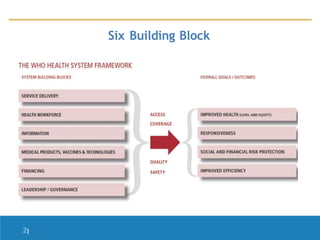
This document outlines the six main building blocks of a health system:
1. Service delivery - Providing integrated, safe, and quality health services to populations through various means such as in homes, communities, workplaces, and health facilities.
2. Health workforce - All individuals involved in improving health, including providers, managers, support workers, paid and unpaid workers in both public and private sectors. The density of the health workforce is strongly correlated with health outcomes.
3. Health information systems - Systems that ensure the production, analysis, dissemination and use of reliable health information on determinants, system performance, and health status to detect and contain public health threats.
4. Medical products, vaccines and technologies - Ens