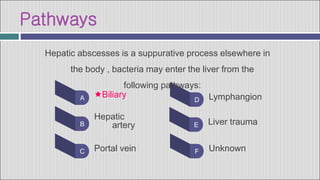
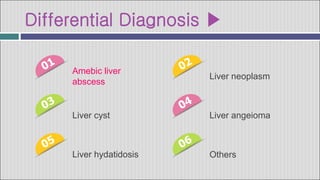
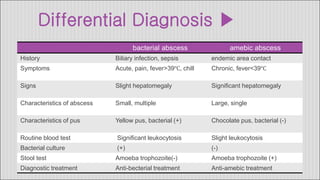
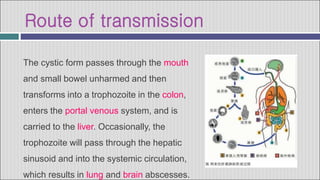
1. Hepatic abscesses can be caused by bacteria, parasites, or fungi. Bacterial abscesses are the most common and can develop when bacteria enter the liver through the biliary tract, bloodstream, or by direct extension from another infected site.
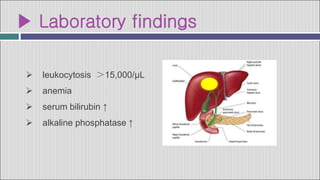
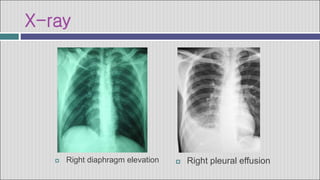
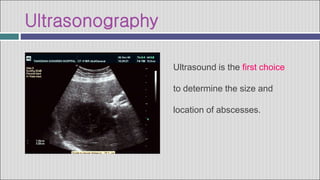
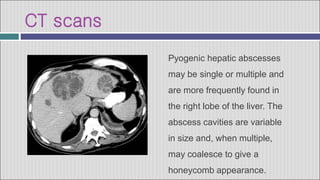
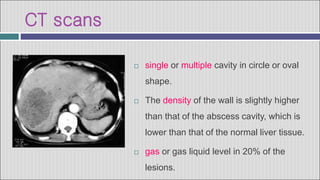
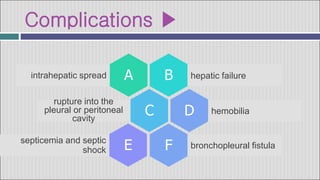
2. Symptoms of a hepatic abscess include fever, chills, right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice. Imaging studies like ultrasound and CT scans are used to identify abscess location, size, and number.
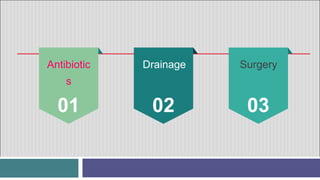
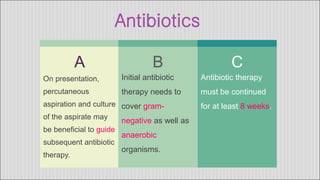
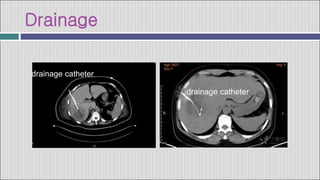
3. Treatment involves antibiotics, drainage of pus via catheter, and sometimes surgery. Amebic abscesses, caused by Entamoeba histolytica infection, present similarly but are generally treated with