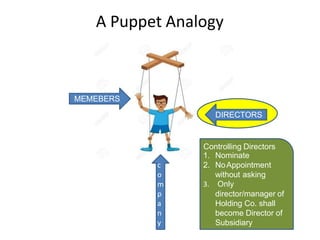
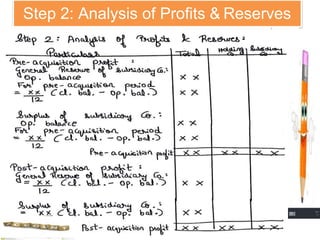
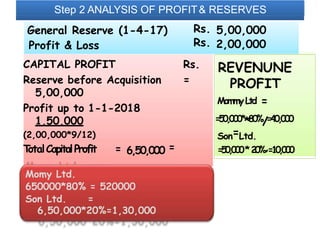
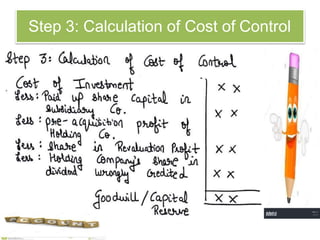
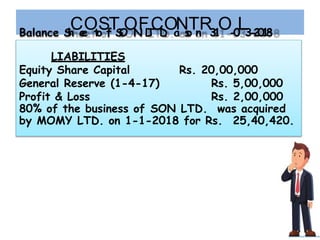
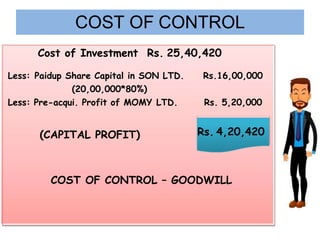
The document discusses key aspects of preparing consolidated financial statements for a holding company and its subsidiaries. It provides definitions for holding company, subsidiary company, and step-down subsidiary company. It outlines the process for preparing consolidated financial statements, including calculating the cost of control, minority interest, treatment of various items like unrealized profits, contingent liabilities, unclaimed dividends, and more. The goal is to eliminate intra-group transactions and account for the holding company's share of profits/reserves and cost of investment in subsidiaries.