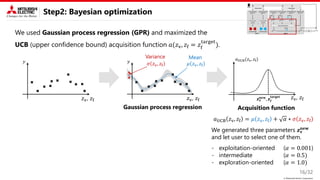
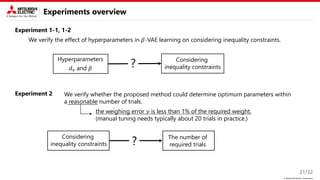
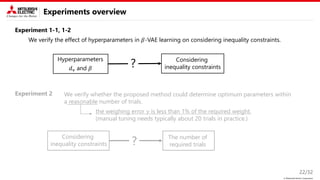
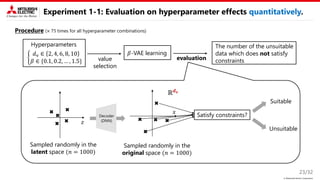
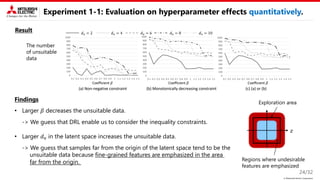
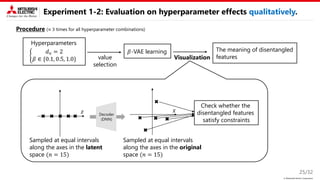
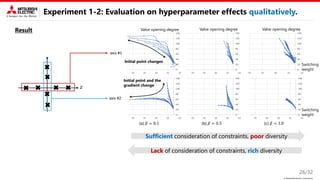
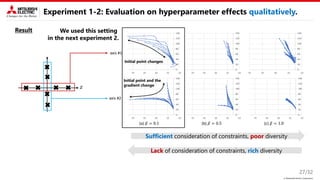
This document describes a proposed method for Bayesian optimization with constraints in high-dimensional spaces. The key ideas are:
1) Decompose parameters into variable and fixed parts to handle known equality constraints.
2) Introduce disentangled representation learning into nonlinear embedding to handle unknown inequality constraints by exploring each latent dimension independently.
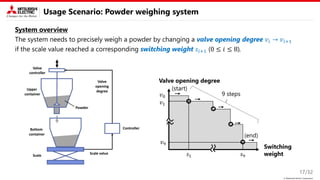
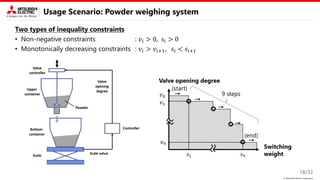
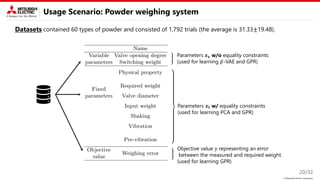
3) Apply the method to parameter optimization for a powder weighing system with constraints like non-negativity and monotonicity. Experiments demonstrate the ability to efficiently explore the parameter space while respecting constraints.

![© Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
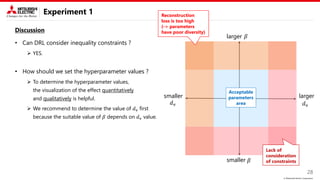
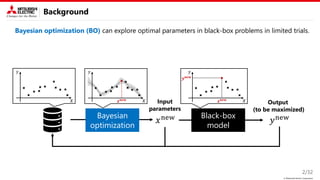
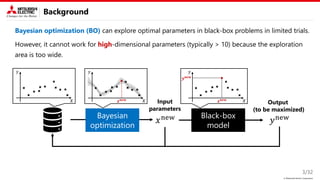
Background
Related works explore parameters in a low-dimensional space acquired by the following methods.
4/32
REMBO [IJCAI’13]
LINEBO [ICML’19]
Efficient exploration
Constraints cannot be explicitly
expressed in the latent space.
Constraints can be easily introduced
Not efficient exploration
(particularly for image and NLP)
Dropout [IJCAI’17]
Original
Dropped
Subspace extraction / Linear embedding
𝒙𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐢𝐧𝐢𝐭
BO in non-dropped
dimensions.
BO in
a single dimension.
BO in random
embedded dimensions.
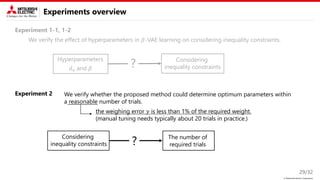
Nonlinear embedding
2. BO in the latent space
𝑦
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰 𝒛
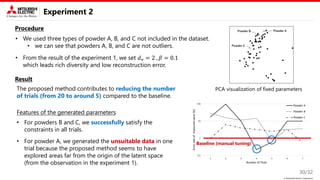
Encoder
(DNN)
𝒙𝟏
𝒙𝟐
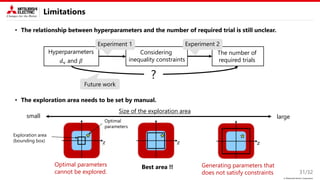
𝒙𝟑
𝒛𝟏
𝒛𝟐
𝒛𝟑
Decoder
(DNN)
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐧𝐞𝐰
1. Encode datasets 3. Decode latent parameters
We tackle this problem !!
𝒙 𝒛
Random
matrix
𝑦
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒛
𝒙](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdpta22miya-220725184651-628fe1aa/85/High-Dimensional-Bayesian-Optimization-with-Constraints-Application-to-Powder-weighing-PDPAT2022-MPS139-4-320.jpg)
![© Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
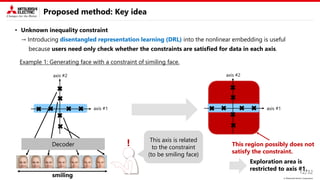
Proposed method: Key idea
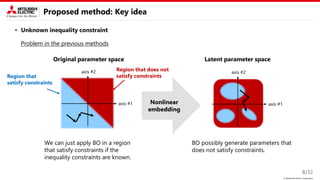
This study focus on two types of constraint.
• Known equality constraint
→ Decomposition into variable and fixed
parameters is useful.
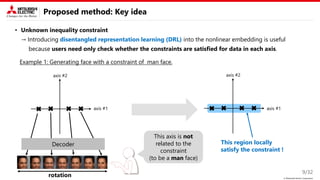
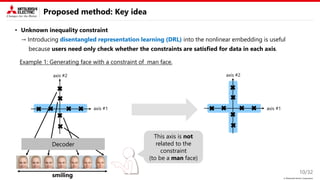
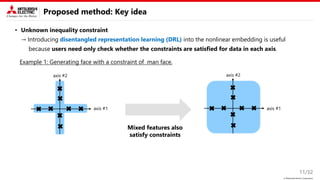
• Unknown inequality constraint
→ Introducing disentangled representation learning (DRL) into the nonlinear embedding is useful.
5/32
Nonlinear embedding
2. Bayesian optimization
on the latent space
𝑦
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒛
Encoder
(DNN)
𝒙𝟏
𝒙𝟐
𝒙𝟑
𝒛𝟏
𝒛𝟐
𝒛𝟑
Decoder
(DNN)
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐧𝐞𝐰
1. Encode datasets 3. Decode datasets
Disentangled representation learning
• Latent parameter is interpretable and
independent
𝒛
Decoder
(DNN)
“rotation”
“smile”
The Figure is from 𝛽-VAE [ICLR’17]
• DRL is generally used to control
generative models (VAE, GAN, …)
Variable parameters w/o
equality constraints
Fixed parameters w/
equality constraints
Parameters
Bayesian
optimization
Explored
parameters
condition
𝒙𝐯
𝒙𝐟 𝒙𝐟
𝒙𝐟
𝒙
𝒙𝐯
𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐯
𝐧𝐞𝐰](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdpta22miya-220725184651-628fe1aa/85/High-Dimensional-Bayesian-Optimization-with-Constraints-Application-to-Powder-weighing-PDPAT2022-MPS139-5-320.jpg)
![© Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
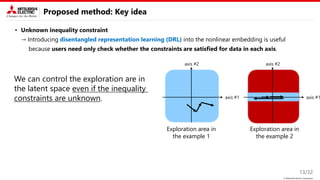
Proposed method: Key idea
This study focus on two types of constraint.
• Known equality constraint
→ Decomposition into variable and fixed
parameters is useful.
• Unknown inequality constraint
→ Introducing disentangled representation learning (DRL) into the nonlinear embedding is useful.
6/32
Nonlinear embedding
2. Bayesian optimization
on the latent space
𝑦
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒛
Encoder
(DNN)
𝒙𝟏
𝒙𝟐
𝒙𝟑
𝒛𝟏
𝒛𝟐
𝒛𝟑
Decoder
(DNN)
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐧𝐞𝐰
1. Encode datasets 3. Decode datasets
Disentangled representation learning
• Latent parameter is interpretable and
independent
𝒛
Decoder
(DNN)
“rotation”
“smile”
The Figure is from 𝛽-VAE [ICLR’17]
• DRL is generally used to control
generative models (VAE, GAN, …)
Variable parameters w/o
equality constraints
Fixed parameters w/
equality constraints
Parameters
Bayesian
optimization
Explored
parameters
condition
𝒙𝐯
𝒙𝐟 𝒙𝐟
𝒙𝐟
𝒙
𝒙𝐯
𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐯
𝐧𝐞𝐰](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdpta22miya-220725184651-628fe1aa/85/High-Dimensional-Bayesian-Optimization-with-Constraints-Application-to-Powder-weighing-PDPAT2022-MPS139-6-320.jpg)
![© Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
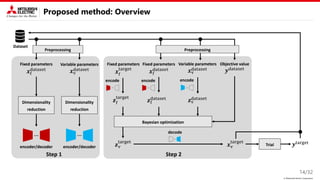
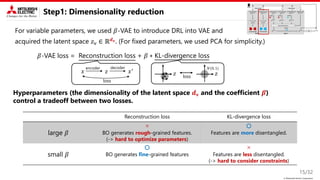
Proposed method: Key idea
This study focus on two types of constraint.
• Known equality constraint
→ Decomposition into variable and fixed
parameters is useful.
• Unknown inequality constraint
→ Introducing disentangled representation learning (DRL) into the nonlinear embedding is useful.
7/32
Nonlinear embedding
2. Bayesian optimization
on the latent space
𝑦
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒛
Encoder
(DNN)
𝒙𝟏
𝒙𝟐
𝒙𝟑
𝒛𝟏
𝒛𝟐
𝒛𝟑
Decoder
(DNN)
𝒛𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐧𝐞𝐰
1. Encode datasets 3. Decode datasets
Disentangled representation learning
• Latent parameter is interpretable and
independent
𝒛
Decoder
(DNN)
“rotation”
“smile”
The Figure is from 𝛽-VAE [ICLR’17]
• DRL is generally used to control
generative models (VAE, GAN, …)
Variable parameters w/o
equality constraints
Fixed parameters w/
equality constraints
Parameters
Bayesian
optimization
Explored
parameters
condition
𝒙𝐯
𝒙𝐟 𝒙𝐟
𝒙𝐟
𝒙
𝒙𝐯
𝐧𝐞𝐰
𝒙𝐯
𝐧𝐞𝐰](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdpta22miya-220725184651-628fe1aa/85/High-Dimensional-Bayesian-Optimization-with-Constraints-Application-to-Powder-weighing-PDPAT2022-MPS139-7-320.jpg)