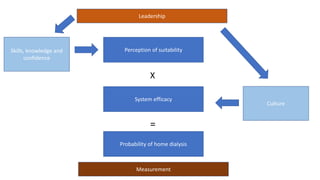
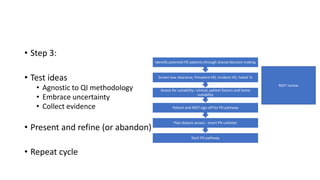
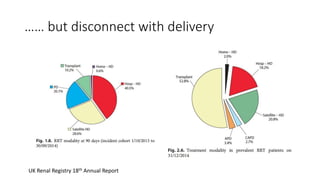
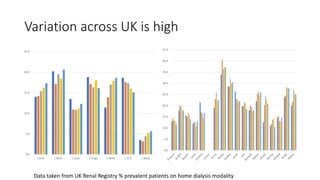
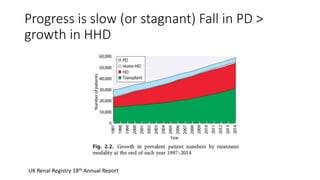
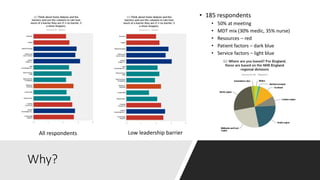
This document discusses a proposed national improvement project called KQuIP to increase home dialysis rates across the UK by addressing regional variation. It would establish regional collaboratives to test ideas and share best practices using a three-phase model of discovery, idea development, and testing cycles. Barriers to greater home dialysis use include financial factors, lack of leadership support and expertise, and perceptions of patient suitability. The project aims to standardize training pathways and measurement while respecting patient choice. Clear vision, leadership, organizational culture, and infrastructure support will be key drivers of success.




![To increase the
proportion of patients on
home dialysis therapies
in England
Clear Vision & Purpose
Leadership
i) Organisational ii) Medical iii) Nursing iv) Patient Leadership
Organisational Culture
Values, behaviours & mindset
Expertise [Knowledge& skills]
Patients
Determining ‘suitable’ home dialysis patients
Develop patient exclusion criteria, dependent on local expertise
Home dialysis training
Effectiveness & experience of training pathway
Patient awareness, recruitment & retention
Patient Education & Informed Choice; Patient & carer experience;
Peer support; Carer support
Organisational Infrastructure
Financial support
Training facilities
Commissioning dialysis consumables and machines
Home modifications
Access to respite care
Multidisciplinary team supported by community team
DRIVER DIAGRAM: Home Dialysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homedialysisra2017-170706100041/85/Home-Dialysis-RA-2017-11-320.jpg)