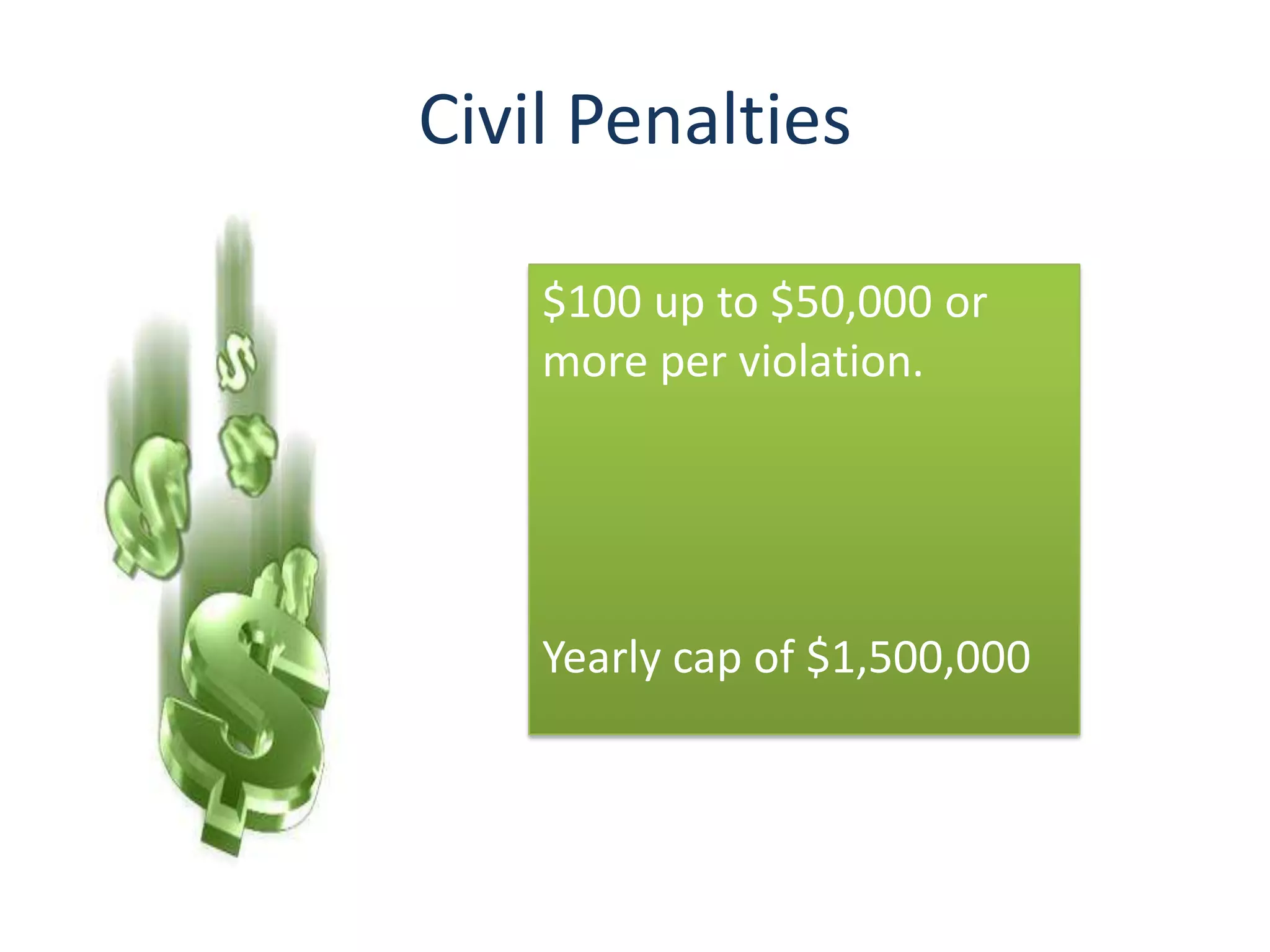
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 protects individuals' private health information. It applies to covered entities like health care providers, insurers, and clearinghouses that store, transmit, or use protected health information. All employees, volunteers, trainees, agents and contractors of covered entities must follow HIPAA rules. HIPAA covers identifiable health information like names, dates, diagnoses, and treatments. The Department of Health and Human Services enforces HIPAA through investigations and compliance reviews, with civil penalties up to $1.5 million and criminal penalties including imprisonment.