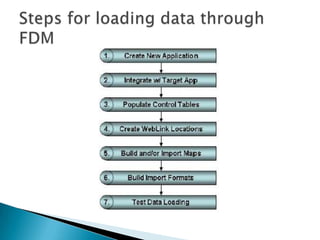
Hyperion is an EPM system that includes applications for planning, consolidation, reporting, dashboards, and analysis. It allows organizations to analyze large amounts of information to support decision making. HFM is Hyperion's financial consolidation and reporting tool. It uses a dimensional data model to consolidate financial data from multiple sources and provide reporting and analysis. Key features include a closed approval process, data validation, currency translation, and automatic eliminations for intercompany transactions.