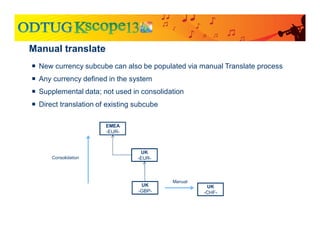
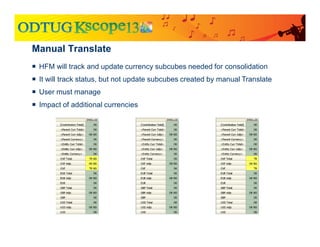
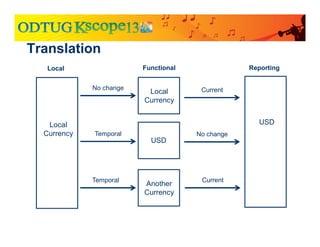
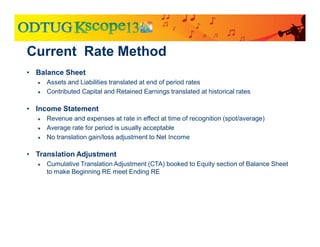
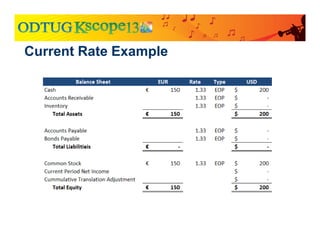
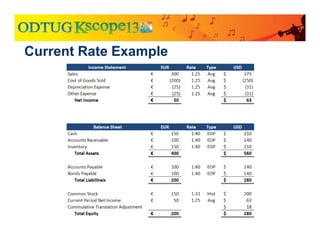
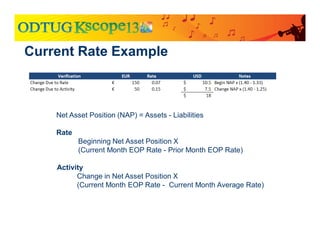
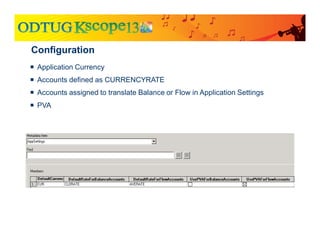
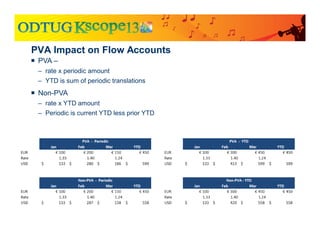
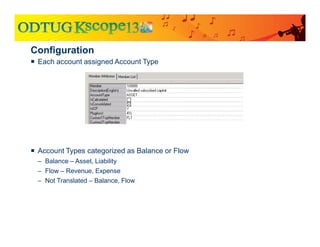
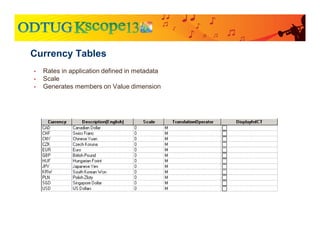
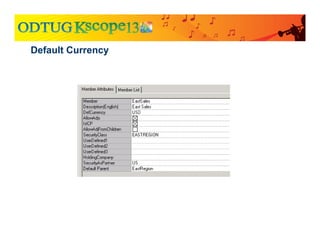
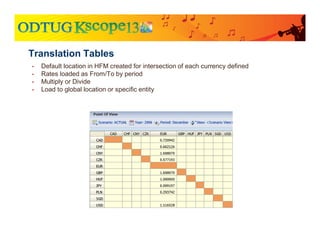
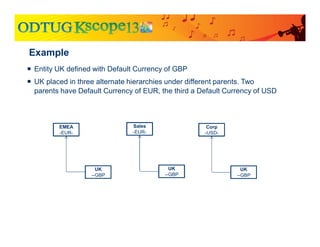
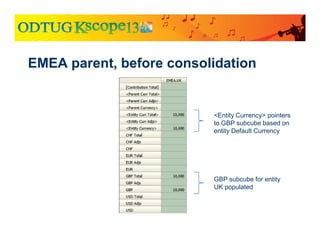
The document discusses currency translation within HFM, detailing methods such as temporal and current rate methodologies, and the implications for financial reporting according to US GAAP and IFRS. It outlines the processes for translating various types of currencies, defining roles for local, functional, and reporting currencies, as well as strategies for managing translation adjustments. Additionally, it highlights configurations required for HFM's currency translation capabilities and the management of subcubes for efficient data handling during consolidation.












![• Direct rate in current entity Italy.EUR -> Italy.USD
• Indirect rate in current entity Italy.USD -> Italy.EUR
• Direct rate in [None] entity [None].EUR -> [None].USD
• Indirect rate in [None] entity [None].USD -> [None].EUR
• Triangulation through application currency
Default Translation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currencytranslationinhfm-180104064412/85/Currency-Translation-in-HFM-24-320.jpg)




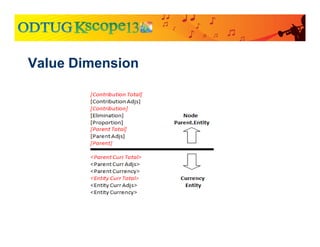
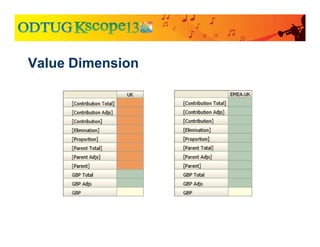
![Two types of subcubes based on the Value Dimension
● Currency Subcubes
● Base data for the entity
● Triplet
● The angle brackets
● Node Subcubes
● Tracks aggregation and eliminations for an entity into a specific parent
● The square brackets – [Elimination], [Proportion], etc.
● Currency of the parent (not identified in member name)
Subcube Types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currencytranslationinhfm-180104064412/85/Currency-Translation-in-HFM-29-320.jpg)
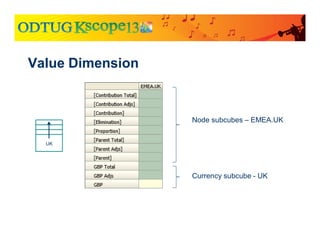
![GBP Total
GBP Adjs
GBP
France
UK
Node subcubes – EMEA.UK
Currency subcube – UK
EMEA
Node subcubes – EMEA.France
Currency subcube – France
Currency subcube - EMEA
HFM Value Dimension
[Elimination]
[Proportion], Etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currencytranslationinhfm-180104064412/85/Currency-Translation-in-HFM-31-320.jpg)


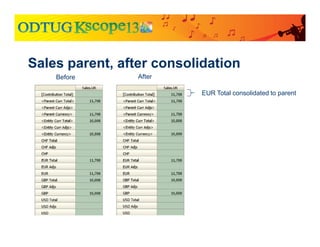



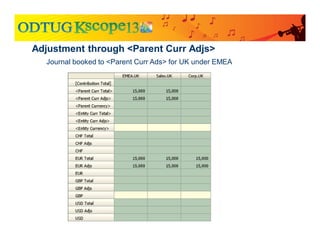
![Compare to adjustment through [Parent Adjs]
Journal booked to [Parent Adjs] for UK under EMEA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currencytranslationinhfm-180104064412/85/Currency-Translation-in-HFM-42-320.jpg)