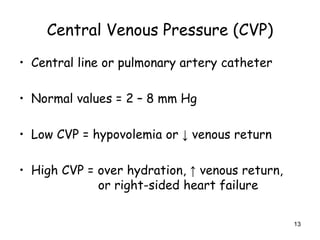
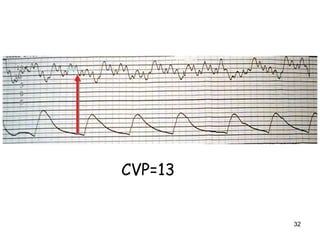
1) Hemodynamic monitoring involves measuring arterial blood pressure, central venous pressure, and continuous airway pressure in order to assess a patient's volume status, cardiac function, and response to treatments.
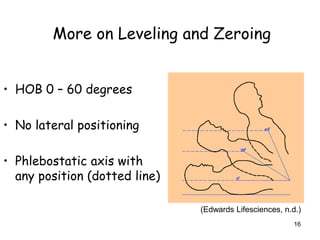
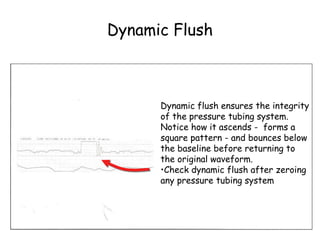
2) Proper technique such as correctly fitting blood pressure cuffs and leveling and zeroing pressure monitoring equipment is important for obtaining accurate readings.
3) Hemodynamic monitoring data along with waveforms should be thoroughly documented including patient position and ventilator settings to provide useful clinical information over time.