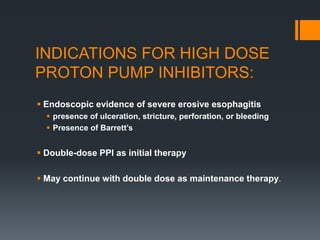
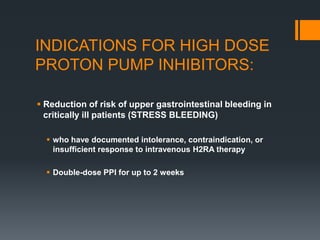
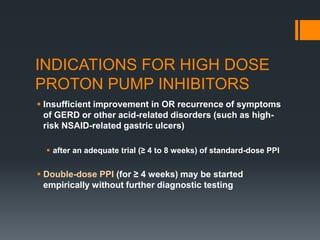
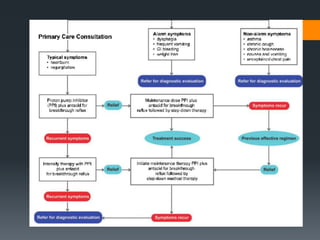
This document outlines criteria for using high-dose oral proton pump inhibitors like Omeprazole 40 mg. It recommends high-dose PPI as initial therapy for certain conditions like gastric ulcers or pathologic hypersecretory conditions. High-dose PPI is also indicated when there is insufficient improvement with standard-dose PPI for conditions like GERD, NSAID-related ulcers, or after a PPI test. Preventing rebleeding of peptic ulcers is another indication. The document discusses reasons for lack of response to standard-dose PPI and evaluating for compliance or alternative diagnoses before increasing to high-dose PPI.