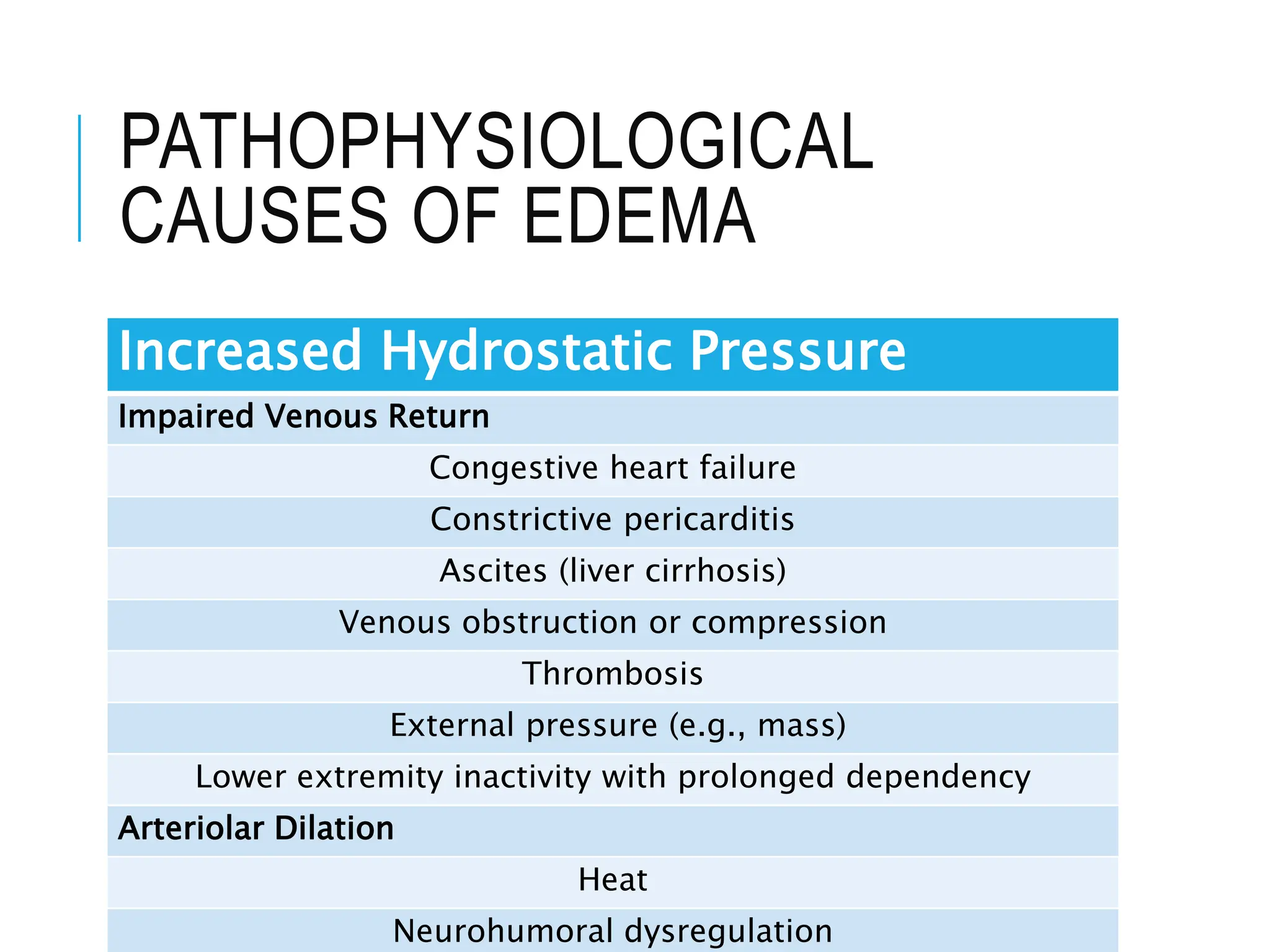
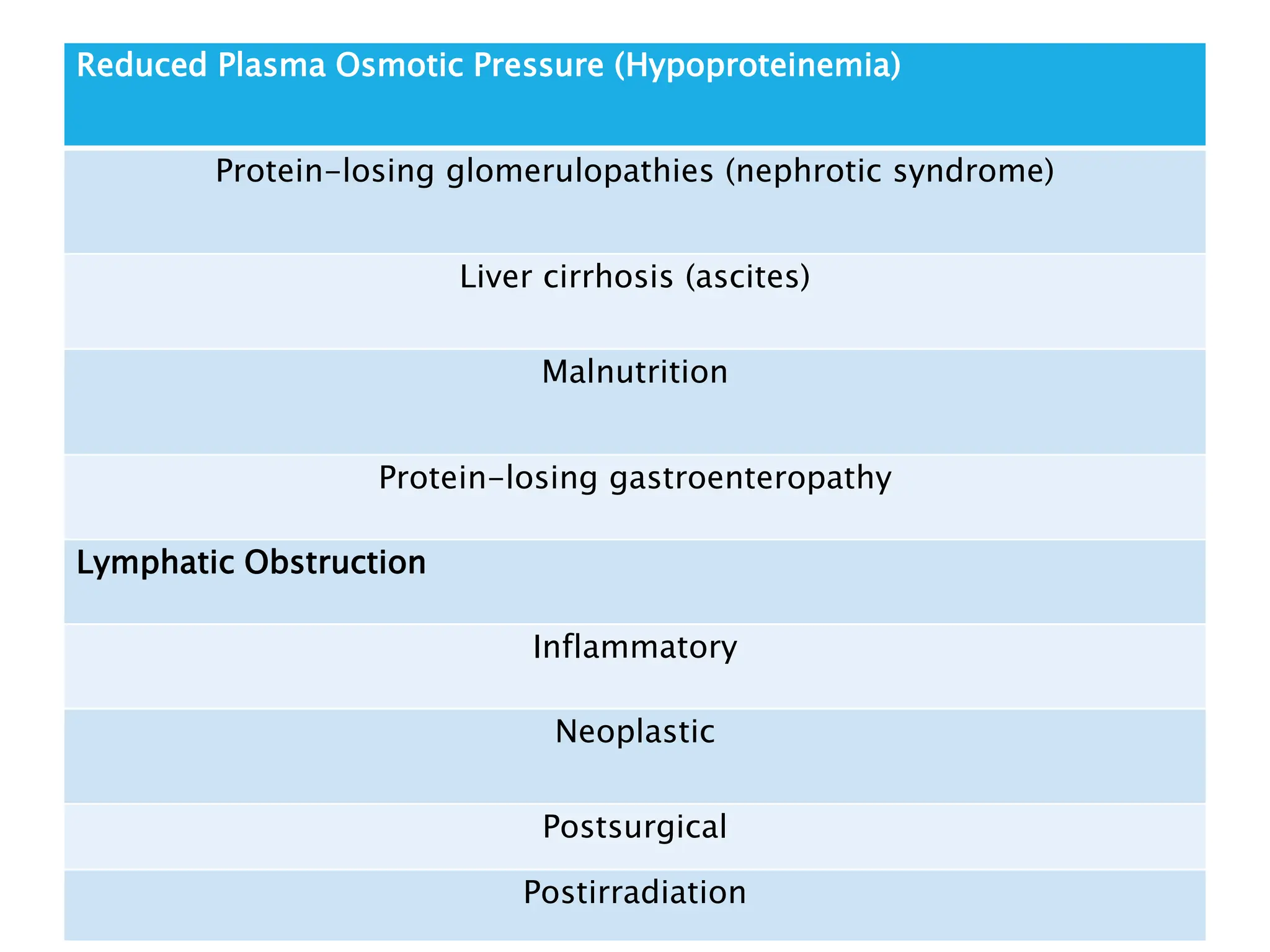
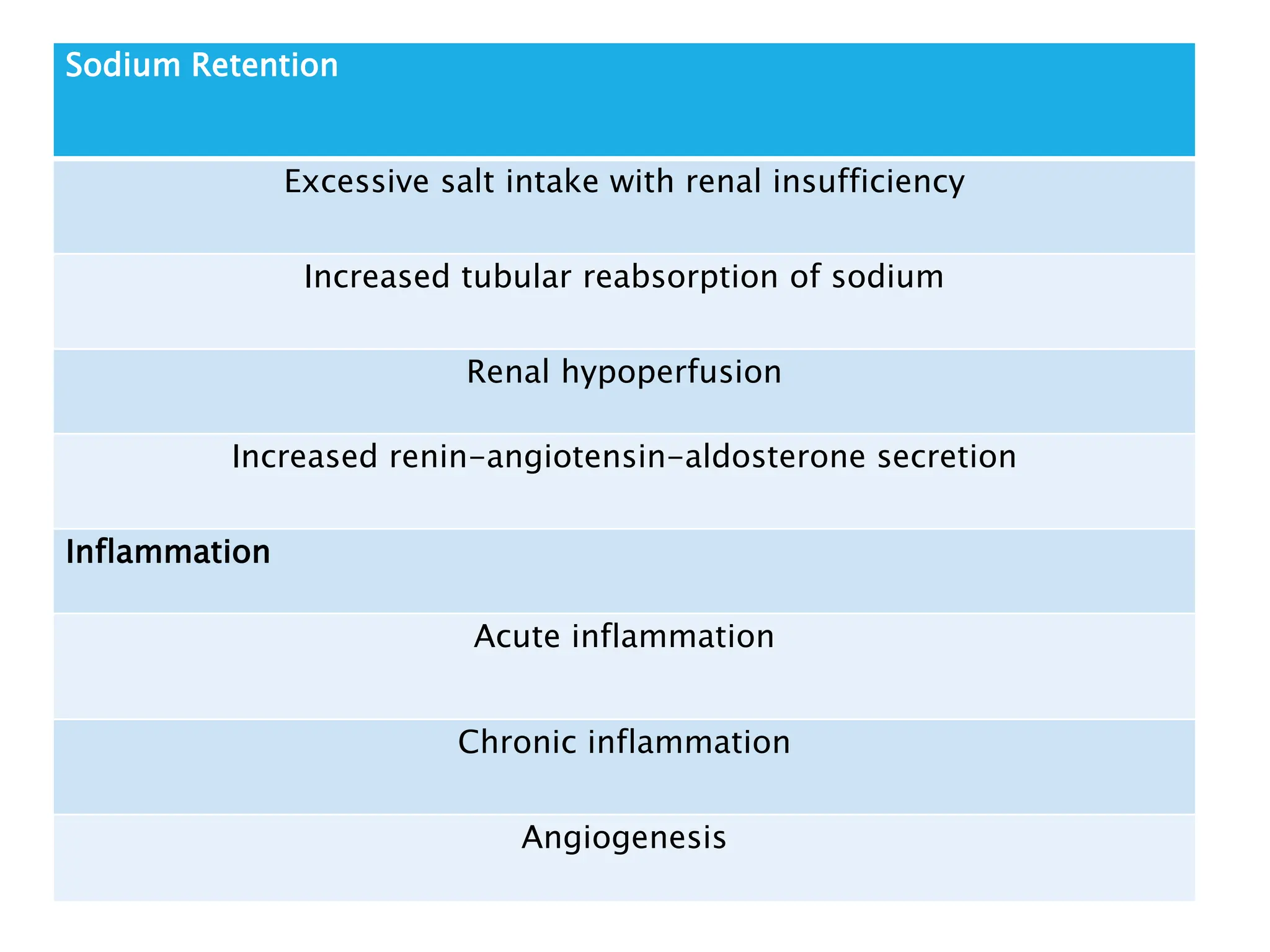
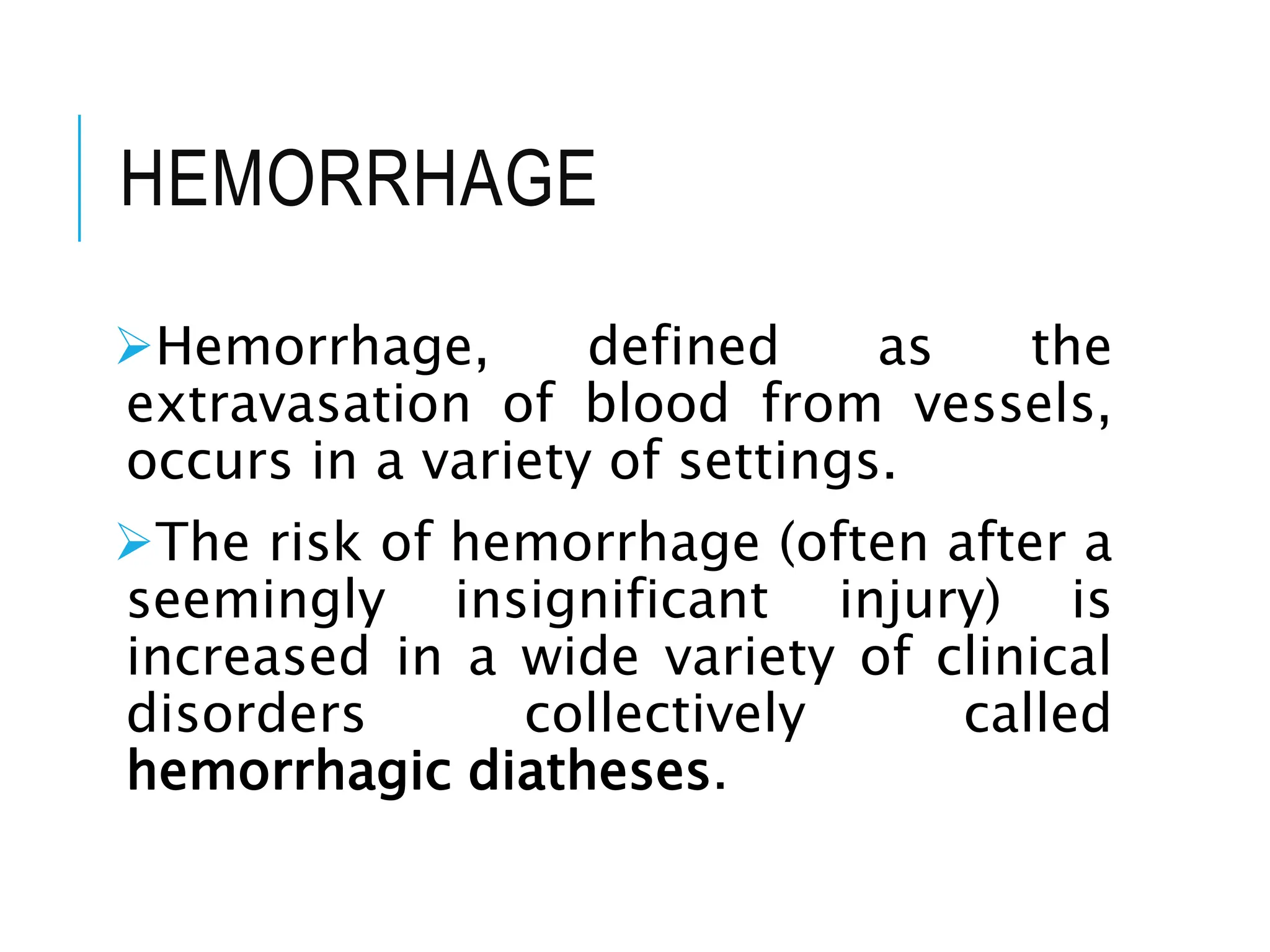
The document discusses hemodynamic disorders, focusing on edema and hemorrhage. Edema is characterized by the accumulation of interstitial fluid, influenced by hydrostatic and osmotic pressures, with various pathophysiological causes and clinical implications. Hemorrhage involves the extravasation of blood and can have varying significance based on location and volume, affecting clinical outcomes based on underlying conditions.